Cayman
Showing 31051–31200 of 45550 results
-
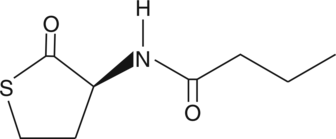
Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density. Controlling bacterial infections by quenching their quorum sensing systems is a promising field of study. The expression of specific target genes, such as transcriptional regulators belonging to the LuxIR family of proteins, is coordinated by synthesis of diffusible acylhomoserine lactone (AHL) molecules. N-butyryl-L-Homocysteine thio-lactone is an analog of N-butyryl-L-homoserine lactone, the small diffusible signaling molecule involved in quorum sensing, thereby controlling gene expression and cellular metabolism.{16309} N-butyryl-L-Homocysteine thio-lactone induces violacein expression in C. violaceum mutants usually not able to produce AHLs.{16309,16308}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10011204 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density. Controlling bacterial infections by quenching their quorum sensing systems is a promising field of study. The expression of specific target genes, such as transcriptional regulators belonging to the LuxIR family of proteins, is coordinated by synthesis of diffusible acylhomoserine lactone (AHL) molecules. N-butyryl-L-Homocysteine thio-lactone is an analog of N-butyryl-L-homoserine lactone, the small diffusible signaling molecule involved in quorum sensing, thereby controlling gene expression and cellular metabolism.{16309} N-butyryl-L-Homocysteine thio-lactone induces violacein expression in C. violaceum mutants usually not able to produce AHLs.{16309,16308}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10011204 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
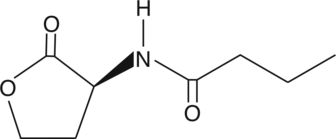
Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density. Controlling bacterial infections by quenching their quorum sensing systems is a promising field of study. The expression of specific target genes, such as transcriptional regulators belonging to the LuxIR family of proteins, is coordinated by synthesis of diffusible acylhomoserine lactone (AHL) molecules. N-butyryl-L-Homoserine lactone is a small diffusible signaling molecule involved in quorum sensing, controlling gene expression, and cellular metabolism.{13434} The diverse applications of this molecule include regulation of virulence in general, infection prevention, and formation of biofilms.{13433,14086,14087,14088,14089,14093}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007898 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density. Controlling bacterial infections by quenching their quorum sensing systems is a promising field of study. The expression of specific target genes, such as transcriptional regulators belonging to the LuxIR family of proteins, is coordinated by synthesis of diffusible acylhomoserine lactone (AHL) molecules. N-butyryl-L-Homoserine lactone is a small diffusible signaling molecule involved in quorum sensing, controlling gene expression, and cellular metabolism.{13434} The diverse applications of this molecule include regulation of virulence in general, infection prevention, and formation of biofilms.{13433,14086,14087,14088,14089,14093}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007898 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density. Controlling bacterial infections by quenching their quorum sensing systems is a promising field of study. The expression of specific target genes, such as transcriptional regulators belonging to the LuxIR family of proteins, is coordinated by synthesis of diffusible acylhomoserine lactone (AHL) molecules. N-butyryl-L-Homoserine lactone is a small diffusible signaling molecule involved in quorum sensing, controlling gene expression, and cellular metabolism.{13434} The diverse applications of this molecule include regulation of virulence in general, infection prevention, and formation of biofilms.{13433,14086,14087,14088,14089,14093}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007898 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density. Controlling bacterial infections by quenching their quorum sensing systems is a promising field of study. The expression of specific target genes, such as transcriptional regulators belonging to the LuxIR family of proteins, is coordinated by synthesis of diffusible acylhomoserine lactone (AHL) molecules. N-butyryl-L-Homoserine lactone is a small diffusible signaling molecule involved in quorum sensing, controlling gene expression, and cellular metabolism.{13434} The diverse applications of this molecule include regulation of virulence in general, infection prevention, and formation of biofilms.{13433,14086,14087,14088,14089,14093}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007898 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
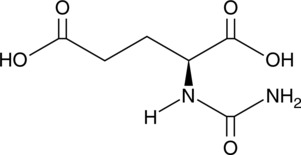
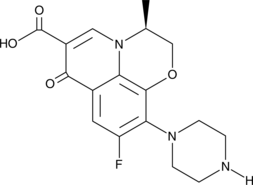
N-Carbamyl-L-glutamic acid is an activator of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase 1 (CPS1), the first enzyme in the urea cycle.{38610} It is a structural analog of N-acetyl-glutamate, an endogenous CPS1 activator. N-Carbamyl-L-glutamic acid (500 mg/kg) reduces 2-ketoisocaproate-induced hyperammonemia in a mouse model of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA lyase deficiency.{38609} It inhibits cell proliferation of a variety of cancer cell lines with IC50 values ranging from 5 to 7.5 nM.{38608} It also inhibits tumor growth by 80 and 82% in orthotopic mouse models of pancreatic and triple-negative breast cancer, respectively, when administered at a dose of 120 mg/kg per day for 10 days. Formulations containing N-carbamyl-L-glutamic acid have been used in the treatment of primary N-acetyl-glutamate synthase deficiency.
Brand:CaymanSKU:23512 - 1 gAvailable on backorder
N-Carbamyl-L-glutamic acid is an activator of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase 1 (CPS1), the first enzyme in the urea cycle.{38610} It is a structural analog of N-acetyl-glutamate, an endogenous CPS1 activator. N-Carbamyl-L-glutamic acid (500 mg/kg) reduces 2-ketoisocaproate-induced hyperammonemia in a mouse model of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA lyase deficiency.{38609} It inhibits cell proliferation of a variety of cancer cell lines with IC50 values ranging from 5 to 7.5 nM.{38608} It also inhibits tumor growth by 80 and 82% in orthotopic mouse models of pancreatic and triple-negative breast cancer, respectively, when administered at a dose of 120 mg/kg per day for 10 days. Formulations containing N-carbamyl-L-glutamic acid have been used in the treatment of primary N-acetyl-glutamate synthase deficiency.
