Cayman
Showing 7651–7800 of 45550 results
-
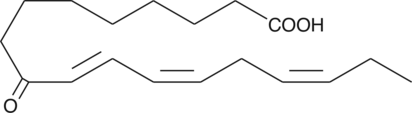
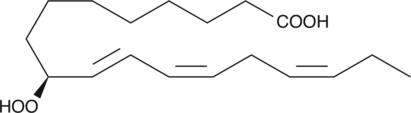
9-OxoOTrE is produced by the oxidation of 9-HpOTrE.{14394} 9-OxoOTrE exhibits antimicrobial activity against plant pathogenic microorganisms including bacteria and fungi.{14395}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10009215 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
9-OxoOTrE is produced by the oxidation of 9-HpOTrE.{14394} 9-OxoOTrE exhibits antimicrobial activity against plant pathogenic microorganisms including bacteria and fungi.{14395}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10009215 - 25 µgAvailable on backorder
9-OxoOTrE is produced by the oxidation of 9-HpOTrE.{14394} 9-OxoOTrE exhibits antimicrobial activity against plant pathogenic microorganisms including bacteria and fungi.{14395}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10009215 - 250 µgAvailable on backorder
9-OxoOTrE is produced by the oxidation of 9-HpOTrE.{14394} 9-OxoOTrE exhibits antimicrobial activity against plant pathogenic microorganisms including bacteria and fungi.{14395}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10009215 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
Branched fatty acid esters of hydroxy fatty acids (FAHFAs) are newly identified endogenous lipids regulated by fasting and high-fat feeding and associated with insulin sensitivity.{27644} Structurally, these esters are comprised of a C-16 or C-18 fatty acid (e.g., palmitoleic, palmitic, oleic, or stearic acid) linked to a hydroxylated C-16 or C-18 lipid. 9-PAHPA is a FAHFA in which palmitic acid is esterified to 9-hydroxy palmitic acid. Among the FAHFA family members, PAHSAs are the most abundant in the adipose tissue of glucose tolerant AG4OX mice, which overexpress the Glut4 glucose transporter specifically in adipose tissue.{27644} As other FAHFAs improve glucose tolerance, stimulate insulin secretion, and have anti-inflammatory effects, 9-PAHPA may be a bioactive lipid with roles in metabolic syndrome and inflammation.{27644}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
Branched fatty acid esters of hydroxy fatty acids (FAHFAs) are newly identified endogenous lipids regulated by fasting and high-fat feeding and associated with insulin sensitivity.{27644} Structurally, these esters are comprised of a C-16 or C-18 fatty acid (e.g., palmitoleic, palmitic, oleic, or stearic acid) linked to a hydroxylated C-16 or C-18 lipid. 9-PAHPA is a FAHFA in which palmitic acid is esterified to 9-hydroxy palmitic acid. Among the FAHFA family members, PAHSAs are the most abundant in the adipose tissue of glucose tolerant AG4OX mice, which overexpress the Glut4 glucose transporter specifically in adipose tissue.{27644} As other FAHFAs improve glucose tolerance, stimulate insulin secretion, and have anti-inflammatory effects, 9-PAHPA may be a bioactive lipid with roles in metabolic syndrome and inflammation.{27644}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
Branched fatty acid esters of hydroxy fatty acids (FAHFAs) are newly identified endogenous lipids regulated by fasting and high-fat feeding and associated with insulin sensitivity.{27644} Structurally, these esters are comprised of a C-16 or C-18 fatty acid (e.g., palmitoleic, palmitic, oleic, or stearic acid) linked to a hydroxylated C-16 or C-18 lipid. 9-PAHPA is a FAHFA in which palmitic acid is esterified to 9-hydroxy palmitic acid. Among the FAHFA family members, PAHSAs are the most abundant in the adipose tissue of glucose tolerant AG4OX mice, which overexpress the Glut4 glucose transporter specifically in adipose tissue.{27644} As other FAHFAs improve glucose tolerance, stimulate insulin secretion, and have anti-inflammatory effects, 9-PAHPA may be a bioactive lipid with roles in metabolic syndrome and inflammation.{27644}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
Branched fatty acid esters of hydroxy fatty acids (FAHFAs) are newly identified endogenous lipids regulated by fasting and high-fat feeding and associated with insulin sensitivity.{27644} Structurally, these esters are comprised of a C-16 or C-18 fatty acid (e.g., palmitoleic, palmitic, oleic, or stearic acid) linked to a hydroxylated C-16 or C-18 lipid. 9-PAHSA is a FAHFA in which palmitic acid is esterified to 9-hydroxy stearic acid. PAHSAs are the most abundant forms of FAHFA in serum as well as white and brown adipose tissues of glucose tolerant AG4OX mice, which overexpress Glut4 specifically in adipose tissue.{27644} 9-PAHSA is the predominant isomer of PAHSA in wild type and AG4OX mice.{27644} It is found in humans and is reduced in the serum and adipose tissues of insulin-resistant humans.{27644} 9-PAHSA improves glucose tolerance, stimulates insulin secretion, and has anti-inflammatory effects in mice.{27644}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
Branched fatty acid esters of hydroxy fatty acids (FAHFAs) are newly identified endogenous lipids regulated by fasting and high-fat feeding and associated with insulin sensitivity.{27644} Structurally, these esters are comprised of a C-16 or C-18 fatty acid (e.g., palmitoleic, palmitic, oleic, or stearic acid) linked to a hydroxylated C-16 or C-18 lipid. 9-PAHSA is a FAHFA in which palmitic acid is esterified to 9-hydroxy stearic acid. PAHSAs are the most abundant forms of FAHFA in serum as well as white and brown adipose tissues of glucose tolerant AG4OX mice, which overexpress Glut4 specifically in adipose tissue.{27644} 9-PAHSA is the predominant isomer of PAHSA in wild type and AG4OX mice.{27644} It is found in humans and is reduced in the serum and adipose tissues of insulin-resistant humans.{27644} 9-PAHSA improves glucose tolerance, stimulates insulin secretion, and has anti-inflammatory effects in mice.{27644}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
Branched fatty acid esters of hydroxy fatty acids (FAHFAs) are newly identified endogenous lipids regulated by fasting and high-fat feeding and associated with insulin sensitivity.{27644} Structurally, these esters are comprised of a C-16 or C-18 fatty acid (e.g., palmitoleic, palmitic, oleic, or stearic acid) linked to a hydroxylated C-16 or C-18 lipid. 9-PAHSA is a FAHFA in which palmitic acid is esterified to 9-hydroxy stearic acid. PAHSAs are the most abundant forms of FAHFA in serum as well as white and brown adipose tissues of glucose tolerant AG4OX mice, which overexpress Glut4 specifically in adipose tissue.{27644} 9-PAHSA is the predominant isomer of PAHSA in wild type and AG4OX mice.{27644} It is found in humans and is reduced in the serum and adipose tissues of insulin-resistant humans.{27644} 9-PAHSA improves glucose tolerance, stimulates insulin secretion, and has anti-inflammatory effects in mice.{27644}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
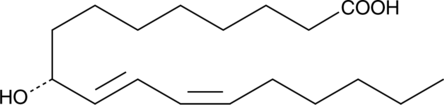
Branched fatty acid esters of hydroxy fatty acids (FAHFAs) are newly identified endogenous lipids regulated by fasting and high-fat feeding and associated with insulin sensitivity in mice.{27644} Structurally, these esters are comprised of a C-16 or C-18 fatty acid (e.g., palmitoleic, palmitic, oleic, or stearic acid) linked to either a C-16 or C-18 hydroxy substituent. 9-POHSA is a FAHFA consisting of palmitoleic acid esterified at the 9-position of hydroxy stearic acid. The levels of POHSA are significantly elevated in serum of glucose tolerant AG4OX mice, which overexpress the Glut4 glucose transporter specifically in adipose tissue.{27644} As other FAHFAs improve glucose tolerance, stimulate insulin secretion, and have anti-inflammatory effects, 9-POHSA may be a bioactive lipid with roles in metabolic syndrome and inflammation.{27644}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
Branched fatty acid esters of hydroxy fatty acids (FAHFAs) are newly identified endogenous lipids regulated by fasting and high-fat feeding and associated with insulin sensitivity in mice.{27644} Structurally, these esters are comprised of a C-16 or C-18 fatty acid (e.g., palmitoleic, palmitic, oleic, or stearic acid) linked to either a C-16 or C-18 hydroxy substituent. 9-POHSA is a FAHFA consisting of palmitoleic acid esterified at the 9-position of hydroxy stearic acid. The levels of POHSA are significantly elevated in serum of glucose tolerant AG4OX mice, which overexpress the Glut4 glucose transporter specifically in adipose tissue.{27644} As other FAHFAs improve glucose tolerance, stimulate insulin secretion, and have anti-inflammatory effects, 9-POHSA may be a bioactive lipid with roles in metabolic syndrome and inflammation.{27644}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
Branched fatty acid esters of hydroxy fatty acids (FAHFAs) are newly identified endogenous lipids regulated by fasting and high-fat feeding and associated with insulin sensitivity in mice.{27644} Structurally, these esters are comprised of a C-16 or C-18 fatty acid (e.g., palmitoleic, palmitic, oleic, or stearic acid) linked to either a C-16 or C-18 hydroxy substituent. 9-POHSA is a FAHFA consisting of palmitoleic acid esterified at the 9-position of hydroxy stearic acid. The levels of POHSA are significantly elevated in serum of glucose tolerant AG4OX mice, which overexpress the Glut4 glucose transporter specifically in adipose tissue.{27644} As other FAHFAs improve glucose tolerance, stimulate insulin secretion, and have anti-inflammatory effects, 9-POHSA may be a bioactive lipid with roles in metabolic syndrome and inflammation.{27644}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
Branched fatty acid esters of hydroxy fatty acids (FAHFAs) are newly identified endogenous lipids regulated by fasting and high-fat feeding and associated with insulin sensitivity.{27644} Structurally, these esters are comprised of a C-16 or C-18 fatty acid (e.g., palmitoleic, palmitic, oleic, or stearic acid) linked to either a C-16 or C-18 hydroxy substituent. 9-SAHSA is a FAHFA in which stearic acid is esterified at the 9th carbon of hydroxy stearic acid. The levels of SAHSA are moderately elevated in the serum of glucose tolerant AG4OX mice, which overexpress the Glut4 glucose transporter specifically in adipose tissue.{27644}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
Branched fatty acid esters of hydroxy fatty acids (FAHFAs) are newly identified endogenous lipids regulated by fasting and high-fat feeding and associated with insulin sensitivity.{27644} Structurally, these esters are comprised of a C-16 or C-18 fatty acid (e.g., palmitoleic, palmitic, oleic, or stearic acid) linked to either a C-16 or C-18 hydroxy substituent. 9-SAHSA is a FAHFA in which stearic acid is esterified at the 9th carbon of hydroxy stearic acid. The levels of SAHSA are moderately elevated in the serum of glucose tolerant AG4OX mice, which overexpress the Glut4 glucose transporter specifically in adipose tissue.{27644}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
Branched fatty acid esters of hydroxy fatty acids (FAHFAs) are newly identified endogenous lipids regulated by fasting and high-fat feeding and associated with insulin sensitivity.{27644} Structurally, these esters are comprised of a C-16 or C-18 fatty acid (e.g., palmitoleic, palmitic, oleic, or stearic acid) linked to either a C-16 or C-18 hydroxy substituent. 9-SAHSA is a FAHFA in which stearic acid is esterified at the 9th carbon of hydroxy stearic acid. The levels of SAHSA are moderately elevated in the serum of glucose tolerant AG4OX mice, which overexpress the Glut4 glucose transporter specifically in adipose tissue.{27644}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
9,10-Anthracenediyl-bis(methylene)dimalonic acid (ABMDMA) is a reagent used to detect singlet oxygen generation. This water-soluble derivative of anthracene can be photobleached by singlet oxygen to its corresponding endoperoxide. This reaction can be monitored spectrophotometrically by recording the decrease in optical density at 400 nm (ABMDMA ex/em max. = 380/407 nm in 0.1 M phosphate pH 7.0).{31532}
Brand:CaymanSKU:19580 -Available on backorder
9,10-Anthracenediyl-bis(methylene)dimalonic acid (ABMDMA) is a reagent used to detect singlet oxygen generation. This water-soluble derivative of anthracene can be photobleached by singlet oxygen to its corresponding endoperoxide. This reaction can be monitored spectrophotometrically by recording the decrease in optical density at 400 nm (ABMDMA ex/em max. = 380/407 nm in 0.1 M phosphate pH 7.0).{31532}
Brand:CaymanSKU:19580 -Available on backorder
9,10-Anthracenediyl-bis(methylene)dimalonic acid (ABMDMA) is a reagent used to detect singlet oxygen generation. This water-soluble derivative of anthracene can be photobleached by singlet oxygen to its corresponding endoperoxide. This reaction can be monitored spectrophotometrically by recording the decrease in optical density at 400 nm (ABMDMA ex/em max. = 380/407 nm in 0.1 M phosphate pH 7.0).{31532}
Brand:CaymanSKU:19580 -Available on backorder
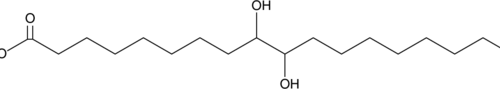
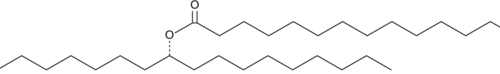
9,10-Dihydroxystearic acid is an oxidation product of oleic acid (Item Nos. 90260 | 24659) that can be formed from oleic acid in HepG2 cells.{52024} It activates peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARα) in CV-1 cells when used at concentrations ranging from 50 to 100 µM.{52025} 9,10-Dihydroxystearic acid (4% in the diet) decreases blood glucose levels, increases insulin sensitivity, and decreases body weight in high-fat diet-fed KKAy diabetic mice.
Brand:CaymanSKU:28612 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
9,10-Dihydroxystearic acid is an oxidation product of oleic acid (Item Nos. 90260 | 24659) that can be formed from oleic acid in HepG2 cells.{52024} It activates peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARα) in CV-1 cells when used at concentrations ranging from 50 to 100 µM.{52025} 9,10-Dihydroxystearic acid (4% in the diet) decreases blood glucose levels, increases insulin sensitivity, and decreases body weight in high-fat diet-fed KKAy diabetic mice.
Brand:CaymanSKU:28612 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
9,10-Dihydroxystearic acid is an oxidation product of oleic acid (Item Nos. 90260 | 24659) that can be formed from oleic acid in HepG2 cells.{52024} It activates peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARα) in CV-1 cells when used at concentrations ranging from 50 to 100 µM.{52025} 9,10-Dihydroxystearic acid (4% in the diet) decreases blood glucose levels, increases insulin sensitivity, and decreases body weight in high-fat diet-fed KKAy diabetic mice.
Brand:CaymanSKU:28612 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
9,10-Dihydroxystearic acid is an oxidation product of oleic acid (Item Nos. 90260 | 24659) that can be formed from oleic acid in HepG2 cells.{52024} It activates peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARα) in CV-1 cells when used at concentrations ranging from 50 to 100 µM.{52025} 9,10-Dihydroxystearic acid (4% in the diet) decreases blood glucose levels, increases insulin sensitivity, and decreases body weight in high-fat diet-fed KKAy diabetic mice.
Brand:CaymanSKU:28612 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Ro 3-1314 is an inhibitor of both COX and lipoxygenase.{1260,1261} Ro 3-1314 inhibits ram seminal vesicle COX with a Ki of 0.6 µM.{1260} It is a more effective inhibitor of COX-1 than of 15-LO, inhibiting 95% and 68%, respectively, of these enzymatic activities when used at a concentration of 48 µM.{1261}
Brand:CaymanSKU:90400 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Ro 3-1314 is an inhibitor of both COX and lipoxygenase.{1260,1261} Ro 3-1314 inhibits ram seminal vesicle COX with a Ki of 0.6 µM.{1260} It is a more effective inhibitor of COX-1 than of 15-LO, inhibiting 95% and 68%, respectively, of these enzymatic activities when used at a concentration of 48 µM.{1261}
Brand:CaymanSKU:90400 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Ro 3-1314 is an inhibitor of both COX and lipoxygenase.{1260,1261} Ro 3-1314 inhibits ram seminal vesicle COX with a Ki of 0.6 µM.{1260} It is a more effective inhibitor of COX-1 than of 15-LO, inhibiting 95% and 68%, respectively, of these enzymatic activities when used at a concentration of 48 µM.{1261}
Brand:CaymanSKU:90400 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
(9E)-Erythromycin A oxime is a metabolite of the semisynthetic antibiotic roxithromycin (Item No. 19465).{43949}
Brand:CaymanSKU:27966 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
(9E)-Erythromycin A oxime is a metabolite of the semisynthetic antibiotic roxithromycin (Item No. 19465).{43949}
Brand:CaymanSKU:27966 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
(9E)-Erythromycin A oxime is a metabolite of the semisynthetic antibiotic roxithromycin (Item No. 19465).{43949}
Brand:CaymanSKU:27966 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
(9E)-Erythromycin A oxime is a metabolite of the semisynthetic antibiotic roxithromycin (Item No. 19465).{43949}
Brand:CaymanSKU:27966 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
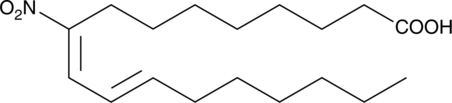
9(E),11(E)-12-nitro Conjugated linoleic acid (9(E),11(E)-12-nitro CLA) is a nitrated fatty acid. It is formed from 9(Z),11(E)-CLA (Item No. 90140) upon exposure to acidified nitrite, peroxynitrite, gaseous nitrogen dioxide, or a combination of myeloperoxidase, hydrogen peroxide, and nitrite.{50928} It is also formed in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages, an effect that can be reduced by the nitric oxide synthase (NOS) inhibitor L-NAME (Item No. 80210).{55206} 9(E),11(E)-12-nitro CLA has been found in human plasma.
Brand:CaymanSKU:30834 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
9(E),11(E)-12-nitro Conjugated linoleic acid (9(E),11(E)-12-nitro CLA) is a nitrated fatty acid. It is formed from 9(Z),11(E)-CLA (Item No. 90140) upon exposure to acidified nitrite, peroxynitrite, gaseous nitrogen dioxide, or a combination of myeloperoxidase, hydrogen peroxide, and nitrite.{50928} It is also formed in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages, an effect that can be reduced by the nitric oxide synthase (NOS) inhibitor L-NAME (Item No. 80210).{55206} 9(E),11(E)-12-nitro CLA has been found in human plasma.
Brand:CaymanSKU:30834 - 250 µgAvailable on backorder
9(E),11(E)-12-nitro Conjugated linoleic acid (9(E),11(E)-12-nitro CLA) is a nitrated fatty acid. It is formed from 9(Z),11(E)-CLA (Item No. 90140) upon exposure to acidified nitrite, peroxynitrite, gaseous nitrogen dioxide, or a combination of myeloperoxidase, hydrogen peroxide, and nitrite.{50928} It is also formed in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages, an effect that can be reduced by the nitric oxide synthase (NOS) inhibitor L-NAME (Item No. 80210).{55206} 9(E),11(E)-12-nitro CLA has been found in human plasma.
Brand:CaymanSKU:30834 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
9(E),11(E)-12-nitro Conjugated linoleic acid (9(E),11(E)-12-nitro CLA) is a nitrated fatty acid. It is formed from 9(Z),11(E)-CLA (Item No. 90140) upon exposure to acidified nitrite, peroxynitrite, gaseous nitrogen dioxide, or a combination of myeloperoxidase, hydrogen peroxide, and nitrite.{50928} It is also formed in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages, an effect that can be reduced by the nitric oxide synthase (NOS) inhibitor L-NAME (Item No. 80210).{55206} 9(E),11(E)-12-nitro CLA has been found in human plasma.
Brand:CaymanSKU:30834 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
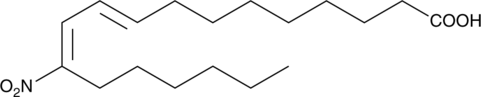
9(E),11(E)-9-nitro Conjugated linoleic acid (9E,11E-9-nitro CLA) is a nitrated fatty acid. It is formed from 9Z,11E-CLA (Item No. 90140) upon exposure to acidified nitrite, peroxynitrite, gaseous nitrogen dioxide, or a combination of myeloperoxidase, hydrogen peroxide, and nitrite.{50928} It is also formed in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages, an effect that can be reduced by the nitric oxide synthase (NOS) inhibitor L-NAME (Item No. 80210).{55206} 9E,11E-9-nitro CLA has been found in human plasma.
Brand:CaymanSKU:30160 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
9(E),11(E)-9-nitro Conjugated linoleic acid (9E,11E-9-nitro CLA) is a nitrated fatty acid. It is formed from 9Z,11E-CLA (Item No. 90140) upon exposure to acidified nitrite, peroxynitrite, gaseous nitrogen dioxide, or a combination of myeloperoxidase, hydrogen peroxide, and nitrite.{50928} It is also formed in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages, an effect that can be reduced by the nitric oxide synthase (NOS) inhibitor L-NAME (Item No. 80210).{55206} 9E,11E-9-nitro CLA has been found in human plasma.
Brand:CaymanSKU:30160 - 250 µgAvailable on backorder
9(E),11(E)-9-nitro Conjugated linoleic acid (9E,11E-9-nitro CLA) is a nitrated fatty acid. It is formed from 9Z,11E-CLA (Item No. 90140) upon exposure to acidified nitrite, peroxynitrite, gaseous nitrogen dioxide, or a combination of myeloperoxidase, hydrogen peroxide, and nitrite.{50928} It is also formed in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages, an effect that can be reduced by the nitric oxide synthase (NOS) inhibitor L-NAME (Item No. 80210).{55206} 9E,11E-9-nitro CLA has been found in human plasma.
Brand:CaymanSKU:30160 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
9(E),11(E)-9-nitro Conjugated linoleic acid (9E,11E-9-nitro CLA) is a nitrated fatty acid. It is formed from 9Z,11E-CLA (Item No. 90140) upon exposure to acidified nitrite, peroxynitrite, gaseous nitrogen dioxide, or a combination of myeloperoxidase, hydrogen peroxide, and nitrite.{50928} It is also formed in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages, an effect that can be reduced by the nitric oxide synthase (NOS) inhibitor L-NAME (Item No. 80210).{55206} 9E,11E-9-nitro CLA has been found in human plasma.
Brand:CaymanSKU:30160 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
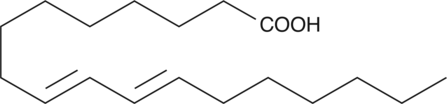
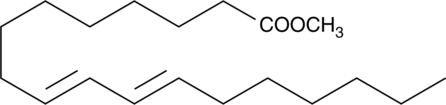
9(E),11(E)-Conjugated linoleic acid (9(E),11(E)-CLA) refers to a family of 8 geometric isomers of linoleic acid in which the two double bonds are contiguous. 9(E),11(E)-CLA is the 9,11 all-trans isomer of linoleic acid. CLA was originally identified in ground beef, but it is also present in a variety of dairy products. CLA is effective at reducing mammary tumors in rats at levels as low as 0.1% by weight of their diet.{1568} [Matreya, LLC. Catalog No. 1181]
Brand:CaymanSKU:90370 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
9(E),11(E)-Conjugated linoleic acid methyl ester has been found in thermally stressed cooking oils and may be used as a marker of adulteration of olive oils with lower quality oils.{38903} [Matreya, LLC. Catalog No. 1257]
Brand:CaymanSKU:24580 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
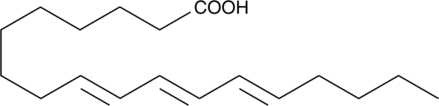
9(E),11(E),13(E)-Octadecatrienoic acid (β-ESA) is a conjugated polyunsaturated fatty acid that is found in plant seed oils and in mixtures of conjugated linolenic acids synthesized by the alkaline isomerization of linolenic acid.{37085} It reduces growth of Caco-2 colon cancer cells in a dose-dependent and time-dependent manner. In vitro, β-ESA induces DNA fragmentation and upregulation of pro-apoptotic Bax mRNA. β-ESA decreases protein expression of the apoptosis suppression factor Bcl-2 and induces apoptosis in T24 bladder cancer cells via production of reactive oxygen species.{37086} It also inhibits bacterial fatty acid dioxygenase with a Ki value of 49 nM in vitro.{37087}
Brand:CaymanSKU:22976 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
9(E),11(E),13(E)-Octadecatrienoic acid (β-ESA) is a conjugated polyunsaturated fatty acid that is found in plant seed oils and in mixtures of conjugated linolenic acids synthesized by the alkaline isomerization of linolenic acid.{37085} It reduces growth of Caco-2 colon cancer cells in a dose-dependent and time-dependent manner. In vitro, β-ESA induces DNA fragmentation and upregulation of pro-apoptotic Bax mRNA. β-ESA decreases protein expression of the apoptosis suppression factor Bcl-2 and induces apoptosis in T24 bladder cancer cells via production of reactive oxygen species.{37086} It also inhibits bacterial fatty acid dioxygenase with a Ki value of 49 nM in vitro.{37087}
Brand:CaymanSKU:22976 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
9(E),11(E),13(E)-Octadecatrienoic acid (β-ESA) is a conjugated polyunsaturated fatty acid that is found in plant seed oils and in mixtures of conjugated linolenic acids synthesized by the alkaline isomerization of linolenic acid.{37085} It reduces growth of Caco-2 colon cancer cells in a dose-dependent and time-dependent manner. In vitro, β-ESA induces DNA fragmentation and upregulation of pro-apoptotic Bax mRNA. β-ESA decreases protein expression of the apoptosis suppression factor Bcl-2 and induces apoptosis in T24 bladder cancer cells via production of reactive oxygen species.{37086} It also inhibits bacterial fatty acid dioxygenase with a Ki value of 49 nM in vitro.{37087}
Brand:CaymanSKU:22976 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
9(E),12(Z)-Octadecadienoic acid is an ω-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid and an isomer of linoleic acid (Item Nos. 90150 | 90150.1 | 21909) that contains a trans double bond at the C9 position. It has been found as a minor component of bovine milk fat and in partially hydrogenated vegetable oils.{53913} 9(E),12(Z)-Octadecadienoic acid levels increase in rabbit meat following supplementation with heated sunflower oil, α-tocopheryl acetate, and zinc.{53914}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10005146 - 2 mgAvailable on backorder
9(E),12(Z)-Octadecadienoic acid is an ω-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid and an isomer of linoleic acid (Item Nos. 90150 | 90150.1 | 21909) that contains a trans double bond at the C9 position. It has been found as a minor component of bovine milk fat and in partially hydrogenated vegetable oils.{53913} 9(E),12(Z)-Octadecadienoic acid levels increase in rabbit meat following supplementation with heated sunflower oil, α-tocopheryl acetate, and zinc.{53914}
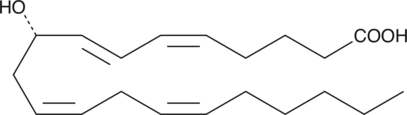
Brand:CaymanSKU:-9(R)-HETE is an enantiomer which makes up 50% of (±)9-HETE (Item No. 34400). At a concentration of 300 nM, 9(R)-HETE activates RXRγ-dependent transcription 1.5 fold relative to a control.{2565} Stereochemical assignment of the (R) enantiomer is based on comparison of chiral HPLC retention times to published results. {30214}
Brand:CaymanSKU:34405 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
9(R)-HETE is an enantiomer which makes up 50% of (±)9-HETE (Item No. 34400). At a concentration of 300 nM, 9(R)-HETE activates RXRγ-dependent transcription 1.5 fold relative to a control.{2565} Stereochemical assignment of the (R) enantiomer is based on comparison of chiral HPLC retention times to published results. {30214}
Brand:CaymanSKU:34405 - 25 µgAvailable on backorder
9(R)-HETE is an enantiomer which makes up 50% of (±)9-HETE (Item No. 34400). At a concentration of 300 nM, 9(R)-HETE activates RXRγ-dependent transcription 1.5 fold relative to a control.{2565} Stereochemical assignment of the (R) enantiomer is based on comparison of chiral HPLC retention times to published results. {30214}
Brand:CaymanSKU:34405 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
9(R)-HODE is one of several monohydroxylated products of linoleic acid. All known mammalian lipoxygenases appear to catalyze the oxygenation of arachidonic and linoleic acid to give products having strictly the (S) configuration at the site of oxygen insertion. However, both human umbilical vein endothelial cells and bovine aorta endothelial cells have been shown to produce 9(R)-HODE when incubated with linoleic acid.{2369,1528} The physiological function of 9(R)-HODE and the enzyme that catalyzes its formation have not been determined.
Brand:CaymanSKU:38405 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
9(R)-HODE is one of several monohydroxylated products of linoleic acid. All known mammalian lipoxygenases appear to catalyze the oxygenation of arachidonic and linoleic acid to give products having strictly the (S) configuration at the site of oxygen insertion. However, both human umbilical vein endothelial cells and bovine aorta endothelial cells have been shown to produce 9(R)-HODE when incubated with linoleic acid.{2369,1528} The physiological function of 9(R)-HODE and the enzyme that catalyzes its formation have not been determined.
Brand:CaymanSKU:38405 - 25 µgAvailable on backorder
9(R)-HODE is one of several monohydroxylated products of linoleic acid. All known mammalian lipoxygenases appear to catalyze the oxygenation of arachidonic and linoleic acid to give products having strictly the (S) configuration at the site of oxygen insertion. However, both human umbilical vein endothelial cells and bovine aorta endothelial cells have been shown to produce 9(R)-HODE when incubated with linoleic acid.{2369,1528} The physiological function of 9(R)-HODE and the enzyme that catalyzes its formation have not been determined.
Brand:CaymanSKU:38405 - 250 µgAvailable on backorder
9(R)-HODE is one of several monohydroxylated products of linoleic acid. All known mammalian lipoxygenases appear to catalyze the oxygenation of arachidonic and linoleic acid to give products having strictly the (S) configuration at the site of oxygen insertion. However, both human umbilical vein endothelial cells and bovine aorta endothelial cells have been shown to produce 9(R)-HODE when incubated with linoleic acid.{2369,1528} The physiological function of 9(R)-HODE and the enzyme that catalyzes its formation have not been determined.
Brand:CaymanSKU:38405 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
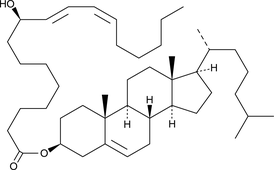
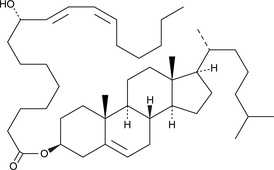
9(R)-HODE cholesteryl ester was originally extracted from atherosclerotic lesions.{2227} It remains uncertain whether the oxidized fatty acid portion of the molecule results from enzymatic lipoxygenation or from random lipid peroxidation.{1126} 9(R)-HODE cholesteryl ester can be used as a standard for analysis of chiral HODE cholesteryl esters.
Brand:CaymanSKU:38406 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
9(R)-HODE cholesteryl ester was originally extracted from atherosclerotic lesions.{2227} It remains uncertain whether the oxidized fatty acid portion of the molecule results from enzymatic lipoxygenation or from random lipid peroxidation.{1126} 9(R)-HODE cholesteryl ester can be used as a standard for analysis of chiral HODE cholesteryl esters.
Brand:CaymanSKU:38406 - 25 µgAvailable on backorder
9(R)-HODE cholesteryl ester was originally extracted from atherosclerotic lesions.{2227} It remains uncertain whether the oxidized fatty acid portion of the molecule results from enzymatic lipoxygenation or from random lipid peroxidation.{1126} 9(R)-HODE cholesteryl ester can be used as a standard for analysis of chiral HODE cholesteryl esters.
Brand:CaymanSKU:38406 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
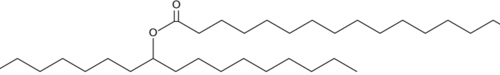
9(R)-PAHSA is a stereoisomer of 9-PAHSA (Item No. 17037), an endogenous lipid that belongs to a collection of branched fatty acid esters of hydroxy fatty acids (FAHFAs).{27644} 9-PAHSA is a FAHFA in which palmitic acid (Item No. 10006627) is esterified to 9-hydroxy stearic acid. 9(R)-PAHSA is the predominant form that accumulates in adipose tissues in AG4OX mice, which overexpress Glut4 specifically in adipose tissue.{34387} Also, cell lines favor the production of 9(R)-PAHSA, and carboxyl ester lipase selectively hydrolyzes 9(S)-PAHSA (Item No. 18023).The use of this optically-active FAHFA product (the “Product”) is covered by U.S. Patent No. 10,240,025 and corresponding foreign counterpart applications. These patents and applications are licensed by Cayman pursuant to an agreement with BT Food, Drug and Personal Care, LLC, and this Product is sold exclusively for research and development purposes only. Product may not be used for human studies, veterinary use or diagnostics, clinical trial work, clinical diagnostics, or any other clinical trial or approval activities related to humans or animals. This limited label license does not grant any right to use the Product or a Product derivative in commercial products or services. This Product may not be re-sold, distributed, or repackaged unless by official Cayman distributors. For information on commercial rights, please contact the outlicensing department at jforest@biosynthetic.com.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
9(R)-PAHSA is a stereoisomer of 9-PAHSA (Item No. 17037), an endogenous lipid that belongs to a collection of branched fatty acid esters of hydroxy fatty acids (FAHFAs).{27644} 9-PAHSA is a FAHFA in which palmitic acid (Item No. 10006627) is esterified to 9-hydroxy stearic acid. 9(R)-PAHSA is the predominant form that accumulates in adipose tissues in AG4OX mice, which overexpress Glut4 specifically in adipose tissue.{34387} Also, cell lines favor the production of 9(R)-PAHSA, and carboxyl ester lipase selectively hydrolyzes 9(S)-PAHSA (Item No. 18023).The use of this optically-active FAHFA product (the “Product”) is covered by U.S. Patent No. 10,240,025 and corresponding foreign counterpart applications. These patents and applications are licensed by Cayman pursuant to an agreement with BT Food, Drug and Personal Care, LLC, and this Product is sold exclusively for research and development purposes only. Product may not be used for human studies, veterinary use or diagnostics, clinical trial work, clinical diagnostics, or any other clinical trial or approval activities related to humans or animals. This limited label license does not grant any right to use the Product or a Product derivative in commercial products or services. This Product may not be re-sold, distributed, or repackaged unless by official Cayman distributors. For information on commercial rights, please contact the outlicensing department at jforest@biosynthetic.com.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
9(R)-Δ6a,10a-THC (exempt preparation) (Item No. 29779) is an analytical reference standard categorized as a synthetic cannabinoid.{45231} It is a potential impurity in or degradant of Δ9-THC. 9(R)-Δ6a,10a-THC is regulated as a Schedule I compound in the United States. 9(R)-Δ6a,10a-THC (exempt preparation) (Item No. 29779) is provided as a DEA exempt preparation. This product is intended for research and forensic applications.
Brand:CaymanSKU:29779 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
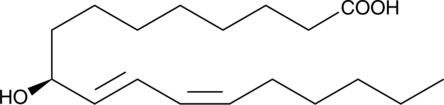
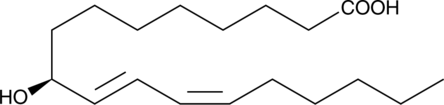
9(S)-HETE is the (S) isomer of the monohydroxy fatty acid (±)9-HETE (Item No. 34400).{30214} It is formed from arachidonic acid (Item Nos. 90010 | 90010.1 | 10006607) by rat liver microsomal cytochrome P450 (CYP).{562} 9(S)-HETE is an agonist of retinoid X receptor γ (RXRγ), inducing RXRγ-dependent transcription when used at a concentration of 300 nM in BHK cell extracts expressing chick RXRγ.{2565}
Brand:CaymanSKU:34410 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
9(S)-HETE is the (S) isomer of the monohydroxy fatty acid (±)9-HETE (Item No. 34400).{30214} It is formed from arachidonic acid (Item Nos. 90010 | 90010.1 | 10006607) by rat liver microsomal cytochrome P450 (CYP).{562} 9(S)-HETE is an agonist of retinoid X receptor γ (RXRγ), inducing RXRγ-dependent transcription when used at a concentration of 300 nM in BHK cell extracts expressing chick RXRγ.{2565}
Brand:CaymanSKU:34410 - 25 µgAvailable on backorder
9(S)-HETE is the (S) isomer of the monohydroxy fatty acid (±)9-HETE (Item No. 34400).{30214} It is formed from arachidonic acid (Item Nos. 90010 | 90010.1 | 10006607) by rat liver microsomal cytochrome P450 (CYP).{562} 9(S)-HETE is an agonist of retinoid X receptor γ (RXRγ), inducing RXRγ-dependent transcription when used at a concentration of 300 nM in BHK cell extracts expressing chick RXRγ.{2565}
Brand:CaymanSKU:34410 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
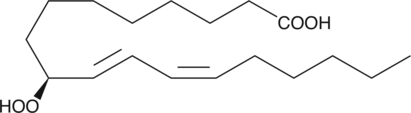
9(S)-HODE is produced by the lipoxygenation of linoleic acid in both plants and animals.{123,2262} It has been detected in atherosclerotic plaques, as an esterified component of membrane phospholipids and in oxidized LDL particles.{2636}
Brand:CaymanSKU:38410 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
9(S)-HODE is produced by the lipoxygenation of linoleic acid in both plants and animals.{123,2262} It has been detected in atherosclerotic plaques, as an esterified component of membrane phospholipids and in oxidized LDL particles.{2636}
Brand:CaymanSKU:38410 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
9(S)-HODE is produced by the lipoxygenation of linoleic acid in both plants and animals.{123,2262} It has been detected in atherosclerotic plaques, as an esterified component of membrane phospholipids and in oxidized LDL particles.{2636}
Brand:CaymanSKU:38410 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
9(S)-HODE cholesteryl ester was originally extracted from atherosclerotic lesions.{2227} It remains uncertain whether the oxidized fatty acid portion of the molecule results from enzymatic lipoxygenation or from random lipid peroxidation.{1126} 9(S)-HODE cholesteryl ester can be used as a standard for analysis of chiral HODE cholesteryl esters.
Brand:CaymanSKU:38411 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
9(S)-HODE cholesteryl ester was originally extracted from atherosclerotic lesions.{2227} It remains uncertain whether the oxidized fatty acid portion of the molecule results from enzymatic lipoxygenation or from random lipid peroxidation.{1126} 9(S)-HODE cholesteryl ester can be used as a standard for analysis of chiral HODE cholesteryl esters.
Brand:CaymanSKU:38411 - 25 µgAvailable on backorder
9(S)-HODE cholesteryl ester was originally extracted from atherosclerotic lesions.{2227} It remains uncertain whether the oxidized fatty acid portion of the molecule results from enzymatic lipoxygenation or from random lipid peroxidation.{1126} 9(S)-HODE cholesteryl ester can be used as a standard for analysis of chiral HODE cholesteryl esters.
Brand:CaymanSKU:38411 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
9(S)-HODE is produced by the lipoxygenation of linoleic acid in both plants and animals.{123,2262} It has been detected in atherosclerotic plaques, as an esterified component of membrane phospholipids and in oxidized LDL particles.{2636} 9(S)-HODE MaxSpec® standard is a quantitative grade standard of 9(S)-HODE (Item No. 38410) that has been prepared specifically for mass spectrometry and related applications where quantitative reproducibility is required. The solution has been prepared gravimetrically and is supplied in a deactivated glass ampule sealed under argon. The concentration was verified by comparison to an independently prepared calibration standard. This 9(S)-HODE MaxSpec® standard is guaranteed to meet identity, purity, stability, and concentration specifications and is provided with a batch-specific certificate of analysis. Ongoing stability testing is performed to ensure the concentration remains accurate throughout the shelf life of the product. Note: The amount of solution added to the vial is in excess of the listed amount. Therefore, it is necessary to accurately measure volumes for preparation of calibration standards. Follow recommended storage and handling conditions to maintain product quality.
Brand:CaymanSKU:23569 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
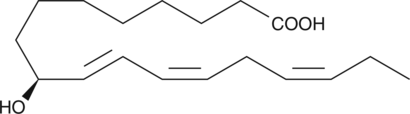
9(S)-HODE-d4 contains four deuterium atoms at the 9, 10, 12, and 13 positions. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of 9(S)-HODE by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. 9(S)-HODE is produced by the lipoxygenation of linoleic acid in both plants and animals.{123,2262} It has been detected in atherosclerotic plaques, as an esterified component of membrane phospholipids and in oxidized low-density lipoproteins particles.{2787}
Brand:CaymanSKU:338410 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
9(S)-HODE-d4 contains four deuterium atoms at the 9, 10, 12, and 13 positions. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of 9(S)-HODE by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. 9(S)-HODE is produced by the lipoxygenation of linoleic acid in both plants and animals.{123,2262} It has been detected in atherosclerotic plaques, as an esterified component of membrane phospholipids and in oxidized low-density lipoproteins particles.{2787}
Brand:CaymanSKU:338410 - 25 µgAvailable on backorder
9(S)-HODE-d4 contains four deuterium atoms at the 9, 10, 12, and 13 positions. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of 9(S)-HODE by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. 9(S)-HODE is produced by the lipoxygenation of linoleic acid in both plants and animals.{123,2262} It has been detected in atherosclerotic plaques, as an esterified component of membrane phospholipids and in oxidized low-density lipoproteins particles.{2787}
Brand:CaymanSKU:338410 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
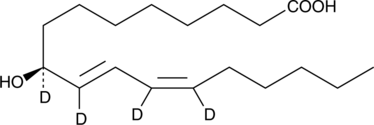
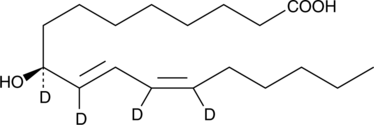
9(S)-HODE-d4 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of 9(S)-HODE by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. 9(S)-HODE is produced by the lipoxygenation of linoleic acid in both plants and animals.{123,2262} It has been detected in atherosclerotic plaques, as an esterified component of membrane phospholipids and in oxidized low-density lipoproteins particles.{2787} 9(S)-HODE-d4 MaxSpec® standard is a quantitative grade standard of 9(S)-HODE-d4 (Item No. 338410) that has been prepared specifically for mass spectrometry and related applications where quantitative reproducibility is required. The solution has been prepared gravimetrically and is supplied in a deactivated glass ampule sealed under argon. The concentration was verified by comparison to an independently prepared calibration standard. This 9(S)-HODE-d4 MaxSpec® standard is guaranteed to meet identity, purity, stability, and concentration specifications and is provided with a batch-specific certificate of analysis. Ongoing stability testing is performed to ensure the concentration remains accurate throughout the shelf life of the product. Note: The amount of solution added to the vial is in excess of the listed amount. Therefore, it is necessary to accurately measure volumes for preparation of calibration standards. Follow recommended storage and handling conditions to maintain product quality.
Brand:CaymanSKU:25368 - 10 µgAvailable on backorder
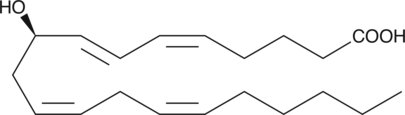
9(S)-HOTrE is a monohydroxy polyunsaturated fatty acid produced by the action of 5-lipoxygenase on α-linolenic acid.{2226} 9(S)-HOTrE is predominantly localized in cellular ester lipids of Glechoma hederacea leaves and is partially released during artificial dehydration.{2264} The biological role of 9(S)-HOTrE in G. hederacea leaves is still undetermined, but it may play a role in natural senescence.{2264} 9(S)-HOTrE is an inhibitor of spore germination and germ tube elongation of rice blast fungus with ED50 values of 45 and 30 ppm, respectively.{8523}
Brand:CaymanSKU:39420 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
9(S)-HOTrE is a monohydroxy polyunsaturated fatty acid produced by the action of 5-lipoxygenase on α-linolenic acid.{2226} 9(S)-HOTrE is predominantly localized in cellular ester lipids of Glechoma hederacea leaves and is partially released during artificial dehydration.{2264} The biological role of 9(S)-HOTrE in G. hederacea leaves is still undetermined, but it may play a role in natural senescence.{2264} 9(S)-HOTrE is an inhibitor of spore germination and germ tube elongation of rice blast fungus with ED50 values of 45 and 30 ppm, respectively.{8523}
Brand:CaymanSKU:39420 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
9(S)-HOTrE is a monohydroxy polyunsaturated fatty acid produced by the action of 5-lipoxygenase on α-linolenic acid.{2226} 9(S)-HOTrE is predominantly localized in cellular ester lipids of Glechoma hederacea leaves and is partially released during artificial dehydration.{2264} The biological role of 9(S)-HOTrE in G. hederacea leaves is still undetermined, but it may play a role in natural senescence.{2264} 9(S)-HOTrE is an inhibitor of spore germination and germ tube elongation of rice blast fungus with ED50 values of 45 and 30 ppm, respectively.{8523}
Brand:CaymanSKU:39420 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
9(S)-HpODE is produced by the action of arachidonate 5-LO on linoleic acid. It can be further metabolized by potato hydroperoxide dehydratase to colneleic acid.{2225,186}
Brand:CaymanSKU:48410 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
9(S)-HpODE is produced by the action of arachidonate 5-LO on linoleic acid. It can be further metabolized by potato hydroperoxide dehydratase to colneleic acid.{2225,186}
Brand:CaymanSKU:48410 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
9(S)-HpODE is produced by the action of arachidonate 5-LO on linoleic acid. It can be further metabolized by potato hydroperoxide dehydratase to colneleic acid.{2225,186}
Brand:CaymanSKU:48410 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
9(S)-HpODE is produced by the action of arachidonate 5-LO on linoleic acid. It can be further metabolized by potato hydroperoxide dehydratase to colneleic acid.{2225,186}
Brand:CaymanSKU:48410 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
9(S)-HpOTrE is a monohydroperoxy polyunsaturated fatty acid produced by the action of 5-lipoxygenase (5-LO) on α-linolenic acid.{2226} It can be further metabolized to colnelenic acid by a divinyl ether synthase activity found in garlic and potato microsomal fractions.{6086,3824} 9(S)-HpOTrE also serves as a substrate for further oxidation by both soybean and potato LOs, resulting in the formation of 9,16-dihydroperoxy acid.{6085,6087} The suicide inactivation of LOs when 9(S)-HpOTrE is used as a substrate is thought to occur via formation of an unstable epoxide.{6083,6084}
Brand:CaymanSKU:45120 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
9(S)-HpOTrE is a monohydroperoxy polyunsaturated fatty acid produced by the action of 5-lipoxygenase (5-LO) on α-linolenic acid.{2226} It can be further metabolized to colnelenic acid by a divinyl ether synthase activity found in garlic and potato microsomal fractions.{6086,3824} 9(S)-HpOTrE also serves as a substrate for further oxidation by both soybean and potato LOs, resulting in the formation of 9,16-dihydroperoxy acid.{6085,6087} The suicide inactivation of LOs when 9(S)-HpOTrE is used as a substrate is thought to occur via formation of an unstable epoxide.{6083,6084}
Brand:CaymanSKU:45120 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder