Description
A cyclic analog of L-glutamate; binds to GluK1, GluK2, GluK3, GluK4, and GluK5 (Kis = 75.9, 12.7, 32.8, 4.7, and 15 nM, respectively); induces calcium influx and membrane depolarization, as well as glutamate release, in rat brain synaptosomes at 5 mM; induces chromatin condensation and nuclear membrane fragmentation in primary neonatal cerebellar granule neurons at 100 µM; induces convulsive behavior in rats (ED50 = 0.51 nmol/animal) and induces seizures in mice (CD50 = 0.39 nmol/animal); has been commonly used to induce seizures in rodents
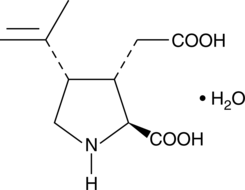
Formal name: 2S-carboxy-4S-(1-methylethenyl)-3S-pyrrolidineacetic acid, monohydrate
Synonyms:
Molecular weight: 231.2
CAS: 58002-62-3
Purity: ≥98%
Formulation: A crystalline solid