Brand:CaymanSKU:23512 - 10 gAvailable on backorder
N-Carbamyl-L-glutamic acid is an activator of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase 1 (CPS1), the first enzyme in the urea cycle.{38610} It is a structural analog of N-acetyl-glutamate, an endogenous CPS1 activator. N-Carbamyl-L-glutamic acid (500 mg/kg) reduces 2-ketoisocaproate-induced hyperammonemia in a mouse model of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA lyase deficiency.{38609} It inhibits cell proliferation of a variety of cancer cell lines with IC50 values ranging from 5 to 7.5 nM.{38608} It also inhibits tumor growth by 80 and 82% in orthotopic mouse models of pancreatic and triple-negative breast cancer, respectively, when administered at a dose of 120 mg/kg per day for 10 days. Formulations containing N-carbamyl-L-glutamic acid have been used in the treatment of primary N-acetyl-glutamate synthase deficiency.
Brand:CaymanSKU:23512 - 25 gAvailable on backorder
N-Carbamyl-L-glutamic acid is an activator of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase 1 (CPS1), the first enzyme in the urea cycle.{38610} It is a structural analog of N-acetyl-glutamate, an endogenous CPS1 activator. N-Carbamyl-L-glutamic acid (500 mg/kg) reduces 2-ketoisocaproate-induced hyperammonemia in a mouse model of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA lyase deficiency.{38609} It inhibits cell proliferation of a variety of cancer cell lines with IC50 values ranging from 5 to 7.5 nM.{38608} It also inhibits tumor growth by 80 and 82% in orthotopic mouse models of pancreatic and triple-negative breast cancer, respectively, when administered at a dose of 120 mg/kg per day for 10 days. Formulations containing N-carbamyl-L-glutamic acid have been used in the treatment of primary N-acetyl-glutamate synthase deficiency.
Brand:CaymanSKU:23512 - 5 gAvailable on backorder
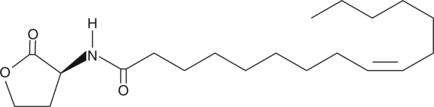
Quorum sensing is a regulatory process used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density.{15370} This regulatory process manifests itself with a variety of phenotypes including biofilm formation and virulence factor production.{13434} Coordinated gene expression is achieved by the production, release, and detection of small diffusible signal molecules called autoinducers. The N-acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) comprise one such class of autoinducers, each of which generally consists of a fatty acid coupled with homoserine lactone (HSL). AHLs vary in acyl group length (C4-C18), in the substitution of C3 (hydrogen, hydroxyl, or oxo group) and in the presence or absence of one or more carbon-carbon double bonds in the fatty acid chain. These differences confer signal specificity through the affinity of transcriptional regulators of the LuxR family.{15398} C16:1-Δ9-(L)-HSL is a long-chain AHL that functions as a quorum sensing signaling molecule in strains of S. meliloti.{15835,15834,15833,15828} Regulating bacterial quorum sensing signaling can be used to inhibit pathogenesis and thus, represents a new approach to antimicrobial therapy in the treatment of infectious diseases.{15369}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10012673 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Quorum sensing is a regulatory process used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density.{15370} This regulatory process manifests itself with a variety of phenotypes including biofilm formation and virulence factor production.{13434} Coordinated gene expression is achieved by the production, release, and detection of small diffusible signal molecules called autoinducers. The N-acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) comprise one such class of autoinducers, each of which generally consists of a fatty acid coupled with homoserine lactone (HSL). AHLs vary in acyl group length (C4-C18), in the substitution of C3 (hydrogen, hydroxyl, or oxo group) and in the presence or absence of one or more carbon-carbon double bonds in the fatty acid chain. These differences confer signal specificity through the affinity of transcriptional regulators of the LuxR family.{15398} C16:1-Δ9-(L)-HSL is a long-chain AHL that functions as a quorum sensing signaling molecule in strains of S. meliloti.{15835,15834,15833,15828} Regulating bacterial quorum sensing signaling can be used to inhibit pathogenesis and thus, represents a new approach to antimicrobial therapy in the treatment of infectious diseases.{15369}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10012673 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
Quorum sensing is a regulatory process used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density.{15370} This regulatory process manifests itself with a variety of phenotypes including biofilm formation and virulence factor production.{13434} Coordinated gene expression is achieved by the production, release, and detection of small diffusible signal molecules called autoinducers. The N-acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) comprise one such class of autoinducers, each of which generally consists of a fatty acid coupled with homoserine lactone (HSL). AHLs vary in acyl group length (C4-C18), in the substitution of C3 (hydrogen, hydroxyl, or oxo group) and in the presence or absence of one or more carbon-carbon double bonds in the fatty acid chain. These differences confer signal specificity through the affinity of transcriptional regulators of the LuxR family.{15398} C16:1-Δ9-(L)-HSL is a long-chain AHL that functions as a quorum sensing signaling molecule in strains of S. meliloti.{15835,15834,15833,15828} Regulating bacterial quorum sensing signaling can be used to inhibit pathogenesis and thus, represents a new approach to antimicrobial therapy in the treatment of infectious diseases.{15369}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10012673 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Quorum sensing is a regulatory process used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density.{15370} This regulatory process manifests itself with a variety of phenotypes including biofilm formation and virulence factor production.{13434} Coordinated gene expression is achieved by the production, release, and detection of small diffusible signal molecules called autoinducers. The N-acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) comprise one such class of autoinducers, each of which generally consists of a fatty acid coupled with homoserine lactone (HSL). AHLs vary in acyl group length (C4-C18), in the substitution of C3 (hydrogen, hydroxyl, or oxo group) and in the presence or absence of one or more carbon-carbon double bonds in the fatty acid chain. These differences confer signal specificity through the affinity of transcriptional regulators of the LuxR family.{15398} C16:1-Δ9-(L)-HSL is a long-chain AHL that functions as a quorum sensing signaling molecule in strains of S. meliloti.{15835,15834,15833,15828} Regulating bacterial quorum sensing signaling can be used to inhibit pathogenesis and thus, represents a new approach to antimicrobial therapy in the treatment of infectious diseases.{15369}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10012673 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
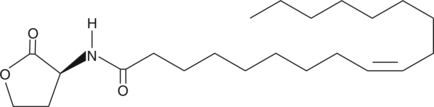
Quorum sensing is a regulatory process used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density.{15370} This regulatory process manifests itself with a variety of phenotypes including biofilm formation and virulence factor production.{13434} Coordinated gene expression is achieved by the production, release, and detection of small diffusible signal molecules called autoinducers. The N-acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) comprise one such class of autoinducers, each of which generally consists of a fatty acid coupled with homoserine lactone (HSL). AHLs vary in acyl group length (C4-C18), in the substitution of C3 (hydrogen, hydroxyl, or oxo group) and in the presence or absence of one or more carbon-carbon double bonds in the fatty acid chain. These differences confer signal specificity through the affinity of transcriptional regulators of the LuxR family.{15398} C18:1-Δ9 cis-(L)-HSL is a long-chain AHL that may have antimicrobial activity{15832} and thus, might be used to inhibit pathogenesis by regulating bacerial quorum sensing signaling.{15369}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10012674 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Quorum sensing is a regulatory process used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density.{15370} This regulatory process manifests itself with a variety of phenotypes including biofilm formation and virulence factor production.{13434} Coordinated gene expression is achieved by the production, release, and detection of small diffusible signal molecules called autoinducers. The N-acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) comprise one such class of autoinducers, each of which generally consists of a fatty acid coupled with homoserine lactone (HSL). AHLs vary in acyl group length (C4-C18), in the substitution of C3 (hydrogen, hydroxyl, or oxo group) and in the presence or absence of one or more carbon-carbon double bonds in the fatty acid chain. These differences confer signal specificity through the affinity of transcriptional regulators of the LuxR family.{15398} C18:1-Δ9 cis-(L)-HSL is a long-chain AHL that may have antimicrobial activity{15832} and thus, might be used to inhibit pathogenesis by regulating bacerial quorum sensing signaling.{15369}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10012674 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
Quorum sensing is a regulatory process used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density.{15370} This regulatory process manifests itself with a variety of phenotypes including biofilm formation and virulence factor production.{13434} Coordinated gene expression is achieved by the production, release, and detection of small diffusible signal molecules called autoinducers. The N-acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) comprise one such class of autoinducers, each of which generally consists of a fatty acid coupled with homoserine lactone (HSL). AHLs vary in acyl group length (C4-C18), in the substitution of C3 (hydrogen, hydroxyl, or oxo group) and in the presence or absence of one or more carbon-carbon double bonds in the fatty acid chain. These differences confer signal specificity through the affinity of transcriptional regulators of the LuxR family.{15398} C18:1-Δ9 cis-(L)-HSL is a long-chain AHL that may have antimicrobial activity{15832} and thus, might be used to inhibit pathogenesis by regulating bacerial quorum sensing signaling.{15369}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10012674 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Quorum sensing is a regulatory process used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density.{15370} This regulatory process manifests itself with a variety of phenotypes including biofilm formation and virulence factor production.{13434} Coordinated gene expression is achieved by the production, release, and detection of small diffusible signal molecules called autoinducers. The N-acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) comprise one such class of autoinducers, each of which generally consists of a fatty acid coupled with homoserine lactone (HSL). AHLs vary in acyl group length (C4-C18), in the substitution of C3 (hydrogen, hydroxyl, or oxo group) and in the presence or absence of one or more carbon-carbon double bonds in the fatty acid chain. These differences confer signal specificity through the affinity of transcriptional regulators of the LuxR family.{15398} C18:1-Δ9 cis-(L)-HSL is a long-chain AHL that may have antimicrobial activity{15832} and thus, might be used to inhibit pathogenesis by regulating bacerial quorum sensing signaling.{15369}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10012674 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
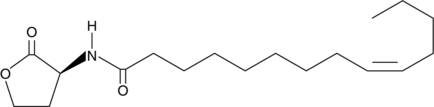
Quorum sensing is a regulatory process used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density.{15370} This regulatory process manifests itself with a variety of phenotypes including biofilm formation and virulence factor production.{13434} Coordinated gene expression is achieved by the production, release, and detection of small diffusible signal molecules called autoinducers. The N-acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) comprise one such class of autoinducers, each of which generally consists of a fatty acid coupled with homoserine lactone (HSL). AHLs vary in acyl group length (C4-C18), in the substitution of C3 (hydrogen, hydroxyl, or oxo group) and in the presence or absence of one or more carbon-carbon double bonds in the fatty acid chain. These differences confer signal specificity through the affinity of transcriptional regulators of the LuxR family.{15398} C14:1-Δ9-cis-(L)-HSL is a long-chain AHL that functions as a signaling molecule in the quorum sensing of A. vitis.{15831} Regulating bacterial quorum sensing signaling can be used to inhibit pathogenesis and thus, represents a new approach to antimicrobial therpy in the treatment of infectious diseases.{15369}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10012672 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Quorum sensing is a regulatory process used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density.{15370} This regulatory process manifests itself with a variety of phenotypes including biofilm formation and virulence factor production.{13434} Coordinated gene expression is achieved by the production, release, and detection of small diffusible signal molecules called autoinducers. The N-acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) comprise one such class of autoinducers, each of which generally consists of a fatty acid coupled with homoserine lactone (HSL). AHLs vary in acyl group length (C4-C18), in the substitution of C3 (hydrogen, hydroxyl, or oxo group) and in the presence or absence of one or more carbon-carbon double bonds in the fatty acid chain. These differences confer signal specificity through the affinity of transcriptional regulators of the LuxR family.{15398} C14:1-Δ9-cis-(L)-HSL is a long-chain AHL that functions as a signaling molecule in the quorum sensing of A. vitis.{15831} Regulating bacterial quorum sensing signaling can be used to inhibit pathogenesis and thus, represents a new approach to antimicrobial therpy in the treatment of infectious diseases.{15369}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10012672 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
Quorum sensing is a regulatory process used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density.{15370} This regulatory process manifests itself with a variety of phenotypes including biofilm formation and virulence factor production.{13434} Coordinated gene expression is achieved by the production, release, and detection of small diffusible signal molecules called autoinducers. The N-acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) comprise one such class of autoinducers, each of which generally consists of a fatty acid coupled with homoserine lactone (HSL). AHLs vary in acyl group length (C4-C18), in the substitution of C3 (hydrogen, hydroxyl, or oxo group) and in the presence or absence of one or more carbon-carbon double bonds in the fatty acid chain. These differences confer signal specificity through the affinity of transcriptional regulators of the LuxR family.{15398} C14:1-Δ9-cis-(L)-HSL is a long-chain AHL that functions as a signaling molecule in the quorum sensing of A. vitis.{15831} Regulating bacterial quorum sensing signaling can be used to inhibit pathogenesis and thus, represents a new approach to antimicrobial therpy in the treatment of infectious diseases.{15369}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10012672 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Quorum sensing is a regulatory process used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density.{15370} This regulatory process manifests itself with a variety of phenotypes including biofilm formation and virulence factor production.{13434} Coordinated gene expression is achieved by the production, release, and detection of small diffusible signal molecules called autoinducers. The N-acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) comprise one such class of autoinducers, each of which generally consists of a fatty acid coupled with homoserine lactone (HSL). AHLs vary in acyl group length (C4-C18), in the substitution of C3 (hydrogen, hydroxyl, or oxo group) and in the presence or absence of one or more carbon-carbon double bonds in the fatty acid chain. These differences confer signal specificity through the affinity of transcriptional regulators of the LuxR family.{15398} C14:1-Δ9-cis-(L)-HSL is a long-chain AHL that functions as a signaling molecule in the quorum sensing of A. vitis.{15831} Regulating bacterial quorum sensing signaling can be used to inhibit pathogenesis and thus, represents a new approach to antimicrobial therpy in the treatment of infectious diseases.{15369}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10012672 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
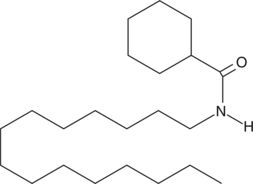
Numerous analogs of fatty acyl ethanolamides potentiate the intrinsic biological activity of endocannabinoids.{10254} This potentiation is ascribed either to inhibition of AEA reuptake into neurons, or inhibition of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) within the neurons. {10647} However, Ueda has recently cloned another amidase, the acidic palmitoyl ethanolamidase (PEAase) that promotes the hydrolysis of palmitoylethanolamide.{9989} N-Cyclohexanecarbonylpentadecylamine is a selective inhibitor of acidic PEAase, inhibiting the enzyme with an IC50 of 4.5 µM, while failing to inhibit FAAH even at 100 µM.{13342}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007739 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Numerous analogs of fatty acyl ethanolamides potentiate the intrinsic biological activity of endocannabinoids.{10254} This potentiation is ascribed either to inhibition of AEA reuptake into neurons, or inhibition of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) within the neurons. {10647} However, Ueda has recently cloned another amidase, the acidic palmitoyl ethanolamidase (PEAase) that promotes the hydrolysis of palmitoylethanolamide.{9989} N-Cyclohexanecarbonylpentadecylamine is a selective inhibitor of acidic PEAase, inhibiting the enzyme with an IC50 of 4.5 µM, while failing to inhibit FAAH even at 100 µM.{13342}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007739 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
Numerous analogs of fatty acyl ethanolamides potentiate the intrinsic biological activity of endocannabinoids.{10254} This potentiation is ascribed either to inhibition of AEA reuptake into neurons, or inhibition of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) within the neurons. {10647} However, Ueda has recently cloned another amidase, the acidic palmitoyl ethanolamidase (PEAase) that promotes the hydrolysis of palmitoylethanolamide.{9989} N-Cyclohexanecarbonylpentadecylamine is a selective inhibitor of acidic PEAase, inhibiting the enzyme with an IC50 of 4.5 µM, while failing to inhibit FAAH even at 100 µM.{13342}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007739 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Numerous analogs of fatty acyl ethanolamides potentiate the intrinsic biological activity of endocannabinoids.{10254} This potentiation is ascribed either to inhibition of AEA reuptake into neurons, or inhibition of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) within the neurons. {10647} However, Ueda has recently cloned another amidase, the acidic palmitoyl ethanolamidase (PEAase) that promotes the hydrolysis of palmitoylethanolamide.{9989} N-Cyclohexanecarbonylpentadecylamine is a selective inhibitor of acidic PEAase, inhibiting the enzyme with an IC50 of 4.5 µM, while failing to inhibit FAAH even at 100 µM.{13342}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007739 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
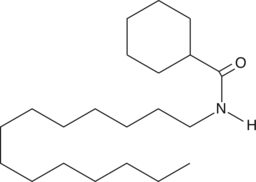
Numerous analogs of fatty acyl ethanolamides potentiate the intrinsic biological activity of endocannabinoids.{10254} This potentiation is ascribed either to inhibition of AEA reuptake into neurons, or inhibition of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) within the neurons. {10647} However, Ueda, et al. has recently cloned another amidase, the acidic PEAase that promotes the hydrolysis of palmitoylethanolamide.{9989} N-Cyclohexanecarbonyltetradecylamine is an analog of N-cyclohexanecarbonyl-pentadecylamine, a selective inhibitor of acidic PEAase with an IC50 value of 4.5 µM, that contains 1 less carbon in the alkyl chain.{13342} The biological activity of N-cyclohexanecarbonyltetradecylamine has not been documented.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008317 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Numerous analogs of fatty acyl ethanolamides potentiate the intrinsic biological activity of endocannabinoids.{10254} This potentiation is ascribed either to inhibition of AEA reuptake into neurons, or inhibition of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) within the neurons. {10647} However, Ueda, et al. has recently cloned another amidase, the acidic PEAase that promotes the hydrolysis of palmitoylethanolamide.{9989} N-Cyclohexanecarbonyltetradecylamine is an analog of N-cyclohexanecarbonyl-pentadecylamine, a selective inhibitor of acidic PEAase with an IC50 value of 4.5 µM, that contains 1 less carbon in the alkyl chain.{13342} The biological activity of N-cyclohexanecarbonyltetradecylamine has not been documented.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008317 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
Numerous analogs of fatty acyl ethanolamides potentiate the intrinsic biological activity of endocannabinoids.{10254} This potentiation is ascribed either to inhibition of AEA reuptake into neurons, or inhibition of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) within the neurons. {10647} However, Ueda, et al. has recently cloned another amidase, the acidic PEAase that promotes the hydrolysis of palmitoylethanolamide.{9989} N-Cyclohexanecarbonyltetradecylamine is an analog of N-cyclohexanecarbonyl-pentadecylamine, a selective inhibitor of acidic PEAase with an IC50 value of 4.5 µM, that contains 1 less carbon in the alkyl chain.{13342} The biological activity of N-cyclohexanecarbonyltetradecylamine has not been documented.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008317 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Numerous analogs of fatty acyl ethanolamides potentiate the intrinsic biological activity of endocannabinoids.{10254} This potentiation is ascribed either to inhibition of AEA reuptake into neurons, or inhibition of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) within the neurons. {10647} However, Ueda, et al. has recently cloned another amidase, the acidic PEAase that promotes the hydrolysis of palmitoylethanolamide.{9989} N-Cyclohexanecarbonyltetradecylamine is an analog of N-cyclohexanecarbonyl-pentadecylamine, a selective inhibitor of acidic PEAase with an IC50 value of 4.5 µM, that contains 1 less carbon in the alkyl chain.{13342} The biological activity of N-cyclohexanecarbonyltetradecylamine has not been documented.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008317 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
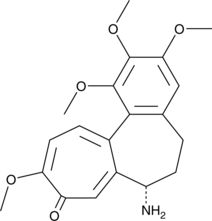
N-Deacetylcolchicine is an inhibitor of tubulin polymerization (IC50 = 3 µM for bovine brain tubulin) and a derivative of the microtubule polymerization inhibitor colchicine (Item No. 9000760).{24891} It stimulates tubulin GTPase activity.{51178}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21697 -Out of stock
N-Deacetylcolchicine is an inhibitor of tubulin polymerization (IC50 = 3 µM for bovine brain tubulin) and a derivative of the microtubule polymerization inhibitor colchicine (Item No. 9000760).{24891} It stimulates tubulin GTPase activity.{51178}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21697 -Out of stock
N-Deacetylcolchicine is an inhibitor of tubulin polymerization (IC50 = 3 µM for bovine brain tubulin) and a derivative of the microtubule polymerization inhibitor colchicine (Item No. 9000760).{24891} It stimulates tubulin GTPase activity.{51178}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21697 -Out of stock
N-Deacetylcolchicine is an inhibitor of tubulin polymerization (IC50 = 3 µM for bovine brain tubulin) and a derivative of the microtubule polymerization inhibitor colchicine (Item No. 9000760).{24891} It stimulates tubulin GTPase activity.{51178}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21697 -Out of stock
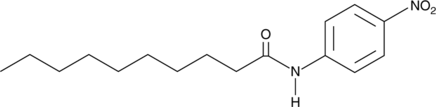
N-Decanoyl p-nitroaniline (DepNA) is one of several nitroaniline fatty acid amides which can be used to measure fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) activity.{8928} FAAH is a relatively unselective enzyme in that it accepts a variety of amide head groups other than the ethanolamine of its endogenous substrate anandamide (AEA). It also will hydrolyze fatty acid amides with fewer carbons and fewer double bonds than arachidonate. Exposure of DepNA to FAAH activity results in the release of the yellow colorimetric dye p-nitroaniline (ε = 13,500 at 410 nm). This allows the fast and convenient measurement of FAAH activity using a 96 well plate spectrophotometer.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10005851 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
N-Decanoyl p-nitroaniline (DepNA) is one of several nitroaniline fatty acid amides which can be used to measure fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) activity.{8928} FAAH is a relatively unselective enzyme in that it accepts a variety of amide head groups other than the ethanolamine of its endogenous substrate anandamide (AEA). It also will hydrolyze fatty acid amides with fewer carbons and fewer double bonds than arachidonate. Exposure of DepNA to FAAH activity results in the release of the yellow colorimetric dye p-nitroaniline (ε = 13,500 at 410 nm). This allows the fast and convenient measurement of FAAH activity using a 96 well plate spectrophotometer.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10005851 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
N-Decanoyl p-nitroaniline (DepNA) is one of several nitroaniline fatty acid amides which can be used to measure fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) activity.{8928} FAAH is a relatively unselective enzyme in that it accepts a variety of amide head groups other than the ethanolamine of its endogenous substrate anandamide (AEA). It also will hydrolyze fatty acid amides with fewer carbons and fewer double bonds than arachidonate. Exposure of DepNA to FAAH activity results in the release of the yellow colorimetric dye p-nitroaniline (ε = 13,500 at 410 nm). This allows the fast and convenient measurement of FAAH activity using a 96 well plate spectrophotometer.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10005851 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
N-Decanoyl p-nitroaniline (DepNA) is one of several nitroaniline fatty acid amides which can be used to measure fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) activity.{8928} FAAH is a relatively unselective enzyme in that it accepts a variety of amide head groups other than the ethanolamine of its endogenous substrate anandamide (AEA). It also will hydrolyze fatty acid amides with fewer carbons and fewer double bonds than arachidonate. Exposure of DepNA to FAAH activity results in the release of the yellow colorimetric dye p-nitroaniline (ε = 13,500 at 410 nm). This allows the fast and convenient measurement of FAAH activity using a 96 well plate spectrophotometer.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10005851 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density. A promising field of study involves controlling bacterial infections by quenching their quorum sensing systems. The expression of specific target genes, such as transcriptional regulators belonging to the LuxIR family of proteins, is coordinated by synthesis of diffusible acylhomoserine lactone (AHL) molecules. N-decanoyl-L-Homoserine lactone is a small diffusible signaling molecule involved in quorum sensing, thereby controlling gene expression and affecting cellular metabolism.{16304} The applications of this molecule include regulation of virulence and exoproteases.{15399}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10011201 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density. A promising field of study involves controlling bacterial infections by quenching their quorum sensing systems. The expression of specific target genes, such as transcriptional regulators belonging to the LuxIR family of proteins, is coordinated by synthesis of diffusible acylhomoserine lactone (AHL) molecules. N-decanoyl-L-Homoserine lactone is a small diffusible signaling molecule involved in quorum sensing, thereby controlling gene expression and affecting cellular metabolism.{16304} The applications of this molecule include regulation of virulence and exoproteases.{15399}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10011201 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density. A promising field of study involves controlling bacterial infections by quenching their quorum sensing systems. The expression of specific target genes, such as transcriptional regulators belonging to the LuxIR family of proteins, is coordinated by synthesis of diffusible acylhomoserine lactone (AHL) molecules. N-decanoyl-L-Homoserine lactone is a small diffusible signaling molecule involved in quorum sensing, thereby controlling gene expression and affecting cellular metabolism.{16304} The applications of this molecule include regulation of virulence and exoproteases.{15399}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10011201 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density. A promising field of study involves controlling bacterial infections by quenching their quorum sensing systems. The expression of specific target genes, such as transcriptional regulators belonging to the LuxIR family of proteins, is coordinated by synthesis of diffusible acylhomoserine lactone (AHL) molecules. N-decanoyl-L-Homoserine lactone is a small diffusible signaling molecule involved in quorum sensing, thereby controlling gene expression and affecting cellular metabolism.{16304} The applications of this molecule include regulation of virulence and exoproteases.{15399}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10011201 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
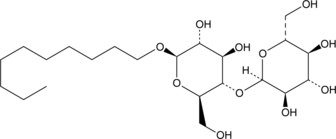
n-Decyl-β-D-maltoside is a nonionic surfactant that is commonly used to solubilize and stabilize membrane proteins.{46041,46042} It has a critical micelle concentration (CMC) value of 1.8 mM and has been used in the expression of functional recombinant GPCRs.
Brand:CaymanSKU:25704 - 1 gAvailable on backorder
n-Decyl-β-D-maltoside is a nonionic surfactant that is commonly used to solubilize and stabilize membrane proteins.{46041,46042} It has a critical micelle concentration (CMC) value of 1.8 mM and has been used in the expression of functional recombinant GPCRs.
Brand:CaymanSKU:25704 - 5 gAvailable on backorder
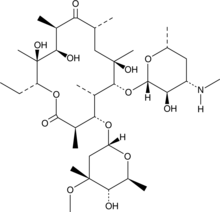
N-Demethylerythromycin A is a metabolite of erythromycin (Item No. 16486).{43941} It is also a fungal metabolite that has been found in S. erythreus and a potential impurity in commercial preparations of erythromycin.{35178}
Brand:CaymanSKU:27988 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
N-Demethylerythromycin A is a metabolite of erythromycin (Item No. 16486).{43941} It is also a fungal metabolite that has been found in S. erythreus and a potential impurity in commercial preparations of erythromycin.{35178}
Brand:CaymanSKU:27988 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
N-Demethylerythromycin A is a metabolite of erythromycin (Item No. 16486).{43941} It is also a fungal metabolite that has been found in S. erythreus and a potential impurity in commercial preparations of erythromycin.{35178}
Brand:CaymanSKU:27988 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
N-Demethylerythromycin A is a metabolite of erythromycin (Item No. 16486).{43941} It is also a fungal metabolite that has been found in S. erythreus and a potential impurity in commercial preparations of erythromycin.{35178}
Brand:CaymanSKU:27988 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
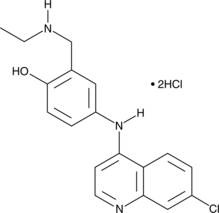
N-desethyl Amodiaquine is a primary metabolite of the antimalarial compound aminodiaquine (Item No. 15954), produced by the action of cytochrome P450 isoform 2C8.{26894} N-desethyl Amodiaquine is highly active against P. falciparum and can synergize with amodiaquine.{26895}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20822 -Out of stock
N-desethyl Amodiaquine is a primary metabolite of the antimalarial compound aminodiaquine (Item No. 15954), produced by the action of cytochrome P450 isoform 2C8.{26894} N-desethyl Amodiaquine is highly active against P. falciparum and can synergize with amodiaquine.{26895}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20822 -Out of stock
N-desethyl Amodiaquine is a primary metabolite of the antimalarial compound aminodiaquine (Item No. 15954), produced by the action of cytochrome P450 isoform 2C8.{26894} N-desethyl Amodiaquine is highly active against P. falciparum and can synergize with amodiaquine.{26895}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20822 -Out of stock
N-desethyl Sunitinib is an active metabolite of sunitinib (Item No. 13159), a small molecule, multi-targeted receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor.{17043,40284} N-desethyl Sunitinib is formed when sunitinib undergoes N-de-ethylation by the cytochrome P450 (CYP) isomer CYP3A4.{40284} N-desethyl Sunitinib is pharmacologically active having similar inhibitory activity to sunitinib.
Brand:CaymanSKU:22292 -Out of stock
N-desethyl Sunitinib is an active metabolite of sunitinib (Item No. 13159), a small molecule, multi-targeted receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor.{17043,40284} N-desethyl Sunitinib is formed when sunitinib undergoes N-de-ethylation by the cytochrome P450 (CYP) isomer CYP3A4.{40284} N-desethyl Sunitinib is pharmacologically active having similar inhibitory activity to sunitinib.
Brand:CaymanSKU:22292 -Out of stock
N-desethyl Sunitinib is an active metabolite of sunitinib (Item No. 13159), a small molecule, multi-targeted receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor.{17043,40284} N-desethyl Sunitinib is formed when sunitinib undergoes N-de-ethylation by the cytochrome P450 (CYP) isomer CYP3A4.{40284} N-desethyl Sunitinib is pharmacologically active having similar inhibitory activity to sunitinib.
Brand:CaymanSKU:22292 -Out of stock
N-desethyl Sunitinib is an active metabolite of sunitinib (Item No. 13159), a small molecule, multi-targeted receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor.{17043,40284} N-desethyl Sunitinib is formed when sunitinib undergoes N-de-ethylation by the cytochrome P450 (CYP) isomer CYP3A4.{40284} N-desethyl Sunitinib is pharmacologically active having similar inhibitory activity to sunitinib.
Brand:CaymanSKU:22292 -Out of stock
N-Desethyl vardenafil is a metabolite of vardenafil (Item No. 14930), a phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitor, that is formed by the action of cytochrome P450 (CYP)3A4 and CYP3A5.{31630}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9001800 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
N-Desethyl vardenafil is a metabolite of vardenafil (Item No. 14930), a phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitor, that is formed by the action of cytochrome P450 (CYP)3A4 and CYP3A5.{31630}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9001800 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
N-Desethyl vardenafil is a metabolite of vardenafil (Item No. 14930), a phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitor, that is formed by the action of cytochrome P450 (CYP)3A4 and CYP3A5.{31630}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9001800 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
Amiodarone (Item No. 15213) is a class III antiarrhythmic agent, in that it prolongs both cardiac action potential and refractoriness by blocking potassium currents.{22478} It inhibits the voltage-gated potassium channel hERG, also known as KCNH2, with an IC50 value of 1 µM.{24593} In humans, cytochrome P450 3A is involved in the metabolism of amiodarone.{29074} N-Desethylamiodarone is the major, active metabolite of amiodarone. This compound has been used as an analytical reference standard for quantifying amiodarone in plasma samples.{29075}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9000537 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Amiodarone (Item No. 15213) is a class III antiarrhythmic agent, in that it prolongs both cardiac action potential and refractoriness by blocking potassium currents.{22478} It inhibits the voltage-gated potassium channel hERG, also known as KCNH2, with an IC50 value of 1 µM.{24593} In humans, cytochrome P450 3A is involved in the metabolism of amiodarone.{29074} N-Desethylamiodarone is the major, active metabolite of amiodarone. This compound has been used as an analytical reference standard for quantifying amiodarone in plasma samples.{29075}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9000537 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
Amiodarone (Item No. 15213) is a class III antiarrhythmic agent, in that it prolongs both cardiac action potential and refractoriness by blocking potassium currents.{22478} It inhibits the voltage-gated potassium channel hERG, also known as KCNH2, with an IC50 value of 1 µM.{24593} In humans, cytochrome P450 3A is involved in the metabolism of amiodarone.{29074} N-Desethylamiodarone is the major, active metabolite of amiodarone. This compound has been used as an analytical reference standard for quantifying amiodarone in plasma samples.{29075}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9000537 - 250 mgAvailable on backorder
Amiodarone (Item No. 15213) is a class III antiarrhythmic agent, in that it prolongs both cardiac action potential and refractoriness by blocking potassium currents.{22478} It inhibits the voltage-gated potassium channel hERG, also known as KCNH2, with an IC50 value of 1 µM.{24593} In humans, cytochrome P450 3A is involved in the metabolism of amiodarone.{29074} N-Desethylamiodarone is the major, active metabolite of amiodarone. This compound has been used as an analytical reference standard for quantifying amiodarone in plasma samples.{29075}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9000537 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
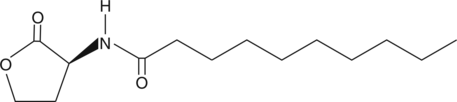
N-desmethyl Bendamustine is an active metabolite of the DNA alkylating agent bendamustine (Item No. 23693).{49043} N-desmethyl Bendamustine is formed through demethylation of the benzimidazole ring in bendamustine by the cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoform CYP1A2. It inhibits proliferation of non-cancerous peripheral blood leukocytes (PBLs; IC50 = 45 µM) and SU-DHL-1, SU-DHL-9, and Daudi lymphoma cells (IC50s = 270, 170, and 120 µM, respectively).
Brand:CaymanSKU:27171 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
N-desmethyl Bendamustine is an active metabolite of the DNA alkylating agent bendamustine (Item No. 23693).{49043} N-desmethyl Bendamustine is formed through demethylation of the benzimidazole ring in bendamustine by the cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoform CYP1A2. It inhibits proliferation of non-cancerous peripheral blood leukocytes (PBLs; IC50 = 45 µM) and SU-DHL-1, SU-DHL-9, and Daudi lymphoma cells (IC50s = 270, 170, and 120 µM, respectively).
Brand:CaymanSKU:27171 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
N-desmethyl Imatinib is a major active metabolite of imatinib (Item No. 13139), an anticancer agent that selectively targets tyrosine kinases, including Bcr-ABL, platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR), and KIT.{17064,17065} N-desmethyl Imatinib is formed when imatinib undergoes demethylation by the cytochrome P450 (CYP) isomer CYP3A4.{40229} N-desmethyl Imatinib has the same in vitro potency at Bcr-ABL kinase as imatinib (IC50 = 38 nM for both) but is only present in plasma at 10-15% of the levels of imatinib, indicating the majority of the anticancer activity can be attributed to the parent compound.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
N-desmethyl Imatinib is a major active metabolite of imatinib (Item No. 13139), an anticancer agent that selectively targets tyrosine kinases, including Bcr-ABL, platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR), and KIT.{17064,17065} N-desmethyl Imatinib is formed when imatinib undergoes demethylation by the cytochrome P450 (CYP) isomer CYP3A4.{40229} N-desmethyl Imatinib has the same in vitro potency at Bcr-ABL kinase as imatinib (IC50 = 38 nM for both) but is only present in plasma at 10-15% of the levels of imatinib, indicating the majority of the anticancer activity can be attributed to the parent compound.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
N-desmethyl Imatinib is a major active metabolite of imatinib (Item No. 13139), an anticancer agent that selectively targets tyrosine kinases, including Bcr-ABL, platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR), and KIT.{17064,17065} N-desmethyl Imatinib is formed when imatinib undergoes demethylation by the cytochrome P450 (CYP) isomer CYP3A4.{40229} N-desmethyl Imatinib has the same in vitro potency at Bcr-ABL kinase as imatinib (IC50 = 38 nM for both) but is only present in plasma at 10-15% of the levels of imatinib, indicating the majority of the anticancer activity can be attributed to the parent compound.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
N-desmethyl Imatinib is a major active metabolite of imatinib (Item No. 13139), an anticancer agent that selectively targets tyrosine kinases, including Bcr-ABL, platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR), and KIT.{17064,17065} N-desmethyl Imatinib is formed when imatinib undergoes demethylation by the cytochrome P450 (CYP) isomer CYP3A4.{40229} N-desmethyl Imatinib has the same in vitro potency at Bcr-ABL kinase as imatinib (IC50 = 38 nM for both) but is only present in plasma at 10-15% of the levels of imatinib, indicating the majority of the anticancer activity can be attributed to the parent compound.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
N-desmethyl Ivabradine is an active metabolite of ivabradine (Item No. 15868).{42971} Ivabradine is metabolized by the cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoform CYP3A4.
Brand:CaymanSKU:27808 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
N-desmethyl Ivabradine is an active metabolite of ivabradine (Item No. 15868).{42971} Ivabradine is metabolized by the cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoform CYP3A4.
Brand:CaymanSKU:27808 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
N-desmethyl Ivabradine is an active metabolite of ivabradine (Item No. 15868).{42971} Ivabradine is metabolized by the cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoform CYP3A4.
Brand:CaymanSKU:27808 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
N-desmethyl Levofloxacin is an active metabolite of the fluoroquinolone antibiotic levofloxacin (Item No. 20382).{45220} It is active against S. aureus, S. epidermidis, B. subtilis, E. coli, P. aeruginosa, and K. pneumoniae (MICs = 4, 1, 1, 0.012, >4, and 0.25 μg/ml, respectively).
Brand:CaymanSKU:27178 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
N-desmethyl Levofloxacin is an active metabolite of the fluoroquinolone antibiotic levofloxacin (Item No. 20382).{45220} It is active against S. aureus, S. epidermidis, B. subtilis, E. coli, P. aeruginosa, and K. pneumoniae (MICs = 4, 1, 1, 0.012, >4, and 0.25 μg/ml, respectively).
Brand:CaymanSKU:27178 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
N-desmethyl Levofloxacin is an active metabolite of the fluoroquinolone antibiotic levofloxacin (Item No. 20382).{45220} It is active against S. aureus, S. epidermidis, B. subtilis, E. coli, P. aeruginosa, and K. pneumoniae (MICs = 4, 1, 1, 0.012, >4, and 0.25 μg/ml, respectively).
Brand:CaymanSKU:27178 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
N-desmethyl Rosiglitazone is a major metabolite of rosiglitazone (Item Nos. 71740 | 71742 | 11884), a potent and selective PPARγ ligand present in formulations that have been used to treat type 2 diabetes.{8461,41078} Rosiglitazone is metabolized by the cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoform CYP2C8 to form N-desmethyl rosiglitazone.
Brand:CaymanSKU:22103 -Out of stock
N-desmethyl Rosiglitazone is a major metabolite of rosiglitazone (Item Nos. 71740 | 71742 | 11884), a potent and selective PPARγ ligand present in formulations that have been used to treat type 2 diabetes.{8461,41078} Rosiglitazone is metabolized by the cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoform CYP2C8 to form N-desmethyl rosiglitazone.
Brand:CaymanSKU:22103 -Out of stock
N-desmethyl Rosiglitazone is a major metabolite of rosiglitazone (Item Nos. 71740 | 71742 | 11884), a potent and selective PPARγ ligand present in formulations that have been used to treat type 2 diabetes.{8461,41078} Rosiglitazone is metabolized by the cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoform CYP2C8 to form N-desmethyl rosiglitazone.
Brand:CaymanSKU:22103 -Out of stock
N-Desmethyl sildenafil is a major metabolite of sildenafil (Item Nos. 10008671 | 14008).{29612,29611,42395} N-Desmethyl sildenafil is formed via oxidative metabolism of sildenafil by the cytochrome (CYP) P450 isoforms CYP3A4, CYP3A5, and CYP3A7.{42395}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
N-Desmethyl sildenafil is a major metabolite of sildenafil (Item Nos. 10008671 | 14008).{29612,29611,42395} N-Desmethyl sildenafil is formed via oxidative metabolism of sildenafil by the cytochrome (CYP) P450 isoforms CYP3A4, CYP3A5, and CYP3A7.{42395}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
N-Desmethyl sildenafil is a major metabolite of sildenafil (Item Nos. 10008671 | 14008).{29612,29611,42395} N-Desmethyl sildenafil is formed via oxidative metabolism of sildenafil by the cytochrome (CYP) P450 isoforms CYP3A4, CYP3A5, and CYP3A7.{42395}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
N-Desmethyl sildenafil is a major metabolite of sildenafil (Item Nos. 10008671 | 14008).{29612,29611,42395} N-Desmethyl sildenafil is formed via oxidative metabolism of sildenafil by the cytochrome (CYP) P450 isoforms CYP3A4, CYP3A5, and CYP3A7.{42395}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder