Description
A neurotoxic non-proteinogenic amino acid; cytotoxic to mouse primary cortical neurons at 3 mM; stimulates release of glutamate and induces oxidative stress in the same cells at 3 mM; enhances amyloid-β (25-35)-induced neuronal cell death in mouse primary cortical neurons at 0.1 mM; induces wet-dog shakes, rigidity, and clonic convulsions in rats at 500 µg/animal; induces parkinsonism in cynomolgus monkeys; has been found in commercial seafood
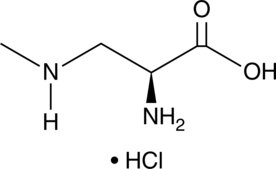
Formal name: 3-(methylamino)-L-alanine, monohydrochloride
Synonyms: BMAA|L-BMAA
Molecular weight: 154.6
CAS: 16012-55-8
Purity: ≥95%
Formulation: A solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Natural Products|Microbial Metabolites||Product Type|Biochemicals|Toxins||Research Area|Neuroscience|Neurodegenerative Disorders|Alzheimer’s Disease||Research Area|Neuroscience|Neurodegenerative Disorders|Parkinson’s Disease||Research Area|Neuroscience|Seizure Disorders||Research Area|Oxidative Stress & Reactive Species|Pro-oxidant Activity