Description
An immunomodulatory compound with diverse biological activities; prevents PMN chemotaxis at 1, 10, and 100 µg/ml; increases IL-2-induced proliferation and IFN-γ production in primary human T cells in vitro; enhances NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity in MM.1S multiple myeloma cells; reduces lung IL-6, TGF-β, VEGF, angiopoietin-1, angiopoietin-2, and collagen type Iα1 expression, inhibits pulmonary angiogenesis, and attenuates fibrosis in a mouse model of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis at 4 mg/animal; induces apoptosis in primary human embryonic fibroblasts (EC50 = 8.9 µM) and induces limb and eye defects in chicken embryos (EC50 = 50 µg/kg egg weight)
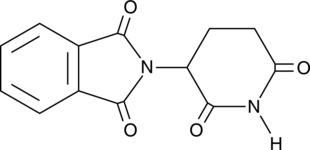
Formal name: 2-(2,6-dioxo-3-piperidinyl)-1H-isoindole-1,3(2H)-dione
Synonyms: N-Phthaloylglutamimide|NSC 527179|NSC 66847
Molecular weight: 258.2
CAS: 50-35-1
Purity: ≥98%
Formulation: A solid
Product Type|Biochemicals||Research Area|Cancer|Cell Death||Research Area|Cancer|Immunology||Research Area|Cardiovascular System|Vasculature|Angiogenesis||Research Area|Cell Biology|Cell Death|Apoptosis||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Adaptive Immunity||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Innate Immunity||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Pulmonary Diseases||Research Area|Toxicology|Cell Health & Viability