Cayman
Showing 3451–3600 of 45550 results
-
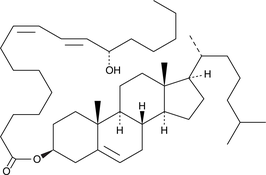
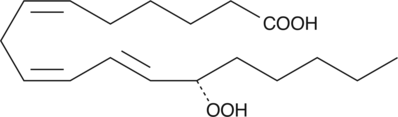
13(S)-HODE cholesteryl ester was originally extracted from atherosclerotic lesions.{2227} It remains uncertain whether the oxidized fatty acid portion of the molecule results from enzymatic lipoxygenation or from random lipid peroxidation.{1126} 13(S)-HODE cholesteryl ester can be used as a standard for analysis of chiral HODE cholesteryl esters.
Brand:CaymanSKU:38611 - 25 µgAvailable on backorder
13(S)-HODE cholesteryl ester was originally extracted from atherosclerotic lesions.{2227} It remains uncertain whether the oxidized fatty acid portion of the molecule results from enzymatic lipoxygenation or from random lipid peroxidation.{1126} 13(S)-HODE cholesteryl ester can be used as a standard for analysis of chiral HODE cholesteryl esters.
Brand:CaymanSKU:38611 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
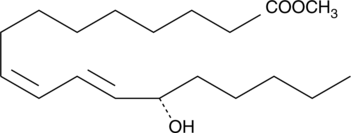
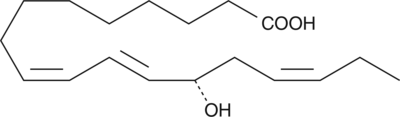
13(S)-hydroxyoctadecadienoic acid (13(S)-HODE) is a 15-lipoxygenase metabolite of linoleic acid produced in endothelial cells, leukocytes, and tumor cells. The biological effects of 13(S)-HODE include inhibition of tumor cell adhesion to the endothelium at concentrations around 1 µM,{592,880} and down regulation of IRGpIIb/IIIa receptor expression.{591} 13(S)-HODE methyl ester is a neutral, more lipophilic form of the free acid that can been used as an analytical standard for 13(S)-HODE.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008875 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
13(S)-hydroxyoctadecadienoic acid (13(S)-HODE) is a 15-lipoxygenase metabolite of linoleic acid produced in endothelial cells, leukocytes, and tumor cells. The biological effects of 13(S)-HODE include inhibition of tumor cell adhesion to the endothelium at concentrations around 1 µM,{592,880} and down regulation of IRGpIIb/IIIa receptor expression.{591} 13(S)-HODE methyl ester is a neutral, more lipophilic form of the free acid that can been used as an analytical standard for 13(S)-HODE.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008875 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
13(S)-hydroxyoctadecadienoic acid (13(S)-HODE) is a 15-lipoxygenase metabolite of linoleic acid produced in endothelial cells, leukocytes, and tumor cells. The biological effects of 13(S)-HODE include inhibition of tumor cell adhesion to the endothelium at concentrations around 1 µM,{592,880} and down regulation of IRGpIIb/IIIa receptor expression.{591} 13(S)-HODE methyl ester is a neutral, more lipophilic form of the free acid that can been used as an analytical standard for 13(S)-HODE.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008875 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
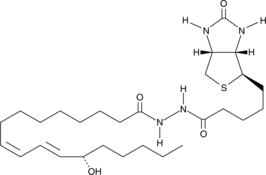
13(S)-HODE is the lipoxygenase metabolite of linoleic acid. 13(S)-HODE modulates the platelet-activating factor, leukotriene B4, and formyl-Met-Leu-Phe-induced calcium influx in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes.{7566} The mechanism by which 13(S)-HODE elicits its inhibitory effect is still unclear. The use of biotinylated 15(S)-HETE as a probe for detecting binding proteins and/or receptors that specifically bind 15(S)-HETE provides a basis for similar use of 13(S)-HODE-biotin.{6482}
Brand:CaymanSKU:38612 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
13(S)-HODE is the lipoxygenase metabolite of linoleic acid. 13(S)-HODE modulates the platelet-activating factor, leukotriene B4, and formyl-Met-Leu-Phe-induced calcium influx in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes.{7566} The mechanism by which 13(S)-HODE elicits its inhibitory effect is still unclear. The use of biotinylated 15(S)-HETE as a probe for detecting binding proteins and/or receptors that specifically bind 15(S)-HETE provides a basis for similar use of 13(S)-HODE-biotin.{6482}
Brand:CaymanSKU:38612 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
13(S)-HODE is the lipoxygenase metabolite of linoleic acid. 13(S)-HODE modulates the platelet-activating factor, leukotriene B4, and formyl-Met-Leu-Phe-induced calcium influx in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes.{7566} The mechanism by which 13(S)-HODE elicits its inhibitory effect is still unclear. The use of biotinylated 15(S)-HETE as a probe for detecting binding proteins and/or receptors that specifically bind 15(S)-HETE provides a basis for similar use of 13(S)-HODE-biotin.{6482}
Brand:CaymanSKU:38612 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
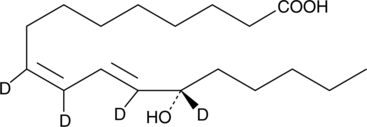
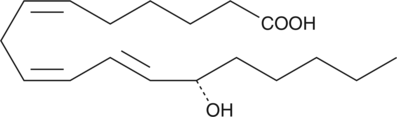
13(S)-HODE-d4 contains four deuterium atoms at the 9, 10, 12, and 13 positions. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of 13(S)-HODE by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. 13(S)-HODE is produced by incubation of linoleic acid with plant and mammalian lipoxygenases. It has been shown to inhibit the adhesion of tumor cells to the endothelium at concentrations around 1 µM,{592,880} and down regulates the expression of the IRGpIIb/IIIa receptor.{591}
Brand:CaymanSKU:338610 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
13(S)-HODE-d4 contains four deuterium atoms at the 9, 10, 12, and 13 positions. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of 13(S)-HODE by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. 13(S)-HODE is produced by incubation of linoleic acid with plant and mammalian lipoxygenases. It has been shown to inhibit the adhesion of tumor cells to the endothelium at concentrations around 1 µM,{592,880} and down regulates the expression of the IRGpIIb/IIIa receptor.{591}
Brand:CaymanSKU:338610 - 25 µgAvailable on backorder
13(S)-HODE-d4 contains four deuterium atoms at the 9, 10, 12, and 13 positions. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of 13(S)-HODE by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. 13(S)-HODE is produced by incubation of linoleic acid with plant and mammalian lipoxygenases. It has been shown to inhibit the adhesion of tumor cells to the endothelium at concentrations around 1 µM,{592,880} and down regulates the expression of the IRGpIIb/IIIa receptor.{591}
Brand:CaymanSKU:338610 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
13(S)-HOTrE is the 15-lipoxygenase (15-LO) product of linolenic acid. It has been detected in cell membranes and as the cholesteryl ester associated with the lesions of atherosclerosis, and in the biomembranes of soybeans exposed to 15-LO.{1126,1525}
Brand:CaymanSKU:39620 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
13(S)-HOTrE is the 15-lipoxygenase (15-LO) product of linolenic acid. It has been detected in cell membranes and as the cholesteryl ester associated with the lesions of atherosclerosis, and in the biomembranes of soybeans exposed to 15-LO.{1126,1525}
Brand:CaymanSKU:39620 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
13(S)-HOTrE is the 15-lipoxygenase (15-LO) product of linolenic acid. It has been detected in cell membranes and as the cholesteryl ester associated with the lesions of atherosclerosis, and in the biomembranes of soybeans exposed to 15-LO.{1126,1525}
Brand:CaymanSKU:39620 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
13(S)-HOTrE(γ) is the 15-LO product of γ-linolenic acid. It is synthesized in human platelets, but its specific function is not known.{2517}
Brand:CaymanSKU:39610 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
13(S)-HOTrE(γ) is the 15-LO product of γ-linolenic acid. It is synthesized in human platelets, but its specific function is not known.{2517}
Brand:CaymanSKU:39610 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
13(S)-HOTrE(γ) is the 15-LO product of γ-linolenic acid. It is synthesized in human platelets, but its specific function is not known.{2517}
Brand:CaymanSKU:39610 - 25 µgAvailable on backorder
13(S)-HOTrE(γ) is the 15-LO product of γ-linolenic acid. It is synthesized in human platelets, but its specific function is not known.{2517}
Brand:CaymanSKU:39610 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
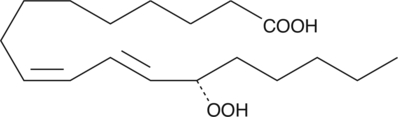
13(S)-HpODE is produced by the oxidation of linoleic acid by lipoxygenase-1 (LO-1) in many plants including soybean, flaxseed, apples, and tea leaves,{123,770} and by 15-LO in mammals.{4193} In plants, 13(S)-HpODE is the preferred substrate for the garlic bulb divinyl ether synthase.{3824} In mammalian tissues, 13(S)-HpODE is generally reduced to 13(S)-HODE (Catalog No. 38610), a compound which exhibits many biological activities.{4193} A direct action for 13(S)-HpODE has been demonstrated in Syrian hamster embryo cells where it stimulates EGF-dependent mitogenesis and up-regulation of EGF-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation.{4902} Membrane-esterified 13(S)-HpODE has been identified in human atherosclerotic plaques.{2406}
Brand:CaymanSKU:48610 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
13(S)-HpODE is produced by the oxidation of linoleic acid by lipoxygenase-1 (LO-1) in many plants including soybean, flaxseed, apples, and tea leaves,{123,770} and by 15-LO in mammals.{4193} In plants, 13(S)-HpODE is the preferred substrate for the garlic bulb divinyl ether synthase.{3824} In mammalian tissues, 13(S)-HpODE is generally reduced to 13(S)-HODE (Catalog No. 38610), a compound which exhibits many biological activities.{4193} A direct action for 13(S)-HpODE has been demonstrated in Syrian hamster embryo cells where it stimulates EGF-dependent mitogenesis and up-regulation of EGF-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation.{4902} Membrane-esterified 13(S)-HpODE has been identified in human atherosclerotic plaques.{2406}
Brand:CaymanSKU:48610 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
13(S)-HpODE is produced by the oxidation of linoleic acid by lipoxygenase-1 (LO-1) in many plants including soybean, flaxseed, apples, and tea leaves,{123,770} and by 15-LO in mammals.{4193} In plants, 13(S)-HpODE is the preferred substrate for the garlic bulb divinyl ether synthase.{3824} In mammalian tissues, 13(S)-HpODE is generally reduced to 13(S)-HODE (Catalog No. 38610), a compound which exhibits many biological activities.{4193} A direct action for 13(S)-HpODE has been demonstrated in Syrian hamster embryo cells where it stimulates EGF-dependent mitogenesis and up-regulation of EGF-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation.{4902} Membrane-esterified 13(S)-HpODE has been identified in human atherosclerotic plaques.{2406}
Brand:CaymanSKU:48610 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
13(S)-HpODE is produced by the oxidation of linoleic acid by lipoxygenase-1 (LO-1) in many plants including soybean, flaxseed, apples, and tea leaves,{123,770} and by 15-LO in mammals.{4193} In plants, 13(S)-HpODE is the preferred substrate for the garlic bulb divinyl ether synthase.{3824} In mammalian tissues, 13(S)-HpODE is generally reduced to 13(S)-HODE (Catalog No. 38610), a compound which exhibits many biological activities.{4193} A direct action for 13(S)-HpODE has been demonstrated in Syrian hamster embryo cells where it stimulates EGF-dependent mitogenesis and up-regulation of EGF-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation.{4902} Membrane-esterified 13(S)-HpODE has been identified in human atherosclerotic plaques.{2406}
Brand:CaymanSKU:48610 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
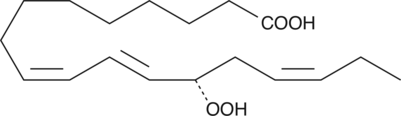
13(S)-HpOTrE is a monohydroperoxy polyunsaturated fatty acid produced in soybeans by the action of soybean LO-2 on esterified α-linolenic acid.{1525} Incubation of soybean seedling biomembranes with soybean LO-2 catalyzes the formation of both 9- and 13-HpOTrE in a molar ratio of 10:1.{1525} In plants, 13(S)-HpOTrE can be metabolized by the hydroperoxide lyase pathway producing aldehyde and oxoacid fragments, or by the hydroperoxide dehydratase pathway producing jasmonic acid.{770,2009,1829} Treatment of tomato leaves with 13-HpOTrE causes induction of proteinase inhibitors, simulating the normal response to wounding.{5107} This data suggests that in plants 13(S)-HpOTrE may participate in a lipid-based signalling system initiated by insect and pathogen attack.
Brand:CaymanSKU:45220 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
13(S)-HpOTrE is a monohydroperoxy polyunsaturated fatty acid produced in soybeans by the action of soybean LO-2 on esterified α-linolenic acid.{1525} Incubation of soybean seedling biomembranes with soybean LO-2 catalyzes the formation of both 9- and 13-HpOTrE in a molar ratio of 10:1.{1525} In plants, 13(S)-HpOTrE can be metabolized by the hydroperoxide lyase pathway producing aldehyde and oxoacid fragments, or by the hydroperoxide dehydratase pathway producing jasmonic acid.{770,2009,1829} Treatment of tomato leaves with 13-HpOTrE causes induction of proteinase inhibitors, simulating the normal response to wounding.{5107} This data suggests that in plants 13(S)-HpOTrE may participate in a lipid-based signalling system initiated by insect and pathogen attack.
Brand:CaymanSKU:45220 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
13(S)-HpOTrE is a monohydroperoxy polyunsaturated fatty acid produced in soybeans by the action of soybean LO-2 on esterified α-linolenic acid.{1525} Incubation of soybean seedling biomembranes with soybean LO-2 catalyzes the formation of both 9- and 13-HpOTrE in a molar ratio of 10:1.{1525} In plants, 13(S)-HpOTrE can be metabolized by the hydroperoxide lyase pathway producing aldehyde and oxoacid fragments, or by the hydroperoxide dehydratase pathway producing jasmonic acid.{770,2009,1829} Treatment of tomato leaves with 13-HpOTrE causes induction of proteinase inhibitors, simulating the normal response to wounding.{5107} This data suggests that in plants 13(S)-HpOTrE may participate in a lipid-based signalling system initiated by insect and pathogen attack.
Brand:CaymanSKU:45220 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
13(S)-HpOTrE(γ) is a monohydroxy PUFA produced by the action of soybean lipoxygenase-1 (LO-1) on γ-linolenic acid.{455} Further action of soybean LO-1 converts 13(S)-HpOTrE(γ) to all four isomers of 6,13-DiHOTrE.{6680} At concentrations greater than 100 µM, 13(S)-HpOTrE(γ) inhibits the activity of soybean LO-1.{119}
Brand:CaymanSKU:45210 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
13(S)-HpOTrE(γ) is a monohydroxy PUFA produced by the action of soybean lipoxygenase-1 (LO-1) on γ-linolenic acid.{455} Further action of soybean LO-1 converts 13(S)-HpOTrE(γ) to all four isomers of 6,13-DiHOTrE.{6680} At concentrations greater than 100 µM, 13(S)-HpOTrE(γ) inhibits the activity of soybean LO-1.{119}
Brand:CaymanSKU:45210 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
13(S)-HpOTrE(γ) is a monohydroxy PUFA produced by the action of soybean lipoxygenase-1 (LO-1) on γ-linolenic acid.{455} Further action of soybean LO-1 converts 13(S)-HpOTrE(γ) to all four isomers of 6,13-DiHOTrE.{6680} At concentrations greater than 100 µM, 13(S)-HpOTrE(γ) inhibits the activity of soybean LO-1.{119}
Brand:CaymanSKU:45210 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
13(S)-HpOTrE(γ) is a monohydroxy PUFA produced by the action of soybean lipoxygenase-1 (LO-1) on γ-linolenic acid.{455} Further action of soybean LO-1 converts 13(S)-HpOTrE(γ) to all four isomers of 6,13-DiHOTrE.{6680} At concentrations greater than 100 µM, 13(S)-HpOTrE(γ) inhibits the activity of soybean LO-1.{119}
Brand:CaymanSKU:45210 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
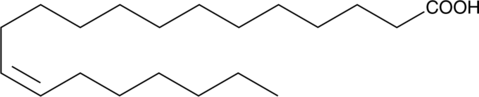
13(Z)-Docosenoic acid is a 22-carbon monounsaturated fatty acid. It is found predominantly in canola oil.{8144} 13(Z)-Docosenoic acid is metabolized to oleic acid in vivo. Diets rich in 13(Z)-docosenoic acid were shown to cause heart lipidosis in experimental animals.{7786,8145} The C-1 amide of docosenoic acid has been identified as one of the anandamide-related neurotransmitters associated with sleep.{1317}
Brand:CaymanSKU:90175 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
13(Z)-Docosenoic acid is a 22-carbon monounsaturated fatty acid. It is found predominantly in canola oil.{8144} 13(Z)-Docosenoic acid is metabolized to oleic acid in vivo. Diets rich in 13(Z)-docosenoic acid were shown to cause heart lipidosis in experimental animals.{7786,8145} The C-1 amide of docosenoic acid has been identified as one of the anandamide-related neurotransmitters associated with sleep.{1317}
Brand:CaymanSKU:90175 - 250 mgAvailable on backorder
13(Z)-Docosenoic acid is a 22-carbon monounsaturated fatty acid. It is found predominantly in canola oil.{8144} 13(Z)-Docosenoic acid is metabolized to oleic acid in vivo. Diets rich in 13(Z)-docosenoic acid were shown to cause heart lipidosis in experimental animals.{7786,8145} The C-1 amide of docosenoic acid has been identified as one of the anandamide-related neurotransmitters associated with sleep.{1317}
Brand:CaymanSKU:90175 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
13(Z)-Docosenoic acid is a 22-carbon monounsaturated fatty acid. It is found predominantly in canola oil.{8144} 13(Z)-Docosenoic acid is metabolized to oleic acid in vivo. Diets rich in 13(Z)-docosenoic acid were shown to cause heart lipidosis in experimental animals.{7786,8145} The C-1 amide of docosenoic acid has been identified as one of the anandamide-related neurotransmitters associated with sleep.{1317}
Brand:CaymanSKU:90175 - 500 mgAvailable on backorder
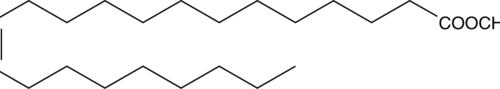
13(Z)-Docosenoic acid methyl ester is a fatty acid methyl ester that is a flavor-active, volatile, and aromatic compound found in cooked commercial shrimp waste.{38924} It is a component of biodiesel formed from C. megalocarpus and C. pentandra oils that contain trierucin.{38925} 13(Z)-Docosenoic acid methyl ester has also been used as a standard for the quantification of 13(Z)-docosenoic acid (Item No. 90175) by GC-MS.{38926}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20568 -Available on backorder
13(Z)-Docosenoic acid methyl ester is a fatty acid methyl ester that is a flavor-active, volatile, and aromatic compound found in cooked commercial shrimp waste.{38924} It is a component of biodiesel formed from C. megalocarpus and C. pentandra oils that contain trierucin.{38925} 13(Z)-Docosenoic acid methyl ester has also been used as a standard for the quantification of 13(Z)-docosenoic acid (Item No. 90175) by GC-MS.{38926}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20568 -Available on backorder
13(Z)-Docosenoic acid methyl ester is a fatty acid methyl ester that is a flavor-active, volatile, and aromatic compound found in cooked commercial shrimp waste.{38924} It is a component of biodiesel formed from C. megalocarpus and C. pentandra oils that contain trierucin.{38925} 13(Z)-Docosenoic acid methyl ester has also been used as a standard for the quantification of 13(Z)-docosenoic acid (Item No. 90175) by GC-MS.{38926}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20568 -Available on backorder
13(Z)-Docosenoic acid methyl ester is a fatty acid methyl ester that is a flavor-active, volatile, and aromatic compound found in cooked commercial shrimp waste.{38924} It is a component of biodiesel formed from C. megalocarpus and C. pentandra oils that contain trierucin.{38925} 13(Z)-Docosenoic acid methyl ester has also been used as a standard for the quantification of 13(Z)-docosenoic acid (Item No. 90175) by GC-MS.{38926}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20568 -Available on backorder
13(Z)-Eicosenoic acid is an ω-7 fatty acid found in a variety of fish from the Indian, Atlantic, and Pacific oceans.{49083} It increases triglyceride accumulation in 3T3-L1 cells when used at a concentration of 50 μM.{49084}
Brand:CaymanSKU:26169 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
13(Z)-Eicosenoic acid is an ω-7 fatty acid found in a variety of fish from the Indian, Atlantic, and Pacific oceans.{49083} It increases triglyceride accumulation in 3T3-L1 cells when used at a concentration of 50 μM.{49084}
Brand:CaymanSKU:26169 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
13(Z)-Eicosenoic acid is an ω-7 fatty acid found in a variety of fish from the Indian, Atlantic, and Pacific oceans.{49083} It increases triglyceride accumulation in 3T3-L1 cells when used at a concentration of 50 μM.{49084}
Brand:CaymanSKU:26169 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
13C15-Nivalenol is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of nivalenol (Item No. 11438) by GC- or LC-MS. Nivalenol is a trichothecene mycotoxin that has been found in Fusarium.{32197} It is lethal to mice (LD50 = 6.9 mg/kg).{59482} Nivalenol (5, 10, and 15 mg/kg) also induces thymic, splenic, and Peyer’s patch cell apoptosis in mice.{59483}
Brand:CaymanSKU:31259 - 1.2 mlAvailable on backorder
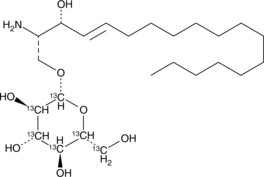
13C6 Glucosylsphingosine (d18:1) is an isotopically enriched form of 1-β-D-glucosylsphingosine (d18:1) (Item No. 23211) that is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of 1-β-D-glucosylsphingosine by GC- or LC-MS. 1-β-D-Glucosylsphingosine is a lysolipid derivative of glucosylcerebroside that decreases activity of glucocerebrosidase in LA-N-2 cells in a dose-dependent manner.{41130,41131} [Matreya, LLC. Catalog No. 2209]
Brand:CaymanSKU:23212 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
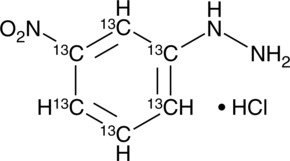
13C6-3-Nitrophenylhydrazine is a 13C-labeled derivatizing reagent for carboxylic acids.{32632} It is useful for LC-MS analysis of volatile acids such as short chain fatty acids.
Brand:CaymanSKU:20744 -Available on backorder
13C6-3-Nitrophenylhydrazine is a 13C-labeled derivatizing reagent for carboxylic acids.{32632} It is useful for LC-MS analysis of volatile acids such as short chain fatty acids.
Brand:CaymanSKU:20744 -Available on backorder
13C6-3-Nitrophenylhydrazine is a 13C-labeled derivatizing reagent for carboxylic acids.{32632} It is useful for LC-MS analysis of volatile acids such as short chain fatty acids.
Brand:CaymanSKU:20744 -Available on backorder
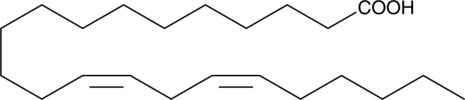
13Z,16Z-Docosadienoic acid is a natural ω-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA). It is an agonist of free fatty acid receptor 4 (FFAR4, also known as GPR120) and strongly inhibits the secretion of ghrelin by isolated mouse gastric cells.{32737} This 20:2 PUFA has been identified in mammals, fish, plants, and anaerobic fungi.{32733,32734,32735,32736,32738}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20749 -Available on backorder
13Z,16Z-Docosadienoic acid is a natural ω-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA). It is an agonist of free fatty acid receptor 4 (FFAR4, also known as GPR120) and strongly inhibits the secretion of ghrelin by isolated mouse gastric cells.{32737} This 20:2 PUFA has been identified in mammals, fish, plants, and anaerobic fungi.{32733,32734,32735,32736,32738}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20749 -Available on backorder
13Z,16Z-Docosadienoic acid is a natural ω-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA). It is an agonist of free fatty acid receptor 4 (FFAR4, also known as GPR120) and strongly inhibits the secretion of ghrelin by isolated mouse gastric cells.{32737} This 20:2 PUFA has been identified in mammals, fish, plants, and anaerobic fungi.{32733,32734,32735,32736,32738}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20749 -Available on backorder
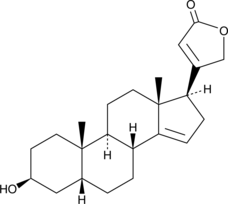
14-Anhydrodigitoxigenin is a cardenolide and a derivative of digitoxin.{48892} It reduces the activity of guinea pig heart Na+/K+-ATPase by 15% when used at a concentration of 10 µM.{48893}
Brand:CaymanSKU:30439 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
14-Anhydrodigitoxigenin is a cardenolide and a derivative of digitoxin.{48892} It reduces the activity of guinea pig heart Na+/K+-ATPase by 15% when used at a concentration of 10 µM.{48893}
Brand:CaymanSKU:30439 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
14-Anhydrodigitoxigenin is a cardenolide and a derivative of digitoxin.{48892} It reduces the activity of guinea pig heart Na+/K+-ATPase by 15% when used at a concentration of 10 µM.{48893}
Brand:CaymanSKU:30439 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
14-Anhydrodigitoxigenin is a cardenolide and a derivative of digitoxin.{48892} It reduces the activity of guinea pig heart Na+/K+-ATPase by 15% when used at a concentration of 10 µM.{48893}
Brand:CaymanSKU:30439 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
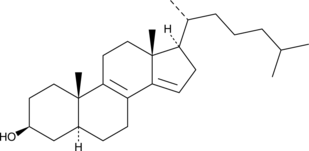
14-dehydro Zymostenol is a precursor to cholesterol (Item No. 9003100).{52493} It increases the percentage of myelin basic protein-positive (MBP+) oligodendrocytes formed from oligodendrocyte precursor cells when used at concentrations of 5.8 and 17 µM.{48202}
Brand:CaymanSKU:29534 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
14-dehydro Zymostenol is a precursor to cholesterol (Item No. 9003100).{52493} It increases the percentage of myelin basic protein-positive (MBP+) oligodendrocytes formed from oligodendrocyte precursor cells when used at concentrations of 5.8 and 17 µM.{48202}
Brand:CaymanSKU:29534 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
14-dehydro Zymostenol is a precursor to cholesterol (Item No. 9003100).{52493} It increases the percentage of myelin basic protein-positive (MBP+) oligodendrocytes formed from oligodendrocyte precursor cells when used at concentrations of 5.8 and 17 µM.{48202}
Brand:CaymanSKU:29534 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
14-deoxy-11,12-didehydro Andrographolide is an analog of the natural diterpenoid andrographolide (Item No. 11679) that can be isolated from A. paniculata.{28452} It retains the anti-inflammatory, antiallergenic, immuno-stimulatory, antiviral, antioxidant, hepatoprotective, and cardiovascular activities of andrographolide without producing cytotoxicity in KB cells (ED50 >20 µg/ml) that can occur with andrographolide 6.5 µg/ml.{28452,21112}
Brand:CaymanSKU:11670 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
14-deoxy-11,12-didehydro Andrographolide is an analog of the natural diterpenoid andrographolide (Item No. 11679) that can be isolated from A. paniculata.{28452} It retains the anti-inflammatory, antiallergenic, immuno-stimulatory, antiviral, antioxidant, hepatoprotective, and cardiovascular activities of andrographolide without producing cytotoxicity in KB cells (ED50 >20 µg/ml) that can occur with andrographolide 6.5 µg/ml.{28452,21112}
Brand:CaymanSKU:11670 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
14-deoxy-11,12-didehydro Andrographolide is an analog of the natural diterpenoid andrographolide (Item No. 11679) that can be isolated from A. paniculata.{28452} It retains the anti-inflammatory, antiallergenic, immuno-stimulatory, antiviral, antioxidant, hepatoprotective, and cardiovascular activities of andrographolide without producing cytotoxicity in KB cells (ED50 >20 µg/ml) that can occur with andrographolide 6.5 µg/ml.{28452,21112}
Brand:CaymanSKU:11670 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
14-deoxy-11,12-didehydro Andrographolide is an analog of the natural diterpenoid andrographolide (Item No. 11679) that can be isolated from A. paniculata.{28452} It retains the anti-inflammatory, antiallergenic, immuno-stimulatory, antiviral, antioxidant, hepatoprotective, and cardiovascular activities of andrographolide without producing cytotoxicity in KB cells (ED50 >20 µg/ml) that can occur with andrographolide 6.5 µg/ml.{28452,21112}
Brand:CaymanSKU:11670 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
14-Deoxyandrographolide is a diterpene lactone that has been found in A. paniculata and has diverse biological activities, including anticancer, hepatoprotective, antioxidative, and antidiabetic properties.{58034},{58035},{58036},{58037} It inhibits the growth of HL-60 cells with a GI50 value of 25.46 µM and is cytotoxic to T47D cells (EC50 = 2.8 µg/ml) but not HepG2 or NCI H23 cells (EC50s = 28.3 and 26.4 µg/ml, respectively).{58034},{58035} 14-Deoxyandrographolide (10 and 25 µM) increases AMPK phosphorylation and glucose uptake in L6 myotubes and potentiates the effect of insulin to increase cell surface levels of GLUT4 in L6-GLUT4myc cells.{58037} It reduces blood glucose levels in rats in a model of streptozotocin-induced diabetes and in db/db diabetic mice when administered at a dose of 100 mg/kg. 14-Deoxyandrographolide reduces ethanol-induced hepatotoxicity in rats when administered at a dose of 15 mg/kg per day for the last four weeks of an eight-week ethanol exposure period.{58036} It also reduces protein carbonyl and thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) levels and increases total glutathione (GSH) levels in isolated rat hepatocytes in the same model.
Brand:CaymanSKU:31140 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
14-Deoxyandrographolide is a diterpene lactone that has been found in A. paniculata and has diverse biological activities, including anticancer, hepatoprotective, antioxidative, and antidiabetic properties.{58034},{58035},{58036},{58037} It inhibits the growth of HL-60 cells with a GI50 value of 25.46 µM and is cytotoxic to T47D cells (EC50 = 2.8 µg/ml) but not HepG2 or NCI H23 cells (EC50s = 28.3 and 26.4 µg/ml, respectively).{58034},{58035} 14-Deoxyandrographolide (10 and 25 µM) increases AMPK phosphorylation and glucose uptake in L6 myotubes and potentiates the effect of insulin to increase cell surface levels of GLUT4 in L6-GLUT4myc cells.{58037} It reduces blood glucose levels in rats in a model of streptozotocin-induced diabetes and in db/db diabetic mice when administered at a dose of 100 mg/kg. 14-Deoxyandrographolide reduces ethanol-induced hepatotoxicity in rats when administered at a dose of 15 mg/kg per day for the last four weeks of an eight-week ethanol exposure period.{58036} It also reduces protein carbonyl and thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) levels and increases total glutathione (GSH) levels in isolated rat hepatocytes in the same model.
Brand:CaymanSKU:31140 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
14-Deoxyandrographolide is a diterpene lactone that has been found in A. paniculata and has diverse biological activities, including anticancer, hepatoprotective, antioxidative, and antidiabetic properties.{58034},{58035},{58036},{58037} It inhibits the growth of HL-60 cells with a GI50 value of 25.46 µM and is cytotoxic to T47D cells (EC50 = 2.8 µg/ml) but not HepG2 or NCI H23 cells (EC50s = 28.3 and 26.4 µg/ml, respectively).{58034},{58035} 14-Deoxyandrographolide (10 and 25 µM) increases AMPK phosphorylation and glucose uptake in L6 myotubes and potentiates the effect of insulin to increase cell surface levels of GLUT4 in L6-GLUT4myc cells.{58037} It reduces blood glucose levels in rats in a model of streptozotocin-induced diabetes and in db/db diabetic mice when administered at a dose of 100 mg/kg. 14-Deoxyandrographolide reduces ethanol-induced hepatotoxicity in rats when administered at a dose of 15 mg/kg per day for the last four weeks of an eight-week ethanol exposure period.{58036} It also reduces protein carbonyl and thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) levels and increases total glutathione (GSH) levels in isolated rat hepatocytes in the same model.
Brand:CaymanSKU:31140 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
14-Deoxyandrographolide is a diterpene lactone that has been found in A. paniculata and has diverse biological activities, including anticancer, hepatoprotective, antioxidative, and antidiabetic properties.{58034},{58035},{58036},{58037} It inhibits the growth of HL-60 cells with a GI50 value of 25.46 µM and is cytotoxic to T47D cells (EC50 = 2.8 µg/ml) but not HepG2 or NCI H23 cells (EC50s = 28.3 and 26.4 µg/ml, respectively).{58034},{58035} 14-Deoxyandrographolide (10 and 25 µM) increases AMPK phosphorylation and glucose uptake in L6 myotubes and potentiates the effect of insulin to increase cell surface levels of GLUT4 in L6-GLUT4myc cells.{58037} It reduces blood glucose levels in rats in a model of streptozotocin-induced diabetes and in db/db diabetic mice when administered at a dose of 100 mg/kg. 14-Deoxyandrographolide reduces ethanol-induced hepatotoxicity in rats when administered at a dose of 15 mg/kg per day for the last four weeks of an eight-week ethanol exposure period.{58036} It also reduces protein carbonyl and thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) levels and increases total glutathione (GSH) levels in isolated rat hepatocytes in the same model.
Brand:CaymanSKU:31140 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
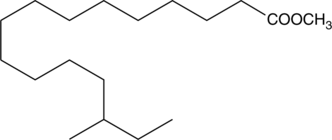
14-methyl Palmitic acid is a methylated fatty acid that has been found in bacteria, bovine milk fat, Aegean jellyfish (A. aurita), and one-humped camel (C. dromedarius) meat and fat.{40922,40923,38743,40924} It is also found in human breast milk and levels are decreased in mature breast milk compared to colostrum.{40925} 14-methyl Palmitic acid is produced in Florida manatee (T. manatus latirostris) liver in response to brevetoxin exposure.{40926} [Matreya, LLC. Catalog No. 1616]
Brand:CaymanSKU:24820 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
14-methyl Palmitic acid is a methylated fatty acid that has been found in bacteria, bovine milk fat, Aegean jellyfish (A. aurita), and one-humped camel (C. dromedarius) meat and fat.{40922,40923,38743,40924} It is also found in human breast milk and levels are decreased in mature breast milk compared to colostrum.{40925} 14-methyl Palmitic acid is produced in Florida manatee (T. manatus latirostris) liver in response to brevetoxin exposure.{40926} [Matreya, LLC. Catalog No. 1616]
Brand:CaymanSKU:24820 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
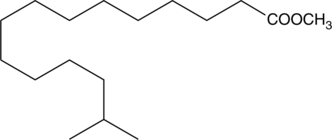
14-methyl Palmitic acid methyl ester is a methylated fatty acid methyl ester that has been found in A. indica leaf extract, S. alboflavus TD-1, and as a minor component in biodiesel produced from C. sorokiniana microalgae.{40917,40921,40919} It is a volatile compound released by maize that reduces growth of F. verticillioides in a concentration-dependent manner.{40920} 14-methyl Palmitic acid methyl ester has been used as a standard for the quantification of 14-methyl palmitic acid (Item No. 24820) in various foods by GC-MS.{40918} [Matreya, LLC. Catalog No. 1614]
Brand:CaymanSKU:24821 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
14-methyl Palmitic acid methyl ester is a methylated fatty acid methyl ester that has been found in A. indica leaf extract, S. alboflavus TD-1, and as a minor component in biodiesel produced from C. sorokiniana microalgae.{40917,40921,40919} It is a volatile compound released by maize that reduces growth of F. verticillioides in a concentration-dependent manner.{40920} 14-methyl Palmitic acid methyl ester has been used as a standard for the quantification of 14-methyl palmitic acid (Item No. 24820) in various foods by GC-MS.{40918} [Matreya, LLC. Catalog No. 1614]
Brand:CaymanSKU:24821 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
14-methyl Palmitic acid methyl ester is a methylated fatty acid methyl ester that has been found in A. indica leaf extract, S. alboflavus TD-1, and as a minor component in biodiesel produced from C. sorokiniana microalgae.{40917,40921,40919} It is a volatile compound released by maize that reduces growth of F. verticillioides in a concentration-dependent manner.{40920} 14-methyl Palmitic acid methyl ester has been used as a standard for the quantification of 14-methyl palmitic acid (Item No. 24820) in various foods by GC-MS.{40918} [Matreya, LLC. Catalog No. 1614]
Brand:CaymanSKU:24821 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
14-methyl Pentadecanoic acid methyl ester is a methylated fatty acid methyl ester that has been found in S. zeai sea sponges as the fatty acyl component of zeamide, A. indica leaf extract, and C. vulgaris and H. pluvialis microalgae.{40928,40917,40927} It is a major component of the vancomycin-induced biofilm produced by vancomycin-resistant S. aureus (VRSA).{40929} 14-methyl Pentadecanoic acid methyl ester has been used as a standard for the quantification of 14-methyl pentadecanoic acid in various foods by GC-MS.{40918} [Matreya, LLC. Catalog No. 1601]
Brand:CaymanSKU:24813 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
14-methyl Pentadecanoic acid methyl ester is a methylated fatty acid methyl ester that has been found in S. zeai sea sponges as the fatty acyl component of zeamide, A. indica leaf extract, and C. vulgaris and H. pluvialis microalgae.{40928,40917,40927} It is a major component of the vancomycin-induced biofilm produced by vancomycin-resistant S. aureus (VRSA).{40929} 14-methyl Pentadecanoic acid methyl ester has been used as a standard for the quantification of 14-methyl pentadecanoic acid in various foods by GC-MS.{40918} [Matreya, LLC. Catalog No. 1601]
Brand:CaymanSKU:24813 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
14-methyl Pentadecanoic acid methyl ester is a methylated fatty acid methyl ester that has been found in S. zeai sea sponges as the fatty acyl component of zeamide, A. indica leaf extract, and C. vulgaris and H. pluvialis microalgae.{40928,40917,40927} It is a major component of the vancomycin-induced biofilm produced by vancomycin-resistant S. aureus (VRSA).{40929} 14-methyl Pentadecanoic acid methyl ester has been used as a standard for the quantification of 14-methyl pentadecanoic acid in various foods by GC-MS.{40918} [Matreya, LLC. Catalog No. 1601]
Brand:CaymanSKU:24813 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
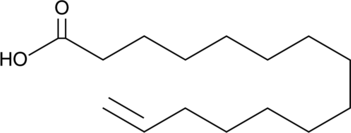
14-Pentadecenoic acid is a 15-carbon, long-chain fatty acid that contains an alkene functional group on the terminal carbon of its aliphatic tail. The oxidation pattern of this fatty acid resulting from growth of M. cerificans at the expense of the parent alkene has been reported.{31487} 14-Pentadecenoic acid has been used in the fabrication of fibrous scaffold biomaterials for tissue engineering applications and for the construction of metallomesogenic side-chain polymers that coat capillary columns used in gas chromatography.{31485,31486}
Brand:CaymanSKU:19724 -Available on backorder
14-Pentadecenoic acid is a 15-carbon, long-chain fatty acid that contains an alkene functional group on the terminal carbon of its aliphatic tail. The oxidation pattern of this fatty acid resulting from growth of M. cerificans at the expense of the parent alkene has been reported.{31487} 14-Pentadecenoic acid has been used in the fabrication of fibrous scaffold biomaterials for tissue engineering applications and for the construction of metallomesogenic side-chain polymers that coat capillary columns used in gas chromatography.{31485,31486}
Brand:CaymanSKU:19724 -Available on backorder
14-Pentadecenoic acid is a 15-carbon, long-chain fatty acid that contains an alkene functional group on the terminal carbon of its aliphatic tail. The oxidation pattern of this fatty acid resulting from growth of M. cerificans at the expense of the parent alkene has been reported.{31487} 14-Pentadecenoic acid has been used in the fabrication of fibrous scaffold biomaterials for tissue engineering applications and for the construction of metallomesogenic side-chain polymers that coat capillary columns used in gas chromatography.{31485,31486}
Brand:CaymanSKU:19724 -Available on backorder
14-Pentadecenoic acid is a 15-carbon, long-chain fatty acid that contains an alkene functional group on the terminal carbon of its aliphatic tail. The oxidation pattern of this fatty acid resulting from growth of M. cerificans at the expense of the parent alkene has been reported.{31487} 14-Pentadecenoic acid has been used in the fabrication of fibrous scaffold biomaterials for tissue engineering applications and for the construction of metallomesogenic side-chain polymers that coat capillary columns used in gas chromatography.{31485,31486}
Brand:CaymanSKU:19724 -Available on backorder
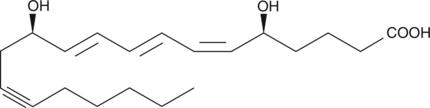
Leukotriene B4 (LTB4) is a dihydroxy fatty acid derived from arachidonic acid through the 5-lipoxygenase pathway.{521,948} It promotes a number of leukocyte functions including aggregation, stimulation of ion fluxes, enhancement of lysosomal enzyme release, superoxide anion production, chemotaxis, and chemokinesis.{329,82} At least two LTB4 receptors, termed BLT1 and BLT2, have been identified. 14,15-dehydro LTB4 is a LTB4 receptor antagonist that has a higher binding affinity for BLT1, demonstrating a Ki value of 27 nM, compared to BLT2, which has a Ki value of 473 nM.{8743} 14,15-dehydro LTB4 inhibits LTB4-induced release of lysozymes from rat polymorphonuclear leukoctyes with an IC50 value of 1 µM.{384}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20150 -Available on backorder
Leukotriene B4 (LTB4) is a dihydroxy fatty acid derived from arachidonic acid through the 5-lipoxygenase pathway.{521,948} It promotes a number of leukocyte functions including aggregation, stimulation of ion fluxes, enhancement of lysosomal enzyme release, superoxide anion production, chemotaxis, and chemokinesis.{329,82} At least two LTB4 receptors, termed BLT1 and BLT2, have been identified. 14,15-dehydro LTB4 is a LTB4 receptor antagonist that has a higher binding affinity for BLT1, demonstrating a Ki value of 27 nM, compared to BLT2, which has a Ki value of 473 nM.{8743} 14,15-dehydro LTB4 inhibits LTB4-induced release of lysozymes from rat polymorphonuclear leukoctyes with an IC50 value of 1 µM.{384}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20150 -Available on backorder
Leukotriene B4 (LTB4) is a dihydroxy fatty acid derived from arachidonic acid through the 5-lipoxygenase pathway.{521,948} It promotes a number of leukocyte functions including aggregation, stimulation of ion fluxes, enhancement of lysosomal enzyme release, superoxide anion production, chemotaxis, and chemokinesis.{329,82} At least two LTB4 receptors, termed BLT1 and BLT2, have been identified. 14,15-dehydro LTB4 is a LTB4 receptor antagonist that has a higher binding affinity for BLT1, demonstrating a Ki value of 27 nM, compared to BLT2, which has a Ki value of 473 nM.{8743} 14,15-dehydro LTB4 inhibits LTB4-induced release of lysozymes from rat polymorphonuclear leukoctyes with an IC50 value of 1 µM.{384}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20150 -Available on backorder
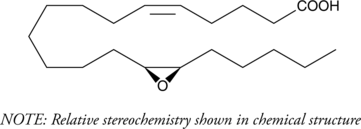
Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs), such as 11(12)-EET and 14(15)-EET, are cytochrome P450 metabolites of arachidonic acid that have been identified as endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factors with vasodilator activity.{12391} 14,15-EE-5(Z)-E is a structural analog of 14,15-epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (14,15-EET) that antagonizes EET-induced relaxation of vascular smooth muscle.{14412} Relaxation of U46619-constricted bovine arteries by 14,15-EET could be inhibited approximately 80% by 14,15-EE-5(Z)-E at a concentration of 10 µM. 14,15-EE-5(Z)-E does not appear to antagonize nitric oxide- or iloprost-mediated vascular relaxation.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10004946 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs), such as 11(12)-EET and 14(15)-EET, are cytochrome P450 metabolites of arachidonic acid that have been identified as endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factors with vasodilator activity.{12391} 14,15-EE-5(Z)-E is a structural analog of 14,15-epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (14,15-EET) that antagonizes EET-induced relaxation of vascular smooth muscle.{14412} Relaxation of U46619-constricted bovine arteries by 14,15-EET could be inhibited approximately 80% by 14,15-EE-5(Z)-E at a concentration of 10 µM. 14,15-EE-5(Z)-E does not appear to antagonize nitric oxide- or iloprost-mediated vascular relaxation.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10004946 - 25 µgAvailable on backorder
Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs), such as 11(12)-EET and 14(15)-EET, are cytochrome P450 metabolites of arachidonic acid that have been identified as endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factors with vasodilator activity.{12391} 14,15-EE-5(Z)-E is a structural analog of 14,15-epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (14,15-EET) that antagonizes EET-induced relaxation of vascular smooth muscle.{14412} Relaxation of U46619-constricted bovine arteries by 14,15-EET could be inhibited approximately 80% by 14,15-EE-5(Z)-E at a concentration of 10 µM. 14,15-EE-5(Z)-E does not appear to antagonize nitric oxide- or iloprost-mediated vascular relaxation.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10004946 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder