Cayman
Showing 10051–10200 of 45550 results
-
Arachidonic acid is an essential fatty acid and a precursor for all prostaglandins, thromboxanes, and leukotrienes. Virtually all cellular arachidonic acid is esterified in membrane phospholipids where its presence is tightly regulated through multiple interconnected pathways.{3656} Free arachidonic acid is a transient, critical substrate for the biosynthesis of eicosanoid second messengers. Receptor-stimulated release, metabolism, and re-uptake of free arachidonate are all important aspects of cell signaling and inflammation.{314}
Brand:CaymanSKU:90010 - 250 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonic acid is an essential fatty acid and a precursor for all prostaglandins, thromboxanes, and leukotrienes. Virtually all cellular arachidonic acid is esterified in membrane phospholipids where its presence is tightly regulated through multiple interconnected pathways.{3656} Free arachidonic acid is a transient, critical substrate for the biosynthesis of eicosanoid second messengers. Receptor-stimulated release, metabolism, and re-uptake of free arachidonate are all important aspects of cell signaling and inflammation.{314}
Brand:CaymanSKU:90010 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonic acid is an essential fatty acid and a precursor for all prostaglandins, thromboxanes, and leukotrienes. Virtually all cellular arachidonic acid is esterified in membrane phospholipids where its presence is tightly regulated through multiple interconnected pathways.{3656} Free arachidonic acid is a transient, critical substrate for the biosynthesis of eicosanoid second messengers. Receptor-stimulated release, metabolism, and re-uptake of free arachidonate are all important aspects of cell signaling and inflammation.{314}
Brand:CaymanSKU:90010 - 500 mgAvailable on backorder
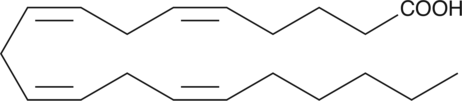
Arachidonic acid is an essential fatty acid and a precursor for all prostaglandins, thromboxanes, and leukotrienes. Virtually all cellular arachidonic acid is esterified in membrane phospholipids where its presence is tightly regulated through multiple interconnected pathways.{3656} Free arachidonic acid is a transient, critical substrate for the biosynthesis of eicosanoid second messengers. Receptor-stimulated release, metabolism, and re-uptake of free arachidonate are all important aspects of cell signaling and inflammation.{314} Arachidonic acid oxidizes spontaneously on exposure to room air, yielding a complex mixture of fatty acid peroxides. Arachidonic acid (peroxide free) contains the antioxidant BHT (Item No. 89910). BHT-free arachidonic acid (Item Nos. 90010 | 10006607) is also available.
Brand:CaymanSKU:90010.1 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonic acid is an essential fatty acid and a precursor for all prostaglandins, thromboxanes, and leukotrienes. Virtually all cellular arachidonic acid is esterified in membrane phospholipids where its presence is tightly regulated through multiple interconnected pathways.{3656} Free arachidonic acid is a transient, critical substrate for the biosynthesis of eicosanoid second messengers. Receptor-stimulated release, metabolism, and re-uptake of free arachidonate are all important aspects of cell signaling and inflammation.{314} Arachidonic acid oxidizes spontaneously on exposure to room air, yielding a complex mixture of fatty acid peroxides. Arachidonic acid (peroxide free) contains the antioxidant BHT (Item No. 89910). BHT-free arachidonic acid (Item Nos. 90010 | 10006607) is also available.
Brand:CaymanSKU:90010.1 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonic acid is an essential fatty acid and a precursor for all prostaglandins, thromboxanes, and leukotrienes. Virtually all cellular arachidonic acid is esterified in membrane phospholipids where its presence is tightly regulated through multiple interconnected pathways.{3656} Free arachidonic acid is a transient, critical substrate for the biosynthesis of eicosanoid second messengers. Receptor-stimulated release, metabolism, and re-uptake of free arachidonate are all important aspects of cell signaling and inflammation.{314} Arachidonic acid oxidizes spontaneously on exposure to room air, yielding a complex mixture of fatty acid peroxides. Arachidonic acid (peroxide free) contains the antioxidant BHT (Item No. 89910). BHT-free arachidonic acid (Item Nos. 90010 | 10006607) is also available.
Brand:CaymanSKU:90010.1 - 250 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonic acid is an essential fatty acid and a precursor for all prostaglandins, thromboxanes, and leukotrienes. Virtually all cellular arachidonic acid is esterified in membrane phospholipids where its presence is tightly regulated through multiple interconnected pathways.{3656} Free arachidonic acid is a transient, critical substrate for the biosynthesis of eicosanoid second messengers. Receptor-stimulated release, metabolism, and re-uptake of free arachidonate are all important aspects of cell signaling and inflammation.{314} Arachidonic acid oxidizes spontaneously on exposure to room air, yielding a complex mixture of fatty acid peroxides. Arachidonic acid (peroxide free) contains the antioxidant BHT (Item No. 89910). BHT-free arachidonic acid (Item Nos. 90010 | 10006607) is also available.
