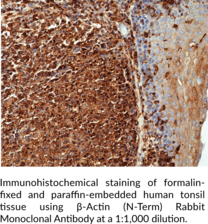
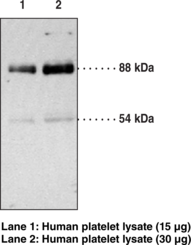
Description
β-Actin is a cytoskeletal protein with roles in cell division, migration, and homeostasis that is encoded by ACTB in humans.{52776,52777} It is ubiquitously expressed, localized to the cytosol, and conserved from birds to mammals. β-Actin is enriched at the leading edge of migrating cells and Actb-/- mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) exhibit decreased migration velocity, increased apoptosis, and decreased proliferation.{52776} Actb knockout is early embryonic lethal in mice, indicating that β-actin is essential for embryonic development. ACTBR183W and ACTBE346K gain-of-function mutations have been found in patients with deafness, developmental mutations, and juvenile-onset dystonia and neutrophil dysfunction, respectively.{52778} Cayman’s β-Actin (N-Term) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody can be used for chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP), immunocytochemistry (ICC), immunohistochemistry (IHC), immunoprecipitation (IP), and Western blot (WB) applications.
Synonyms: Actin β|Actin, Cytoplasmic 1|β-Cytoskeletal Actin
Immunogen: Peptide from the N-terminal region of β-actin
Formulation: 100 µl of protein A-affinity purified monoclonal antibody
Isotype: IgG
Applications: ChIP, ICC, IHC, IP, WB
Origin:
Stability: 365 days
Application|ELISA||Application|Flow Cytometry||Application|Immunocytochemistry||Application|Immunohistochemistry||Application|Immunoprecipitation||Application|Western Blot||Product Type|Antibodies|Monoclonal Antibodies||Research Area|Cell Biology|Cytoskeleton & Motor Proteins||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Innate Immunity