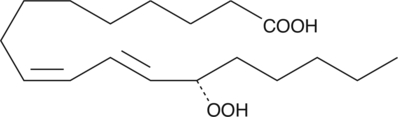
Description
13(S)-HpODE is produced by the oxidation of linoleic acid by LO-1 in many plants including soybean, flaxseed, apples, and tea leaves,{123,770} and by 15-LO in mammals.{4193} In plants, 13(S)-HpODE is the preferred substrate for the garlic bulb divinyl ether synthase.{3824} In mammalian tissues, 13(S)-HpODE is generally reduced to 13(S)-HODE, a compound which exhibits many biological activities.{4193} A direct action for 13(S)-HpODE has been demonstrated in Syrian hamster embryo cells where it stimulates EGF-dependent mitogenesis and up-regulation of EGF-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation.{4902} Membrane-esterified 13(S)-HpODE has been identified in human atherosclerotic plaques.{2406}
Formal name: 13S-hydroperoxy-9Z,11E-octadecadienoic acid
Synonyms:
Molecular weight: 312.4
CAS: 33964-75-9
Purity: ≥95%
Formulation: A solution in ethanol