Description
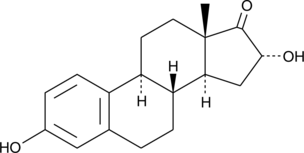
A hydroxylated metabolite of estrone as well as an interconversion product with estriol; formed by CYP1A1, CYP3A5, CYP3A4, and CYP3A7; binds covalently and persistently activates estrogen receptors; increases cell proliferation and does not suppress TNF-α secretion
Formal name: 3,16α-dihydroxy-estra-1,3,5(10)-trien-17-one
Synonyms: 16α-OHE1
Molecular weight: 286.4
CAS: 566-76-7
Purity: ≥98%
Formulation: A crystalline solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Lipids|Sterol Lipids||Product Type|Biochemicals|Receptor Pharmacology|Agonists||Product Type|Biochemicals|Xenobiotic Metabolites||Research Area|Cancer||Research Area|Endocrinology & Metabolism|Hormones & Receptors|Estrogens & Progestins||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Autoimmunity|Rheumatoid Arthritis