Brand:CaymanSKU:90010.1 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
Polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) are essential nutrients that show distinct deficiency syndromes when not present in adequate amounts in the diet.{5525,8460} Virtually all cellular arachidonic acid is esterified in membrane phospholipids where its presence is tightly regulated through multiple interconnected pathways.{3656} Free arachidonic acid is a transient, critical substrate for the biosynthesis of eicosanoid second messengers. Receptor-stimulated release, metabolism, and re-uptake of free arachidonate are all important aspects of cell signalling and inflammation.{314}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10006607 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
Polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) are essential nutrients that show distinct deficiency syndromes when not present in adequate amounts in the diet.{5525,8460} Virtually all cellular arachidonic acid is esterified in membrane phospholipids where its presence is tightly regulated through multiple interconnected pathways.{3656} Free arachidonic acid is a transient, critical substrate for the biosynthesis of eicosanoid second messengers. Receptor-stimulated release, metabolism, and re-uptake of free arachidonate are all important aspects of cell signalling and inflammation.{314}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10006607 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
Polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) are essential nutrients that show distinct deficiency syndromes when not present in adequate amounts in the diet.{5525,8460} Virtually all cellular arachidonic acid is esterified in membrane phospholipids where its presence is tightly regulated through multiple interconnected pathways.{3656} Free arachidonic acid is a transient, critical substrate for the biosynthesis of eicosanoid second messengers. Receptor-stimulated release, metabolism, and re-uptake of free arachidonate are all important aspects of cell signalling and inflammation.{314}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10006607 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
Polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) are essential nutrients that show distinct deficiency syndromes when not present in adequate amounts in the diet.{5525,8460} Virtually all cellular arachidonic acid is esterified in membrane phospholipids where its presence is tightly regulated through multiple interconnected pathways.{3656} Free arachidonic acid is a transient, critical substrate for the biosynthesis of eicosanoid second messengers. Receptor-stimulated release, metabolism, and re-uptake of free arachidonate are all important aspects of cell signalling and inflammation.{314}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10006607 - 500 mgAvailable on backorder
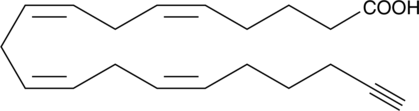
Arachidonic acid alkyne is a form of arachidonic acid with an ω-terminal alkyne. The terminal alkyne group can be used in click chemistry linking reactions to tag arachidonic acid with fluorescent or biotinylated labels for analysis of its metabolism and biological activity.{17991,17992} Because the alkyne group is at the ω-terminus, this compound can be used to easily tag metabolites and derivatives.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10538 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonic acid alkyne is a form of arachidonic acid with an ω-terminal alkyne. The terminal alkyne group can be used in click chemistry linking reactions to tag arachidonic acid with fluorescent or biotinylated labels for analysis of its metabolism and biological activity.{17991,17992} Because the alkyne group is at the ω-terminus, this compound can be used to easily tag metabolites and derivatives.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10538 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonic acid alkyne is a form of arachidonic acid with an ω-terminal alkyne. The terminal alkyne group can be used in click chemistry linking reactions to tag arachidonic acid with fluorescent or biotinylated labels for analysis of its metabolism and biological activity.{17991,17992} Because the alkyne group is at the ω-terminus, this compound can be used to easily tag metabolites and derivatives.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10538 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
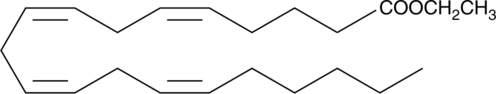
Arachidonic acid is the keystone essential fatty acid at the origin of the arachidonic acid cascade. It is converted by cyclooxygenase, lipoxygenase, and epoxygenase enzymes into more than one hundred fifty different potent primary autacoid metabolites in species ranging from fungi to plants to mammals. Arachidonic acid is stored in tissue phospholipids in esterified form, where it comprises a small but critically controlled percentage of the polyunsaturated fatty acid pool.{8460} Arachidonic acid ethyl ester is a more lipophilic form of arachidonic acid that can be incorporated into dietary regimens or fed to cultured cells as a source of exogenous arachidonate. It is one of the fatty acid ethyl esters that increase cytosolic Ca2+ concentration leading to pancreatic acinar cell injury due to excessive consumption of ethanol.{14120} Whereas arachidonic acid inhibits dopamine uptake, the ethyl esterified version does not retain this property.{14121}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008200 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonic acid is the keystone essential fatty acid at the origin of the arachidonic acid cascade. It is converted by cyclooxygenase, lipoxygenase, and epoxygenase enzymes into more than one hundred fifty different potent primary autacoid metabolites in species ranging from fungi to plants to mammals. Arachidonic acid is stored in tissue phospholipids in esterified form, where it comprises a small but critically controlled percentage of the polyunsaturated fatty acid pool.{8460} Arachidonic acid ethyl ester is a more lipophilic form of arachidonic acid that can be incorporated into dietary regimens or fed to cultured cells as a source of exogenous arachidonate. It is one of the fatty acid ethyl esters that increase cytosolic Ca2+ concentration leading to pancreatic acinar cell injury due to excessive consumption of ethanol.{14120} Whereas arachidonic acid inhibits dopamine uptake, the ethyl esterified version does not retain this property.{14121}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008200 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonic acid is the keystone essential fatty acid at the origin of the arachidonic acid cascade. It is converted by cyclooxygenase, lipoxygenase, and epoxygenase enzymes into more than one hundred fifty different potent primary autacoid metabolites in species ranging from fungi to plants to mammals. Arachidonic acid is stored in tissue phospholipids in esterified form, where it comprises a small but critically controlled percentage of the polyunsaturated fatty acid pool.{8460} Arachidonic acid ethyl ester is a more lipophilic form of arachidonic acid that can be incorporated into dietary regimens or fed to cultured cells as a source of exogenous arachidonate. It is one of the fatty acid ethyl esters that increase cytosolic Ca2+ concentration leading to pancreatic acinar cell injury due to excessive consumption of ethanol.{14120} Whereas arachidonic acid inhibits dopamine uptake, the ethyl esterified version does not retain this property.{14121}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008200 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonic acid is the keystone essential fatty acid at the origin of the arachidonic acid cascade. It is converted by cyclooxygenase, lipoxygenase, and epoxygenase enzymes into more than one hundred fifty different potent primary autacoid metabolites in species ranging from fungi to plants to mammals. Arachidonic acid is stored in tissue phospholipids in esterified form, where it comprises a small but critically controlled percentage of the polyunsaturated fatty acid pool.{8460} Arachidonic acid ethyl ester is a more lipophilic form of arachidonic acid that can be incorporated into dietary regimens or fed to cultured cells as a source of exogenous arachidonate. It is one of the fatty acid ethyl esters that increase cytosolic Ca2+ concentration leading to pancreatic acinar cell injury due to excessive consumption of ethanol.{14120} Whereas arachidonic acid inhibits dopamine uptake, the ethyl esterified version does not retain this property.{14121}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008200 - 500 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonic acid is an essential fatty acid and a precursor for all prostaglandins, thromboxanes, and leukotrienes. Virtually all cellular arachidonic acid is esterified in membrane phospholipids where its presence is tightly regulated through multiple interconnected pathways.{3656} Free arachidonic acid is a transient, critical substrate for the biosynthesis of eicosanoid second messengers. Receptor-stimulated release, metabolism, and re-uptake of free arachidonate are all important aspects of cell signaling and inflammation.{314} Arachidonic acid MaxSpec® standard is a quantitative grade standard of arachidonic acid (Item No. 90010) that has been prepared specifically for mass spectrometry and related applications where quantitative reproducibility is required. The solution has been prepared gravimetrically and is supplied in a deactivated glass ampule sealed under argon. The concentration was verified by comparison to an independently prepared calibration standard. This arachidonic acid MaxSpec® standard is guaranteed to meet identity, purity, stability, and concentration specifications and is provided with a batch-specific certificate of analysis. Ongoing stability testing is performed to ensure the concentration remains accurate throughout the shelf life of the product. Note: The amount of solution added to the vial is in excess of the listed amount. Therefore, it is necessary to accurately measure volumes for preparation of calibration standards. Follow recommended storage and handling conditions to maintain product quality.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007268 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonic acid methyl ester is an esterified form of arachidonic acid (Item Nos. 90010 | 90010.1 | 10006607). It is commonly used as a reference standard for the quantification of arachidonic acid in biological samples and as a source of exogenous arachidonic acid in cells and in vivo.{1932,2293,52818,52817}
Brand:CaymanSKU:90014 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonic acid methyl ester is an esterified form of arachidonic acid (Item Nos. 90010 | 90010.1 | 10006607). It is commonly used as a reference standard for the quantification of arachidonic acid in biological samples and as a source of exogenous arachidonic acid in cells and in vivo.{1932,2293,52818,52817}
Brand:CaymanSKU:90014 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonic acid methyl ester is an esterified form of arachidonic acid (Item Nos. 90010 | 90010.1 | 10006607). It is commonly used as a reference standard for the quantification of arachidonic acid in biological samples and as a source of exogenous arachidonic acid in cells and in vivo.{1932,2293,52818,52817}
Brand:CaymanSKU:90014 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonic acid methyl ester is an esterified form of arachidonic acid (Item Nos. 90010 | 90010.1 | 10006607). It is commonly used as a reference standard for the quantification of arachidonic acid in biological samples and as a source of exogenous arachidonic acid in cells and in vivo.{1932,2293,52818,52817}
Brand:CaymanSKU:90014 - 500 mgAvailable on backorder
Virtually all cellular arachidonic acid is esterified in membrane phospholipids where its presence is tightly regulated through multiple interconnected pathways.{3656} Free arachidonic acid is a transient, critical substrate for the biosynthesis of eicosanoid second messengers. Receptor-stimulated release, metabolism, and re-uptake of free arachidonate are all important aspects of cell signalling and inflammation.{314} Arachidonic acid-biotin was designed to allow arachidonic acid to be detected in complexes with protein binding partners such as fatty acid binding proteins (FABPs). It is thus a tool to be used in the general elucidation of the signaling and transport of free arachidonic acid.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007466 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Virtually all cellular arachidonic acid is esterified in membrane phospholipids where its presence is tightly regulated through multiple interconnected pathways.{3656} Free arachidonic acid is a transient, critical substrate for the biosynthesis of eicosanoid second messengers. Receptor-stimulated release, metabolism, and re-uptake of free arachidonate are all important aspects of cell signalling and inflammation.{314} Arachidonic acid-biotin was designed to allow arachidonic acid to be detected in complexes with protein binding partners such as fatty acid binding proteins (FABPs). It is thus a tool to be used in the general elucidation of the signaling and transport of free arachidonic acid.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007466 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Virtually all cellular arachidonic acid is esterified in membrane phospholipids where its presence is tightly regulated through multiple interconnected pathways.{3656} Free arachidonic acid is a transient, critical substrate for the biosynthesis of eicosanoid second messengers. Receptor-stimulated release, metabolism, and re-uptake of free arachidonate are all important aspects of cell signalling and inflammation.{314} Arachidonic acid-biotin was designed to allow arachidonic acid to be detected in complexes with protein binding partners such as fatty acid binding proteins (FABPs). It is thus a tool to be used in the general elucidation of the signaling and transport of free arachidonic acid.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007466 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonic acid-d5 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of arachidonic acid (Item Nos. 90010 | 90010.1 | 10006607) by GC- or LC-MS. Arachidonic acid is an essential fatty acid and a precursor for all prostaglandins, thromboxanes, and leukotrienes. Virtually all cellular arachidonic acid is esterified in membrane phospholipids where its presence is tightly regulated through multiple interconnected pathways.{3656} Free arachidonic acid is a transient, critical substrate for the biosynthesis of eicosanoid second messengers. Receptor-stimulated release, metabolism, and re-uptake of free arachidonate are all important aspects of cell signaling and inflammation.{314}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9000477 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonic acid-d5 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of arachidonic acid (Item Nos. 90010 | 90010.1 | 10006607) by GC- or LC-MS. Arachidonic acid is an essential fatty acid and a precursor for all prostaglandins, thromboxanes, and leukotrienes. Virtually all cellular arachidonic acid is esterified in membrane phospholipids where its presence is tightly regulated through multiple interconnected pathways.{3656} Free arachidonic acid is a transient, critical substrate for the biosynthesis of eicosanoid second messengers. Receptor-stimulated release, metabolism, and re-uptake of free arachidonate are all important aspects of cell signaling and inflammation.{314}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9000477 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonic acid-d5 methyl ester is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of arachidonic acid methyl ester (Item No. 90014) by GC- or LC-MS. Arachidonic acid methyl ester is an esterified form of arachidonic acid (Item Nos. 90010 | 90010.1 | 10006607). It is commonly used as a reference standard for the quantification of arachidonic acid in biological samples and as a source of exogenous arachidonic acid in cells and in vivo.{1932,2293,52818,52817}
Brand:CaymanSKU:32535 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonic acid-d5 methyl ester is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of arachidonic acid methyl ester (Item No. 90014) by GC- or LC-MS. Arachidonic acid methyl ester is an esterified form of arachidonic acid (Item Nos. 90010 | 90010.1 | 10006607). It is commonly used as a reference standard for the quantification of arachidonic acid in biological samples and as a source of exogenous arachidonic acid in cells and in vivo.{1932,2293,52818,52817}
Brand:CaymanSKU:32535 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
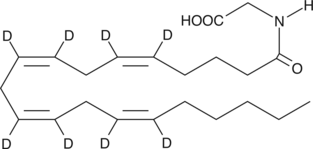
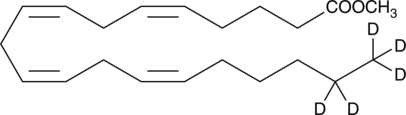
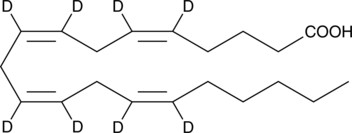
Arachidonic acid-d8 contains eight deuterium atoms at the 5, 6, 8, 9, 11, 12, 14, and 15 positions. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of arachidonic acid by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. Arachidonic acid is an essential fatty acid and a precursor for all prostaglandins, thromboxanes, and leukotrienes. Virtually all cellular arachidonic acid is esterified in membrane phospholipids where its presence is tightly regulated through multiple interconnected pathways.{314} Free arachidonic acid is a transient, critical substrate for the biosynthesis of eicosanoid second messengers. Receptor-stimulated release, metabolism, and re-uptake of free arachidonate are all important aspects of cell signaling and inflammation.{3656}
Brand:CaymanSKU:390010 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonic acid-d8 contains eight deuterium atoms at the 5, 6, 8, 9, 11, 12, 14, and 15 positions. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of arachidonic acid by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. Arachidonic acid is an essential fatty acid and a precursor for all prostaglandins, thromboxanes, and leukotrienes. Virtually all cellular arachidonic acid is esterified in membrane phospholipids where its presence is tightly regulated through multiple interconnected pathways.{314} Free arachidonic acid is a transient, critical substrate for the biosynthesis of eicosanoid second messengers. Receptor-stimulated release, metabolism, and re-uptake of free arachidonate are all important aspects of cell signaling and inflammation.{3656}
Brand:CaymanSKU:390010 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonic acid-d8 contains eight deuterium atoms at the 5, 6, 8, 9, 11, 12, 14, and 15 positions. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of arachidonic acid by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. Arachidonic acid is an essential fatty acid and a precursor for all prostaglandins, thromboxanes, and leukotrienes. Virtually all cellular arachidonic acid is esterified in membrane phospholipids where its presence is tightly regulated through multiple interconnected pathways.{314} Free arachidonic acid is a transient, critical substrate for the biosynthesis of eicosanoid second messengers. Receptor-stimulated release, metabolism, and re-uptake of free arachidonate are all important aspects of cell signaling and inflammation.{3656}
Brand:CaymanSKU:390010 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
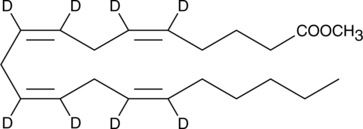
Arachidonic acid-d8 methyl ester is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of arachidonic acid methyl ester (Item No. 90014) by GC- or LC-MS. Arachidonic acid methyl ester is an esterified form of arachidonic acid (Item Nos. 90010 | 90010.1 | 10006607). It is commonly used as a reference standard for the quantification of arachidonic acid in biological samples and as a source of exogenous arachidonic acid in cells and in vivo.{1932,2293,52818,52817}
Brand:CaymanSKU:390014 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonic acid-d8 methyl ester is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of arachidonic acid methyl ester (Item No. 90014) by GC- or LC-MS. Arachidonic acid methyl ester is an esterified form of arachidonic acid (Item Nos. 90010 | 90010.1 | 10006607). It is commonly used as a reference standard for the quantification of arachidonic acid in biological samples and as a source of exogenous arachidonic acid in cells and in vivo.{1932,2293,52818,52817}
Brand:CaymanSKU:390014 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonic acid-d8 methyl ester is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of arachidonic acid methyl ester (Item No. 90014) by GC- or LC-MS. Arachidonic acid methyl ester is an esterified form of arachidonic acid (Item Nos. 90010 | 90010.1 | 10006607). It is commonly used as a reference standard for the quantification of arachidonic acid in biological samples and as a source of exogenous arachidonic acid in cells and in vivo.{1932,2293,52818,52817}
Brand:CaymanSKU:390014 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
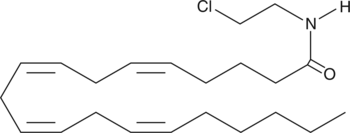
Arachidonoyl 2-chloroethylamide (ACEA) is a potent and selective cannabinoid (CB) receptor 1 agonist with Ki values of 1.4 and >2,000 nM for CB1 and CB2 receptors, respectively.{7912} In whole animal experiments, ACEA induces hypothermia in mice with the same efficacy as arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA; Item No. 90050), in spite of its higher affinity for the CB1 receptor. These data have been interpreted to indicate that ACEA may be a substrate for fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), and thus only transiently available in whole animal experiments.{9573}
Brand:CaymanSKU:91054 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl 2-chloroethylamide (ACEA) is a potent and selective cannabinoid (CB) receptor 1 agonist with Ki values of 1.4 and >2,000 nM for CB1 and CB2 receptors, respectively.{7912} In whole animal experiments, ACEA induces hypothermia in mice with the same efficacy as arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA; Item No. 90050), in spite of its higher affinity for the CB1 receptor. These data have been interpreted to indicate that ACEA may be a substrate for fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), and thus only transiently available in whole animal experiments.{9573}
Brand:CaymanSKU:91054 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl 2-chloroethylamide (ACEA) is a potent and selective cannabinoid (CB) receptor 1 agonist with Ki values of 1.4 and >2,000 nM for CB1 and CB2 receptors, respectively.{7912} In whole animal experiments, ACEA induces hypothermia in mice with the same efficacy as arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA; Item No. 90050), in spite of its higher affinity for the CB1 receptor. These data have been interpreted to indicate that ACEA may be a substrate for fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), and thus only transiently available in whole animal experiments.{9573}
Brand:CaymanSKU:91054 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl 2-chloroethylamide (ACEA) is a potent and selective cannabinoid (CB) receptor 1 agonist with Ki values of 1.4 and >2,000 nM for CB1 and CB2 receptors, respectively.{7912} In whole animal experiments, ACEA induces hypothermia in mice with the same efficacy as arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA; Item No. 90050), in spite of its higher affinity for the CB1 receptor. These data have been interpreted to indicate that ACEA may be a substrate for fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), and thus only transiently available in whole animal experiments.{9573}
Brand:CaymanSKU:91054 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
Anandamide (AEA) is an endogenous cannabinoid that binds to both central cannabinoid (CB1) and peripheral cannabinoid (CB2) receptors. The biological actions of AEA are terminated by cellular uptake and hydrolysis of the amide bond by the enzyme fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH). Arachidonoyl amide is an analog of anandamide (AEA) that lacks the hydroxyethyl moiety. It is hydrolyzed by FAAH more effectively than AEA but exhibits significantly weaker binding to the human CB1 receptor with a Ki of 9.6 µM.{2713,13257} Arachidonoyl amide and AEA exhibit similar binding and translocation into cells via the AEA transporter. It inhibits [3H]-AEA uptake into human astrocytoma cells with an IC50 of 9 µM.{13757} Arachidonoyl amide also inhibits rat glial gap junction cell-cell communication by 90% at a concentration of 20 µM.{8122}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007295 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Anandamide (AEA) is an endogenous cannabinoid that binds to both central cannabinoid (CB1) and peripheral cannabinoid (CB2) receptors. The biological actions of AEA are terminated by cellular uptake and hydrolysis of the amide bond by the enzyme fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH). Arachidonoyl amide is an analog of anandamide (AEA) that lacks the hydroxyethyl moiety. It is hydrolyzed by FAAH more effectively than AEA but exhibits significantly weaker binding to the human CB1 receptor with a Ki of 9.6 µM.{2713,13257} Arachidonoyl amide and AEA exhibit similar binding and translocation into cells via the AEA transporter. It inhibits [3H]-AEA uptake into human astrocytoma cells with an IC50 of 9 µM.{13757} Arachidonoyl amide also inhibits rat glial gap junction cell-cell communication by 90% at a concentration of 20 µM.{8122}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007295 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
Anandamide (AEA) is an endogenous cannabinoid that binds to both central cannabinoid (CB1) and peripheral cannabinoid (CB2) receptors. The biological actions of AEA are terminated by cellular uptake and hydrolysis of the amide bond by the enzyme fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH). Arachidonoyl amide is an analog of anandamide (AEA) that lacks the hydroxyethyl moiety. It is hydrolyzed by FAAH more effectively than AEA but exhibits significantly weaker binding to the human CB1 receptor with a Ki of 9.6 µM.{2713,13257} Arachidonoyl amide and AEA exhibit similar binding and translocation into cells via the AEA transporter. It inhibits [3H]-AEA uptake into human astrocytoma cells with an IC50 of 9 µM.{13757} Arachidonoyl amide also inhibits rat glial gap junction cell-cell communication by 90% at a concentration of 20 µM.{8122}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007295 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Anandamide (AEA) is an endogenous cannabinoid that binds to both central cannabinoid (CB1) and peripheral cannabinoid (CB2) receptors. The biological actions of AEA are terminated by cellular uptake and hydrolysis of the amide bond by the enzyme fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH). Arachidonoyl amide is an analog of anandamide (AEA) that lacks the hydroxyethyl moiety. It is hydrolyzed by FAAH more effectively than AEA but exhibits significantly weaker binding to the human CB1 receptor with a Ki of 9.6 µM.{2713,13257} Arachidonoyl amide and AEA exhibit similar binding and translocation into cells via the AEA transporter. It inhibits [3H]-AEA uptake into human astrocytoma cells with an IC50 of 9 µM.{13757} Arachidonoyl amide also inhibits rat glial gap junction cell-cell communication by 90% at a concentration of 20 µM.{8122}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007295 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
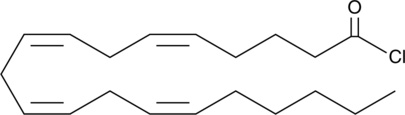
Arachidonoyl chloride is a derivative of arachidonic acid (Item No. 90010). It has been used as an intermediate in the synthesis of arachidonic acid derivatives.{14398}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
Arachidonoyl chloride is a derivative of arachidonic acid (Item No. 90010). It has been used as an intermediate in the synthesis of arachidonic acid derivatives.{14398}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
Arachidonoyl chloride is a derivative of arachidonic acid (Item No. 90010). It has been used as an intermediate in the synthesis of arachidonic acid derivatives.{14398}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
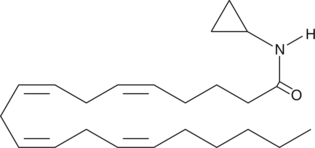
Arachidonoyl cyclopropylamide (ACPA) is a potent and selective cannabinoid (CB) receptor 1 agonist with Ki values of 2.2 and 715 nM for CB1 and CB2 receptors, respectively.{7912} In whole animal experiments, ACPA induces hypothermia in mice with the same efficacy as arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA; Item No. 90050), in spite of its higher affinity for the CB1 receptor. These data have been interpreted to indicate that ACEA may be a substrate for fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), and thus only transiently available in whole animal experiments.{9573}
Brand:CaymanSKU:91053 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl cyclopropylamide (ACPA) is a potent and selective cannabinoid (CB) receptor 1 agonist with Ki values of 2.2 and 715 nM for CB1 and CB2 receptors, respectively.{7912} In whole animal experiments, ACPA induces hypothermia in mice with the same efficacy as arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA; Item No. 90050), in spite of its higher affinity for the CB1 receptor. These data have been interpreted to indicate that ACEA may be a substrate for fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), and thus only transiently available in whole animal experiments.{9573}
Brand:CaymanSKU:91053 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl cyclopropylamide (ACPA) is a potent and selective cannabinoid (CB) receptor 1 agonist with Ki values of 2.2 and 715 nM for CB1 and CB2 receptors, respectively.{7912} In whole animal experiments, ACPA induces hypothermia in mice with the same efficacy as arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA; Item No. 90050), in spite of its higher affinity for the CB1 receptor. These data have been interpreted to indicate that ACEA may be a substrate for fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), and thus only transiently available in whole animal experiments.{9573}
Brand:CaymanSKU:91053 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl cyclopropylamide (ACPA) is a potent and selective cannabinoid (CB) receptor 1 agonist with Ki values of 2.2 and 715 nM for CB1 and CB2 receptors, respectively.{7912} In whole animal experiments, ACPA induces hypothermia in mice with the same efficacy as arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA; Item No. 90050), in spite of its higher affinity for the CB1 receptor. These data have been interpreted to indicate that ACEA may be a substrate for fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), and thus only transiently available in whole animal experiments.{9573}
Brand:CaymanSKU:91053 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
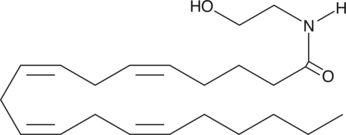
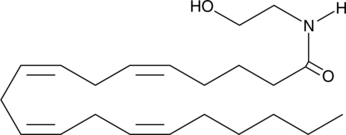
Arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA) is the ethanolamine amide of arachidonic acid, originally isolated from porcine brain.{1134} AEA is an endogenous cannabinoid neurotransmitter that binds to both cannabinoid 1 (CB1) and CB2 receptors.{2713} AEA has Ki values ranging from 61 to 543 nM for CB1 receptors and from 279 to 1,940 nM for CB2 receptors.{7912}
Brand:CaymanSKU:90050 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA) is the ethanolamine amide of arachidonic acid, originally isolated from porcine brain.{1134} AEA is an endogenous cannabinoid neurotransmitter that binds to both cannabinoid 1 (CB1) and CB2 receptors.{2713} AEA has Ki values ranging from 61 to 543 nM for CB1 receptors and from 279 to 1,940 nM for CB2 receptors.{7912}
Brand:CaymanSKU:90050 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA) is the ethanolamine amide of arachidonic acid, originally isolated from porcine brain.{1134} AEA is an endogenous cannabinoid neurotransmitter that binds to both cannabinoid 1 (CB1) and CB2 receptors.{2713} AEA has Ki values ranging from 61 to 543 nM for CB1 receptors and from 279 to 1,940 nM for CB2 receptors.{7912}
Brand:CaymanSKU:90050 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA) is the ethanolamine amide of arachidonic acid, originally isolated from porcine brain.{1134} AEA is an endogenous cannabinoid neurotransmitter that binds to both cannabinoid 1 (CB1) and CB2 receptors.{2713} AEA has Ki values ranging from 61 to 543 nM for CB1 receptors and from 279 to 1,940 nM for CB2 receptors.{7912}
Brand:CaymanSKU:90050 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
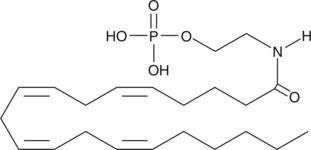
Arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA) is the ethanolamine amide of arachidonic acid (Item No. 90010), first isolated from porcine brain.{1134} AEA is an endogenous cannabinoid neurotransmitter that binds to both central cannabinoid (CB1) and peripheral cannabinoid (CB2) receptors.{2713} AEA inhibits the specific binding of [3H]-HU-243 to synaptosomal membranes with a Ki value of 52 nM, compared to 46 nM for Δ9-THC (Item Nos. 12068 | ISO60157).{1134} AEA MaxSpec® standard is a quantitative grade standard of AEA (Item No. 90050) that has been prepared specifically for mass spectrometry or any application where quantitative reproducibility is required. The solution has been prepared gravimetrically and is supplied in a deactivated glass ampule sealed under argon. The concentration was verified by comparison to an independently prepared calibration standard. This AEA MaxSpec® standard is guaranteed to meet identity, purity, stability, and concentration specifications and is provided with a batch-specific certificate of analysis. Ongoing stability testing is performed to ensure the concentration remains accurate throughout the shelf life of the product. Note: The amount of solution added to the vial is in excess of the listed amount. Therefore, it is necessary to accurately measure volumes for preparation of calibration standards. Follow recommended storage and handling conditions to maintain product quality.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007270 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA; Item No. 90050) was the first endogenous cannabinoid (CB) to be isolated and characterized as an agonist acting on the same receptors (CB1 and CB2) as Δ9-THC (Item No. 12068).{1134,2713} Since that time, a number of related endocannabinoids have been isolated, most notably 2-arachidonoyl glycerol (2-AG; Item No. 62160).{2713} The phosphate ester of AEA, AEA-P, has been tested as a water soluble prodrug version of AEA in the treatment of C6 glioma cells in vivo. Here it acts with essentially the same potency as AEA.{11520} However, when tested for inhibition of AEA binding to isolated rat brain CB1 receptors, AEA-P is about 5-fold less potent as an agonist with a Ki of about 200 nM.{9580} The phosphate esters of AEA and its analogs are also structural variants of lysophosphatidic acid (LPA). However, the effects of AEA-P on the various LPA receptors have not been tested.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10180 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA; Item No. 90050) was the first endogenous cannabinoid (CB) to be isolated and characterized as an agonist acting on the same receptors (CB1 and CB2) as Δ9-THC (Item No. 12068).{1134,2713} Since that time, a number of related endocannabinoids have been isolated, most notably 2-arachidonoyl glycerol (2-AG; Item No. 62160).{2713} The phosphate ester of AEA, AEA-P, has been tested as a water soluble prodrug version of AEA in the treatment of C6 glioma cells in vivo. Here it acts with essentially the same potency as AEA.{11520} However, when tested for inhibition of AEA binding to isolated rat brain CB1 receptors, AEA-P is about 5-fold less potent as an agonist with a Ki of about 200 nM.{9580} The phosphate esters of AEA and its analogs are also structural variants of lysophosphatidic acid (LPA). However, the effects of AEA-P on the various LPA receptors have not been tested.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10180 - 250 µgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA; Item No. 90050) was the first endogenous cannabinoid (CB) to be isolated and characterized as an agonist acting on the same receptors (CB1 and CB2) as Δ9-THC (Item No. 12068).{1134,2713} Since that time, a number of related endocannabinoids have been isolated, most notably 2-arachidonoyl glycerol (2-AG; Item No. 62160).{2713} The phosphate ester of AEA, AEA-P, has been tested as a water soluble prodrug version of AEA in the treatment of C6 glioma cells in vivo. Here it acts with essentially the same potency as AEA.{11520} However, when tested for inhibition of AEA binding to isolated rat brain CB1 receptors, AEA-P is about 5-fold less potent as an agonist with a Ki of about 200 nM.{9580} The phosphate esters of AEA and its analogs are also structural variants of lysophosphatidic acid (LPA). However, the effects of AEA-P on the various LPA receptors have not been tested.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10180 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA; Item No. 90050) was the first endogenous cannabinoid (CB) to be isolated and characterized as an agonist acting on the same receptors (CB1 and CB2) as Δ9-THC (Item No. 12068).{1134,2713} Since that time, a number of related endocannabinoids have been isolated, most notably 2-arachidonoyl glycerol (2-AG; Item No. 62160).{2713} The phosphate ester of AEA, AEA-P, has been tested as a water soluble prodrug version of AEA in the treatment of C6 glioma cells in vivo. Here it acts with essentially the same potency as AEA.{11520} However, when tested for inhibition of AEA binding to isolated rat brain CB1 receptors, AEA-P is about 5-fold less potent as an agonist with a Ki of about 200 nM.{9580} The phosphate esters of AEA and its analogs are also structural variants of lysophosphatidic acid (LPA). However, the effects of AEA-P on the various LPA receptors have not been tested.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10180 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
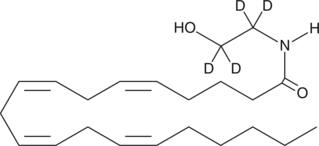
Arachidonoyl ethanolamide-d4 (AEA-d4) contains four deuterium atoms at the hydroxyethyl 1,1′,2, and 2′ positions. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of AEA by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. AEA is the ethanolamine amide of arachidonic acid, first isolated from porcine brain.{1134} It is an endogenous cannabinoid neurotransmitter that binds to both central cannabinoid (CB1) and peripheral cannabinoid (CB2) receptors and mimics the pharmacologic effects of Δ9-THC.{2713} AEA inhibits the specific binding of [3H]-HU-243 to synaptosomal membranes with a Ki value of 52 nM, compared to 46 nM for Δ9-THC.{1134}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10011178 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl ethanolamide-d4 (AEA-d4) contains four deuterium atoms at the hydroxyethyl 1,1′,2, and 2′ positions. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of AEA by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. AEA is the ethanolamine amide of arachidonic acid, first isolated from porcine brain.{1134} It is an endogenous cannabinoid neurotransmitter that binds to both central cannabinoid (CB1) and peripheral cannabinoid (CB2) receptors and mimics the pharmacologic effects of Δ9-THC.{2713} AEA inhibits the specific binding of [3H]-HU-243 to synaptosomal membranes with a Ki value of 52 nM, compared to 46 nM for Δ9-THC.{1134}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10011178 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl ethanolamide-d4 (AEA-d4) contains four deuterium atoms at the hydroxyethyl 1,1′,2, and 2′ positions. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of AEA by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. AEA is the ethanolamine amide of arachidonic acid, first isolated from porcine brain.{1134} It is an endogenous cannabinoid neurotransmitter that binds to both central cannabinoid (CB1) and peripheral cannabinoid (CB2) receptors and mimics the pharmacologic effects of Δ9-THC.{2713} AEA inhibits the specific binding of [3H]-HU-243 to synaptosomal membranes with a Ki value of 52 nM, compared to 46 nM for Δ9-THC.{1134}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10011178 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl ethanolamide-d4 (AEA-d4) contains four deuterium atoms at the hydroxyethyl 1,1′,2, and 2′ positions. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of AEA by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. AEA is the ethanolamine amide of arachidonic acid, first isolated from porcine brain.{1134} It is an endogenous cannabinoid neurotransmitter that binds to both central cannabinoid (CB1) and peripheral cannabinoid (CB2) receptors and mimics the pharmacologic effects of Δ9-THC.{2713} AEA inhibits the specific binding of [3H]-HU-243 to synaptosomal membranes with a Ki value of 52 nM, compared to 46 nM for Δ9-THC.{1134}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10011178 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
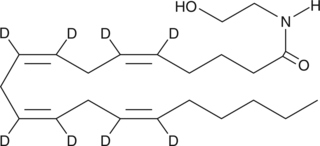
Arachidonoyl ethanolamide-d8 (AEA-8) contains eight deuterium atoms at the 5, 6, 8, 9, 11, 12, 14, and 15 positions. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of AEA by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. AEA is the ethanolamine amide of arachidonic acid, first isolated from porcine brain.{1134} It is an endogenous cannabinoid neurotransmitter that binds to both CB1 and CB2 receptors.{2713} AEA inhibits the specific binding of [3H]-HU-243 to synaptosomal membranes with a Ki value of 52 nM, compared to 46 nM for Δ9-THC.{1134}
Brand:CaymanSKU:390050 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl ethanolamide-d8 (AEA-8) contains eight deuterium atoms at the 5, 6, 8, 9, 11, 12, 14, and 15 positions. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of AEA by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. AEA is the ethanolamine amide of arachidonic acid, first isolated from porcine brain.{1134} It is an endogenous cannabinoid neurotransmitter that binds to both CB1 and CB2 receptors.{2713} AEA inhibits the specific binding of [3H]-HU-243 to synaptosomal membranes with a Ki value of 52 nM, compared to 46 nM for Δ9-THC.{1134}
Brand:CaymanSKU:390050 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl ethanolamide-d8 (AEA-8) contains eight deuterium atoms at the 5, 6, 8, 9, 11, 12, 14, and 15 positions. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of AEA by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. AEA is the ethanolamine amide of arachidonic acid, first isolated from porcine brain.{1134} It is an endogenous cannabinoid neurotransmitter that binds to both CB1 and CB2 receptors.{2713} AEA inhibits the specific binding of [3H]-HU-243 to synaptosomal membranes with a Ki value of 52 nM, compared to 46 nM for Δ9-THC.{1134}
Brand:CaymanSKU:390050 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl ethanolamide-d8 (AEA-8) contains eight deuterium atoms at the 5, 6, 8, 9, 11, 12, 14, and 15 positions. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of AEA by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. AEA is the ethanolamine amide of arachidonic acid, first isolated from porcine brain.{1134} It is an endogenous cannabinoid neurotransmitter that binds to both CB1 and CB2 receptors.{2713} AEA inhibits the specific binding of [3H]-HU-243 to synaptosomal membranes with a Ki value of 52 nM, compared to 46 nM for Δ9-THC.{1134}
Brand:CaymanSKU:390050 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
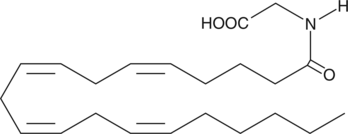
Arachidonoyl glycine (N-arachidonyl glycine; NAGly) has been isolated from cell cultures treated with arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA; anandamide),{9578} from extracts of mammalian brain,{9579,9589} and has also been synthesized as an analog of AEA for structure/activity testing.{9580} NAGly may be produced endogenously via oxidation of AEA, or by transacylation of arachidonoyl CoA. NAGly is reported to have analgesic activities in whole animal experiments.{9578,9579,9589} Since it seems to be a very poor ligand for the CB1 receptor,{9580} these effects are probably mediated via other signaling pathways.
Brand:CaymanSKU:90051 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl glycine (N-arachidonyl glycine; NAGly) has been isolated from cell cultures treated with arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA; anandamide),{9578} from extracts of mammalian brain,{9579,9589} and has also been synthesized as an analog of AEA for structure/activity testing.{9580} NAGly may be produced endogenously via oxidation of AEA, or by transacylation of arachidonoyl CoA. NAGly is reported to have analgesic activities in whole animal experiments.{9578,9579,9589} Since it seems to be a very poor ligand for the CB1 receptor,{9580} these effects are probably mediated via other signaling pathways.
Brand:CaymanSKU:90051 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl glycine (N-arachidonyl glycine; NAGly) has been isolated from cell cultures treated with arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA; anandamide),{9578} from extracts of mammalian brain,{9579,9589} and has also been synthesized as an analog of AEA for structure/activity testing.{9580} NAGly may be produced endogenously via oxidation of AEA, or by transacylation of arachidonoyl CoA. NAGly is reported to have analgesic activities in whole animal experiments.{9578,9579,9589} Since it seems to be a very poor ligand for the CB1 receptor,{9580} these effects are probably mediated via other signaling pathways.
Brand:CaymanSKU:90051 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl glycine (N-arachidonyl glycine; NAGly) has been isolated from cell cultures treated with arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA; anandamide),{9578} from extracts of mammalian brain,{9579,9589} and has also been synthesized as an analog of AEA for structure/activity testing.{9580} NAGly may be produced endogenously via oxidation of AEA, or by transacylation of arachidonoyl CoA. NAGly is reported to have analgesic activities in whole animal experiments.{9578,9579,9589} Since it seems to be a very poor ligand for the CB1 receptor,{9580} these effects are probably mediated via other signaling pathways.
Brand:CaymanSKU:90051 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl glycine-d8 (NAGly-d8) contains eight deuterium atoms at the 5, 6, 8, 9, 11, 12, 14, and 15 positions. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of NAGly by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. NAGly has been isolated from cell cultures treated with arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA),{9578} from extracts of mammalian brain,{9579,9589} and has also been synthesized as an analog of AEA for structure/activity testing.{9580} NAGly may be produced endogenously via oxidation of AEA, or by transacylation of arachidonoyl coenzyme A. NAGly is reported to have analgesic activities in whole animal experiments.{9578,9579,9589} Since it seems to be a very poor ligand for the CB1 receptor,{9580} these effects are probably mediated via other signalling pathways.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007531 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl glycine-d8 (NAGly-d8) contains eight deuterium atoms at the 5, 6, 8, 9, 11, 12, 14, and 15 positions. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of NAGly by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. NAGly has been isolated from cell cultures treated with arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA),{9578} from extracts of mammalian brain,{9579,9589} and has also been synthesized as an analog of AEA for structure/activity testing.{9580} NAGly may be produced endogenously via oxidation of AEA, or by transacylation of arachidonoyl coenzyme A. NAGly is reported to have analgesic activities in whole animal experiments.{9578,9579,9589} Since it seems to be a very poor ligand for the CB1 receptor,{9580} these effects are probably mediated via other signalling pathways.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007531 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl glycine-d8 (NAGly-d8) contains eight deuterium atoms at the 5, 6, 8, 9, 11, 12, 14, and 15 positions. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of NAGly by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. NAGly has been isolated from cell cultures treated with arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA),{9578} from extracts of mammalian brain,{9579,9589} and has also been synthesized as an analog of AEA for structure/activity testing.{9580} NAGly may be produced endogenously via oxidation of AEA, or by transacylation of arachidonoyl coenzyme A. NAGly is reported to have analgesic activities in whole animal experiments.{9578,9579,9589} Since it seems to be a very poor ligand for the CB1 receptor,{9580} these effects are probably mediated via other signalling pathways.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007531 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl glycine-d8 (NAGly-d8) contains eight deuterium atoms at the 5, 6, 8, 9, 11, 12, 14, and 15 positions. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of NAGly by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. NAGly has been isolated from cell cultures treated with arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA),{9578} from extracts of mammalian brain,{9579,9589} and has also been synthesized as an analog of AEA for structure/activity testing.{9580} NAGly may be produced endogenously via oxidation of AEA, or by transacylation of arachidonoyl coenzyme A. NAGly is reported to have analgesic activities in whole animal experiments.{9578,9579,9589} Since it seems to be a very poor ligand for the CB1 receptor,{9580} these effects are probably mediated via other signalling pathways.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007531 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl m-Nitroaniline (AmNA) is one of several nitroaniline fatty acid amides which can be used to measure fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) activity.{8928} FAAH is a relatively unselective enzyme in that it accepts a variety of amide head groups other than the ethanolamine of its nominal endogenous substrate anandamide (arachidonyl ethanolamide; AEA). It also will hydrolyze fatty acid amides with fewer carbons and fewer double bonds than arachidonate (see also Decanoyl m-Nitroaniline; Item No. 90349). Exposure of AmNA to FAAH activity results in the release of the yellow colorimetric dye m-nitroaniline (ε = 13,500 at 410 nm). This offers the potential for fast and convenient measurements of FAAH activity using a 96 well plate spectrophotometer.
Brand:CaymanSKU:90059 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl m-Nitroaniline (AmNA) is one of several nitroaniline fatty acid amides which can be used to measure fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) activity.{8928} FAAH is a relatively unselective enzyme in that it accepts a variety of amide head groups other than the ethanolamine of its nominal endogenous substrate anandamide (arachidonyl ethanolamide; AEA). It also will hydrolyze fatty acid amides with fewer carbons and fewer double bonds than arachidonate (see also Decanoyl m-Nitroaniline; Item No. 90349). Exposure of AmNA to FAAH activity results in the release of the yellow colorimetric dye m-nitroaniline (ε = 13,500 at 410 nm). This offers the potential for fast and convenient measurements of FAAH activity using a 96 well plate spectrophotometer.
Brand:CaymanSKU:90059 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl m-Nitroaniline (AmNA) is one of several nitroaniline fatty acid amides which can be used to measure fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) activity.{8928} FAAH is a relatively unselective enzyme in that it accepts a variety of amide head groups other than the ethanolamine of its nominal endogenous substrate anandamide (arachidonyl ethanolamide; AEA). It also will hydrolyze fatty acid amides with fewer carbons and fewer double bonds than arachidonate (see also Decanoyl m-Nitroaniline; Item No. 90349). Exposure of AmNA to FAAH activity results in the release of the yellow colorimetric dye m-nitroaniline (ε = 13,500 at 410 nm). This offers the potential for fast and convenient measurements of FAAH activity using a 96 well plate spectrophotometer.
Brand:CaymanSKU:90059 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl m-Nitroaniline (AmNA) is one of several nitroaniline fatty acid amides which can be used to measure fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) activity.{8928} FAAH is a relatively unselective enzyme in that it accepts a variety of amide head groups other than the ethanolamine of its nominal endogenous substrate anandamide (arachidonyl ethanolamide; AEA). It also will hydrolyze fatty acid amides with fewer carbons and fewer double bonds than arachidonate (see also Decanoyl m-Nitroaniline; Item No. 90349). Exposure of AmNA to FAAH activity results in the release of the yellow colorimetric dye m-nitroaniline (ε = 13,500 at 410 nm). This offers the potential for fast and convenient measurements of FAAH activity using a 96 well plate spectrophotometer.
Brand:CaymanSKU:90059 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl p-nitroaniline (ApNA) is one of several nitroaniline fatty acid amides which can be used to measure fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) activity.{8928} FAAH is a relatively unselective enzyme in that it accepts a variety of amide head groups other than the ethanolamine of its nominal endogenous substrate anandamide (AEA; Item No. 90050). It also will hydrolyze fatty acid amides with fewer carbons and fewer double bonds than arachidonate. (See also Decanoyl p-Nitroaniline – Catalog No. 90349). Exposure of ApNA to FAAH activity results in the release of the yellow colorimetric dye p-nitroaniline (ε = 13,500 at 382 nm). This offers the potential for fast and convenient measurements of FAAH activity using a 96-well plate spectrophotometer.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10168 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
![Arachidonamide is an analog of AEA that lacks the hydroxyethyl moiety. It is hydrolyzed by FAAH more effectively than AEA but exhibits significantly weaker binding to the human CB1 receptor with a Ki value of 9.6 µM. Arachidonamide and AEA exhibit similar binding and translocation into cells via the AEA transporter. Arachidonamide inhibits [3H]-AEA uptake into human astrocytoma cells with an IC50 value of 9 µM and inhibits rat glial gap junction cell-cell communication by 90% at a concentration of 20 µM.](https://interpriseusa.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/06/10007295.png)