Description
A DHA epoxygenase metabolite found in rat brain and spinal cord that acts as a preferred substrate for sEH (Km = 3.2 µM); demonstrates antihyperalgesic activity in inflammatory and neuropathic pain models and potently inhibits angiogenesis and tumor growth in in vitro assays
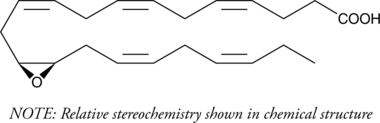
Formal name: (±)-(4Z,7Z,10Z)-12-[3-(2Z,5Z)-2,5-octadien-1-yl-2-oxiranyl]-4,7,10-dodecatrienoic acid
Synonyms: (±)13,14-EDP|(±)13,14-EpDPE|(±)13,14-epoxy Docosapentaenoic Acid|(±)13,14-epoxy DPA
Molecular weight: 344.5
CAS: 895127-64-7
Purity: ≥95%
Formulation: A solution in ethanol
Product Type|Biochemicals|Lipids|Docosanoids||Research Area|Cancer|Angiogenesis||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation||Research Area|Lipid Biochemistry|Cytochrome P450 Pathways||Research Area|Neuroscience|Pain Research