Description
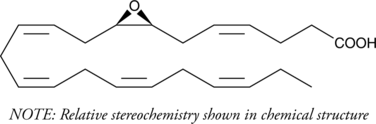
An epoxide derivative of DHA that is generated by the action of CYP450 epoxygenases; naturally occurring in plasma and brain and spinal cord tissues and is increased following dietary supplementation with ω-3 fatty acids; a substrate of soluble epoxide hydrolase (KM = 15 µM)
Formal name: (±)-(4Z)-6-[3-(2Z,5Z,8Z,11Z)-2,5,8,11-tetradecatetraen-1-yl-2-oxiranyl]-4-hexenoic acid
Synonyms: (±)7,8-EDP|(±)7,8-EpDPE|(±)7,8-epoxy Docosapentaenoic Acid|(±)7,8-epoxy DPA
Molecular weight: 344.5
CAS: 895127-66-9
Purity: ≥95%
Formulation: A solution in ethanol
Product Type|Biochemicals|Lipids|Docosanoids||Research Area|Cancer|Angiogenesis||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation||Research Area|Lipid Biochemistry|Cytochrome P450 Pathways||Research Area|Neuroscience|Pain Research