Cayman
Showing 30901–31050 of 45550 results
-
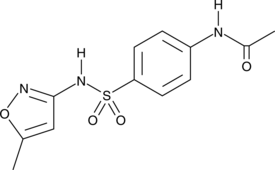
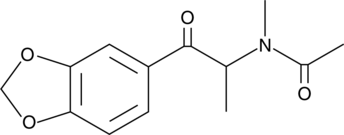
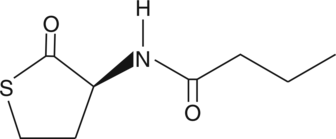
N-acetyl Sulfamethoxazole is a metabolite of sulfamethoxazole, an antibiotic with antiviral activity, that can be detected in urine.{27032,28148}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
-
N-acetyl Sulfamethoxazole is a metabolite of sulfamethoxazole, an antibiotic with antiviral activity, that can be detected in urine.{27032,28148}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
-
N-acetyl Sulfamethoxazole is a metabolite of sulfamethoxazole, an antibiotic with antiviral activity, that can be detected in urine.{27032,28148}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
-
N-acetyl Sulfamethoxazole is a metabolite of sulfamethoxazole, an antibiotic with antiviral activity, that can be detected in urine.{27032,28148}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
-
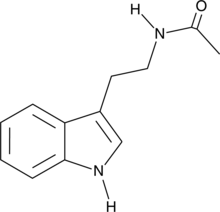
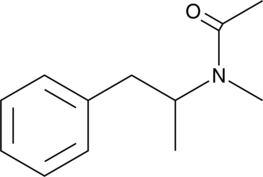
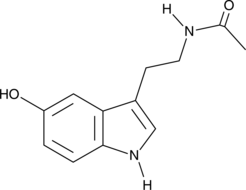
N-acetyl Tryptamine is a structural analog of melatonin (5-methoxy-N-acetyltryptamine; Item No. 14427) that binds the melatonin MT2 receptor (Ki = 41 nM).{30340} It acts as a melatonin receptor antagonist in frog skin and chicken retina and as a partial agonist in rabbit retina.{30338,30339,26017} N-acetyl Tryptamine is also a reaction product of assays for serotonin N-acetyltransferase, the penultimate enzyme in the melatonin biosynthetic pathway.{30337}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
-
N-acetyl Tryptamine is a structural analog of melatonin (5-methoxy-N-acetyltryptamine; Item No. 14427) that binds the melatonin MT2 receptor (Ki = 41 nM).{30340} It acts as a melatonin receptor antagonist in frog skin and chicken retina and as a partial agonist in rabbit retina.{30338,30339,26017} N-acetyl Tryptamine is also a reaction product of assays for serotonin N-acetyltransferase, the penultimate enzyme in the melatonin biosynthetic pathway.{30337}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
-
N-acetyl Tryptamine is a structural analog of melatonin (5-methoxy-N-acetyltryptamine; Item No. 14427) that binds the melatonin MT2 receptor (Ki = 41 nM).{30340} It acts as a melatonin receptor antagonist in frog skin and chicken retina and as a partial agonist in rabbit retina.{30338,30339,26017} N-acetyl Tryptamine is also a reaction product of assays for serotonin N-acetyltransferase, the penultimate enzyme in the melatonin biosynthetic pathway.{30337}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
-
N-acetyl Tryptamine is a structural analog of melatonin (5-methoxy-N-acetyltryptamine; Item No. 14427) that binds the melatonin MT2 receptor (Ki = 41 nM).{30340} It acts as a melatonin receptor antagonist in frog skin and chicken retina and as a partial agonist in rabbit retina.{30338,30339,26017} N-acetyl Tryptamine is also a reaction product of assays for serotonin N-acetyltransferase, the penultimate enzyme in the melatonin biosynthetic pathway.{30337}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
-
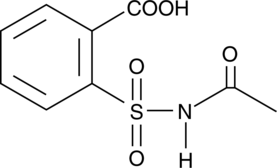
N-acetyl-2-carboxy Benzenesulfonamide is a structural analog of aspirin that acts as a non-selective inhibitor of cyclooxygenase (COX) with a COX-2 selectivity index of 0.23.{13010} In vitro studies showed that N-acetyl-2-carboxy Benzenesulfonamide is a more potent inhibitor of COX-1/COX-2 with IC50 values of 0.06 µM and 0.25 µM, respectively, than aspirin with IC50 values of 0.35 µM and 2.4 µM, respectively.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008284 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
-
N-acetyl-2-carboxy Benzenesulfonamide is a structural analog of aspirin that acts as a non-selective inhibitor of cyclooxygenase (COX) with a COX-2 selectivity index of 0.23.{13010} In vitro studies showed that N-acetyl-2-carboxy Benzenesulfonamide is a more potent inhibitor of COX-1/COX-2 with IC50 values of 0.06 µM and 0.25 µM, respectively, than aspirin with IC50 values of 0.35 µM and 2.4 µM, respectively.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008284 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
-
N-acetyl-2-carboxy Benzenesulfonamide is a structural analog of aspirin that acts as a non-selective inhibitor of cyclooxygenase (COX) with a COX-2 selectivity index of 0.23.{13010} In vitro studies showed that N-acetyl-2-carboxy Benzenesulfonamide is a more potent inhibitor of COX-1/COX-2 with IC50 values of 0.06 µM and 0.25 µM, respectively, than aspirin with IC50 values of 0.35 µM and 2.4 µM, respectively.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008284 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
-
N-acetyl-2-carboxy Benzenesulfonamide is a structural analog of aspirin that acts as a non-selective inhibitor of cyclooxygenase (COX) with a COX-2 selectivity index of 0.23.{13010} In vitro studies showed that N-acetyl-2-carboxy Benzenesulfonamide is a more potent inhibitor of COX-1/COX-2 with IC50 values of 0.06 µM and 0.25 µM, respectively, than aspirin with IC50 values of 0.35 µM and 2.4 µM, respectively.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008284 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
-
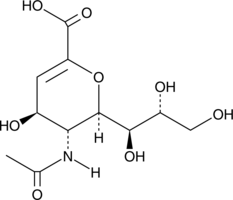
N-acetyl-2,3-dehydro-2-Deoxyneuraminic acid (DANA) is an inhibitor of human neuraminidases (sialidases) NEU1-4 (IC50s = 143, 43, 61, and 74 μM, respectively).{38566} In vivo, DANA (30 μl of a 5 mM solution) reduces latency to first seizure and increases seizure duration in a rat model of potassium-induced seizures.{38567}
Brand:CaymanSKU:19939 -Available on backorder
-
N-acetyl-2,3-dehydro-2-Deoxyneuraminic acid (DANA) is an inhibitor of human neuraminidases (sialidases) NEU1-4 (IC50s = 143, 43, 61, and 74 μM, respectively).{38566} In vivo, DANA (30 μl of a 5 mM solution) reduces latency to first seizure and increases seizure duration in a rat model of potassium-induced seizures.{38567}
Brand:CaymanSKU:19939 -Available on backorder
-
N-acetyl-2,3-dehydro-2-Deoxyneuraminic acid (DANA) is an inhibitor of human neuraminidases (sialidases) NEU1-4 (IC50s = 143, 43, 61, and 74 μM, respectively).{38566} In vivo, DANA (30 μl of a 5 mM solution) reduces latency to first seizure and increases seizure duration in a rat model of potassium-induced seizures.{38567}
Brand:CaymanSKU:19939 -Available on backorder
-
N-acetyl-3,4-Methylenedioxymethcathinone (N-acetyl-3,4-MDMC) is an acetylated analog of methylone (Item No. 10986), the MDMA-type designer drug that has been detected in products marketed as bath salts, plant food, and tablets.{19508,19756} The biological actions of N-acetyl-3,4-MDMC are unknown. This product is intended for forensic and research purposes.
Brand:CaymanSKU:9001492 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
-
N-acetyl-3,4-Methylenedioxymethcathinone (N-acetyl-3,4-MDMC) is an acetylated analog of methylone (Item No. 10986), the MDMA-type designer drug that has been detected in products marketed as bath salts, plant food, and tablets.{19508,19756} The biological actions of N-acetyl-3,4-MDMC are unknown. This product is intended for forensic and research purposes.
Brand:CaymanSKU:9001492 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
-
N-acetyl-3,4-Methylenedioxymethcathinone (N-acetyl-3,4-MDMC) is an acetylated analog of methylone (Item No. 10986), the MDMA-type designer drug that has been detected in products marketed as bath salts, plant food, and tablets.{19508,19756} The biological actions of N-acetyl-3,4-MDMC are unknown. This product is intended for forensic and research purposes.
Brand:CaymanSKU:9001492 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
-
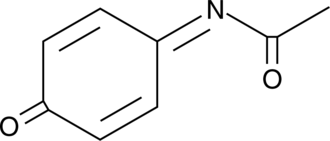
N-Acetyl-4-benzoquinone imine (NAPQI) is a cytochrome P450 3A4 and 2E1 metabolite of acetaminophen that can be toxic to the liver when acetaminophen is consumed in large doses.{7361} At therapeutic doses of acetaminophen, NAPQI is inactivated by conjugation with glutathione. However, following toxic doses of acetaminophen, available liver reserves of glutathione are quickly depleted due to clearance of excess NAPQI, which enables hepatic proteins to become covalently modified by reactive metabolites and eventually results in hepatocyte necrosis.{7361}
Brand:CaymanSKU:- -
N-Acetyl-4-benzoquinone imine (NAPQI) is a cytochrome P450 3A4 and 2E1 metabolite of acetaminophen that can be toxic to the liver when acetaminophen is consumed in large doses.{7361} At therapeutic doses of acetaminophen, NAPQI is inactivated by conjugation with glutathione. However, following toxic doses of acetaminophen, available liver reserves of glutathione are quickly depleted due to clearance of excess NAPQI, which enables hepatic proteins to become covalently modified by reactive metabolites and eventually results in hepatocyte necrosis.{7361}
Brand:CaymanSKU:- -
N-Acetyl-4-benzoquinone imine (NAPQI) is a cytochrome P450 3A4 and 2E1 metabolite of acetaminophen that can be toxic to the liver when acetaminophen is consumed in large doses.{7361} At therapeutic doses of acetaminophen, NAPQI is inactivated by conjugation with glutathione. However, following toxic doses of acetaminophen, available liver reserves of glutathione are quickly depleted due to clearance of excess NAPQI, which enables hepatic proteins to become covalently modified by reactive metabolites and eventually results in hepatocyte necrosis.{7361}
Brand:CaymanSKU:- -
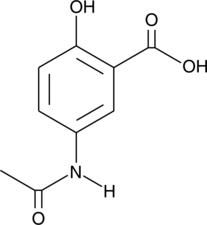
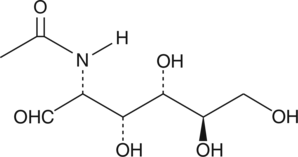
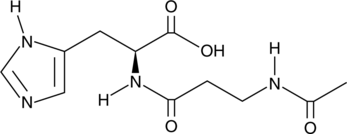
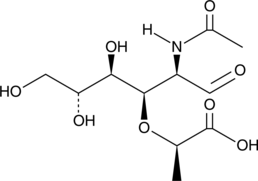
N-acetyl-5-Aminosalicylic acid is a metabolite of the anti-inflammatory agent 5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA; Item No. 70265) and its prodrug form, sulfasalazine (Item No. 15025).{42753,8455} It is formed in the liver, intestinal lumen, and colonic epithelial cells via N-acetyltransferases.{42754} It reduces IFN-γ binding to colonic epithelial cells by 24% when used at a concentration of 10 mM.{42756} N-acetyl-5-Aminosalicylic acid (100 µM) scavenges 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH; Item No. 14805) radicals in a cell-free assay and inhibits base hydroxylation in DNA stimulated by hydroxy radicals.{42753,42755} Unlike sulfasalazine, N-acetyl-5-aminosalicylic acid does not inhibit 15-hydroxy prostaglandin dehydrogenase (PGDH).{8455} Urinary levels of N-acetyl-5-aminosalicylic acid have been used as a marker of 5-ASA adherence in patients with inflammatory bowel disease.{42757}
Brand:CaymanSKU:27618 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
-
N-acetyl-5-Aminosalicylic acid is a metabolite of the anti-inflammatory agent 5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA; Item No. 70265) and its prodrug form, sulfasalazine (Item No. 15025).{42753,8455} It is formed in the liver, intestinal lumen, and colonic epithelial cells via N-acetyltransferases.{42754} It reduces IFN-γ binding to colonic epithelial cells by 24% when used at a concentration of 10 mM.{42756} N-acetyl-5-Aminosalicylic acid (100 µM) scavenges 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH; Item No. 14805) radicals in a cell-free assay and inhibits base hydroxylation in DNA stimulated by hydroxy radicals.{42753,42755} Unlike sulfasalazine, N-acetyl-5-aminosalicylic acid does not inhibit 15-hydroxy prostaglandin dehydrogenase (PGDH).{8455} Urinary levels of N-acetyl-5-aminosalicylic acid have been used as a marker of 5-ASA adherence in patients with inflammatory bowel disease.{42757}
Brand:CaymanSKU:27618 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
-
N-acetyl-5-Aminosalicylic acid is a metabolite of the anti-inflammatory agent 5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA; Item No. 70265) and its prodrug form, sulfasalazine (Item No. 15025).{42753,8455} It is formed in the liver, intestinal lumen, and colonic epithelial cells via N-acetyltransferases.{42754} It reduces IFN-γ binding to colonic epithelial cells by 24% when used at a concentration of 10 mM.{42756} N-acetyl-5-Aminosalicylic acid (100 µM) scavenges 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH; Item No. 14805) radicals in a cell-free assay and inhibits base hydroxylation in DNA stimulated by hydroxy radicals.{42753,42755} Unlike sulfasalazine, N-acetyl-5-aminosalicylic acid does not inhibit 15-hydroxy prostaglandin dehydrogenase (PGDH).{8455} Urinary levels of N-acetyl-5-aminosalicylic acid have been used as a marker of 5-ASA adherence in patients with inflammatory bowel disease.{42757}
Brand:CaymanSKU:27618 - 250 mgAvailable on backorder
-
N-acetyl-5-Aminosalicylic acid is a metabolite of the anti-inflammatory agent 5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA; Item No. 70265) and its prodrug form, sulfasalazine (Item No. 15025).{42753,8455} It is formed in the liver, intestinal lumen, and colonic epithelial cells via N-acetyltransferases.{42754} It reduces IFN-γ binding to colonic epithelial cells by 24% when used at a concentration of 10 mM.{42756} N-acetyl-5-Aminosalicylic acid (100 µM) scavenges 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH; Item No. 14805) radicals in a cell-free assay and inhibits base hydroxylation in DNA stimulated by hydroxy radicals.{42753,42755} Unlike sulfasalazine, N-acetyl-5-aminosalicylic acid does not inhibit 15-hydroxy prostaglandin dehydrogenase (PGDH).{8455} Urinary levels of N-acetyl-5-aminosalicylic acid have been used as a marker of 5-ASA adherence in patients with inflammatory bowel disease.{42757}
Brand:CaymanSKU:27618 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
-
N-acetyl-D-Galactosamine (GalNAc) is an amino sugar derivative of galactose and a component of O-GalNAc glycans.{61099,61100} It is transferred from UDP-GalNAc to the hydroxy group of protein serine or threonine residues by polypeptide GalNAc transferase, forming the Tn antigen, during the first step of mucin-type O-glycosylation.{61101,61100} GalNAc has been used as a targeting moiety for liver-targeted delivery of oligonucleotides.{61099}
Brand:CaymanSKU:31728 - 1 gAvailable on backorder
-
N-acetyl-D-Galactosamine (GalNAc) is an amino sugar derivative of galactose and a component of O-GalNAc glycans.{61099,61100} It is transferred from UDP-GalNAc to the hydroxy group of protein serine or threonine residues by polypeptide GalNAc transferase, forming the Tn antigen, during the first step of mucin-type O-glycosylation.{61101,61100} GalNAc has been used as a targeting moiety for liver-targeted delivery of oligonucleotides.{61099}
Brand:CaymanSKU:31728 - 5 gAvailable on backorder
-
N-acetyl-D-Galactosamine (GalNAc) is an amino sugar derivative of galactose and a component of O-GalNAc glycans.{61099,61100} It is transferred from UDP-GalNAc to the hydroxy group of protein serine or threonine residues by polypeptide GalNAc transferase, forming the Tn antigen, during the first step of mucin-type O-glycosylation.{61101,61100} GalNAc has been used as a targeting moiety for liver-targeted delivery of oligonucleotides.{61099}
Brand:CaymanSKU:31728 - 500 mgAvailable on backorder
-
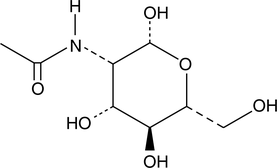
N-acetyl-D-Glucosamine (GlcNAc) is a monosaccharide derivative of glucose. It is released by the action of O-GlcNAcase, in mammalian systems from proteins that have been post-translationally modified with O-GlcNAc. Levels of O-GlcNAcylation proteins from Alzheimer’s disease brain extracts are decreased as compared to that in controls, suggesting that release of GlcNAc may contribute to pathogenesis.{16842} In E. coli, GlcNAc induces the expression of multidrug exporter genes, indicating that this sugar can alter gene expression.{16842} GlcNAc is also the monomeric unit of chitin, which is found in fungi and many invertebrates, including crustaceans, insects, and nematodes. For this reason, chemicals that inhibit the incorporation of GlcNAc into chitin are cytotoxic to these organisms.
Brand:CaymanSKU:- -
N-acetyl-D-Glucosamine (GlcNAc) is a monosaccharide derivative of glucose. It is released by the action of O-GlcNAcase, in mammalian systems from proteins that have been post-translationally modified with O-GlcNAc. Levels of O-GlcNAcylation proteins from Alzheimer’s disease brain extracts are decreased as compared to that in controls, suggesting that release of GlcNAc may contribute to pathogenesis.{16842} In E. coli, GlcNAc induces the expression of multidrug exporter genes, indicating that this sugar can alter gene expression.{16842} GlcNAc is also the monomeric unit of chitin, which is found in fungi and many invertebrates, including crustaceans, insects, and nematodes. For this reason, chemicals that inhibit the incorporation of GlcNAc into chitin are cytotoxic to these organisms.
Brand:CaymanSKU:- -
N-acetyl-D-Glucosamine (GlcNAc) is a monosaccharide derivative of glucose. It is released by the action of O-GlcNAcase, in mammalian systems from proteins that have been post-translationally modified with O-GlcNAc. Levels of O-GlcNAcylation proteins from Alzheimer’s disease brain extracts are decreased as compared to that in controls, suggesting that release of GlcNAc may contribute to pathogenesis.{16842} In E. coli, GlcNAc induces the expression of multidrug exporter genes, indicating that this sugar can alter gene expression.{16842} GlcNAc is also the monomeric unit of chitin, which is found in fungi and many invertebrates, including crustaceans, insects, and nematodes. For this reason, chemicals that inhibit the incorporation of GlcNAc into chitin are cytotoxic to these organisms.
Brand:CaymanSKU:- -
N-acetyl-D-Glucosamine (GlcNAc) is a monosaccharide derivative of glucose. It is released by the action of O-GlcNAcase, in mammalian systems from proteins that have been post-translationally modified with O-GlcNAc. Levels of O-GlcNAcylation proteins from Alzheimer’s disease brain extracts are decreased as compared to that in controls, suggesting that release of GlcNAc may contribute to pathogenesis.{16842} In E. coli, GlcNAc induces the expression of multidrug exporter genes, indicating that this sugar can alter gene expression.{16842} GlcNAc is also the monomeric unit of chitin, which is found in fungi and many invertebrates, including crustaceans, insects, and nematodes. For this reason, chemicals that inhibit the incorporation of GlcNAc into chitin are cytotoxic to these organisms.
Brand:CaymanSKU:- -
N-acetyl-D-Lactosamine is a disaccharide consisting of galactose and N-acetylglucose. It occurs naturally as a structural element in a variety of glycoconjugates.{33091} N-acetyl-D-Lactosamine is used to characterize lectins. {33090}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21043 -Out of stock
-
N-acetyl-D-Lactosamine is a disaccharide consisting of galactose and N-acetylglucose. It occurs naturally as a structural element in a variety of glycoconjugates.{33091} N-acetyl-D-Lactosamine is used to characterize lectins. {33090}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21043 -Out of stock
-
N-acetyl-D-Lactosamine is a disaccharide consisting of galactose and N-acetylglucose. It occurs naturally as a structural element in a variety of glycoconjugates.{33091} N-acetyl-D-Lactosamine is used to characterize lectins. {33090}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21043 -Out of stock
-
N-acetyl-D-Lactosamine is a disaccharide consisting of galactose and N-acetylglucose. It occurs naturally as a structural element in a variety of glycoconjugates.{33091} N-acetyl-D-Lactosamine is used to characterize lectins. {33090}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21043 -Out of stock
-
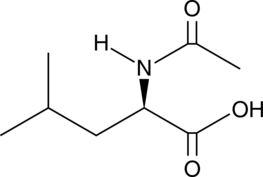
N-acetyl-D-Leucine is a derivative of D-leucine and a substrate for various enzymes in the amidohydrolase superfamily.{48994} It has been used to characterize the function of amidohydrolase enzymes from B. bronchiseptica, S. coelicolor, and G. oxydans.
Brand:CaymanSKU:30489 - 1 gAvailable on backorder
-
N-acetyl-D-Leucine is a derivative of D-leucine and a substrate for various enzymes in the amidohydrolase superfamily.{48994} It has been used to characterize the function of amidohydrolase enzymes from B. bronchiseptica, S. coelicolor, and G. oxydans.
Brand:CaymanSKU:30489 - 500 mgAvailable on backorder
-
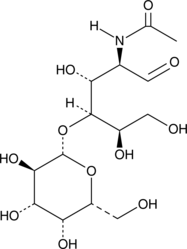
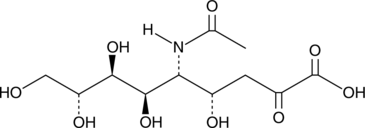
Sialic acids, commonly present as terminal carbohydrates on glycoconjugates, are essential for a variety of cellular functions including cell adhesion and signal recognition as well as the formation and progression of tumors.{16261} Disruption of sialic acid biosynthesis can result in severe glomerular proteinuria or neuromuscular disorders such as hereditary inclusion body myopathy (HIBM).{16263} N-Acetyl-D-mannosamine (ManNAc) is the precursor of all physiological sialic acids. Intraperitoneal injection of ManNAc twice daily at 1,000 mg/kg in C57BL/6 mice for 13 days leads to increased sialylation in kidney, liver, blood cells, brain, spinal cord, muscle, heart, lung, and spleen.{16262} ManNAc reverses hyposialylation and improves glomerular integrity in GneM712T/M712T mice whose key enzyme for sialic acid production has been deleted and may prove therapeutic in the treatment of HIBM.{16263}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10011060 - 1 gAvailable on backorder
-
Sialic acids, commonly present as terminal carbohydrates on glycoconjugates, are essential for a variety of cellular functions including cell adhesion and signal recognition as well as the formation and progression of tumors.{16261} Disruption of sialic acid biosynthesis can result in severe glomerular proteinuria or neuromuscular disorders such as hereditary inclusion body myopathy (HIBM).{16263} N-Acetyl-D-mannosamine (ManNAc) is the precursor of all physiological sialic acids. Intraperitoneal injection of ManNAc twice daily at 1,000 mg/kg in C57BL/6 mice for 13 days leads to increased sialylation in kidney, liver, blood cells, brain, spinal cord, muscle, heart, lung, and spleen.{16262} ManNAc reverses hyposialylation and improves glomerular integrity in GneM712T/M712T mice whose key enzyme for sialic acid production has been deleted and may prove therapeutic in the treatment of HIBM.{16263}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10011060 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
-
Sialic acids, commonly present as terminal carbohydrates on glycoconjugates, are essential for a variety of cellular functions including cell adhesion and signal recognition as well as the formation and progression of tumors.{16261} Disruption of sialic acid biosynthesis can result in severe glomerular proteinuria or neuromuscular disorders such as hereditary inclusion body myopathy (HIBM).{16263} N-Acetyl-D-mannosamine (ManNAc) is the precursor of all physiological sialic acids. Intraperitoneal injection of ManNAc twice daily at 1,000 mg/kg in C57BL/6 mice for 13 days leads to increased sialylation in kidney, liver, blood cells, brain, spinal cord, muscle, heart, lung, and spleen.{16262} ManNAc reverses hyposialylation and improves glomerular integrity in GneM712T/M712T mice whose key enzyme for sialic acid production has been deleted and may prove therapeutic in the treatment of HIBM.{16263}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10011060 - 250 mgAvailable on backorder
-
Sialic acids, commonly present as terminal carbohydrates on glycoconjugates, are essential for a variety of cellular functions including cell adhesion and signal recognition as well as the formation and progression of tumors.{16261} Disruption of sialic acid biosynthesis can result in severe glomerular proteinuria or neuromuscular disorders such as hereditary inclusion body myopathy (HIBM).{16263} N-Acetyl-D-mannosamine (ManNAc) is the precursor of all physiological sialic acids. Intraperitoneal injection of ManNAc twice daily at 1,000 mg/kg in C57BL/6 mice for 13 days leads to increased sialylation in kidney, liver, blood cells, brain, spinal cord, muscle, heart, lung, and spleen.{16262} ManNAc reverses hyposialylation and improves glomerular integrity in GneM712T/M712T mice whose key enzyme for sialic acid production has been deleted and may prove therapeutic in the treatment of HIBM.{16263}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10011060 - 500 mgAvailable on backorder
-
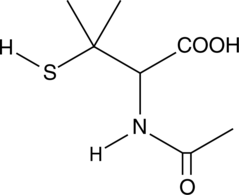
N-Acetyl-DL-penicillamine is a chelating agent.{45968,45972,45969} It inhibits the binding of methyl mercury to isolated human erythrocytes by 50% and removes 50% of methyl mercury ions from methyl mercury-loaded blood cells when used at a concentration of 1 mM.{45968,45972} N-Acetyl-DL-penicillamine (3 mmol/kg per day, p.o.) reduces the biological half-life of mercury and decreases liver, kidney, brain, and blood mercury levels, as well as increases urinary excretion of mercury in a concentration-dependent manner, in mice when administered following injection of methyl mercuric chloride. It decreases mercuric chloride-induced mortality in mice when administered orally at a dose of 1.6 mmol/kg.{45969} N-Acetyl-DL-penicillamine is also an analog of SNAP (Item No. 82250) that does not generate nitric oxide and has been used as a negative control in experiments using SNAP.{45970,45971}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10010404 - 1 gAvailable on backorder
-
N-Acetyl-DL-penicillamine is a chelating agent.{45968,45972,45969} It inhibits the binding of methyl mercury to isolated human erythrocytes by 50% and removes 50% of methyl mercury ions from methyl mercury-loaded blood cells when used at a concentration of 1 mM.{45968,45972} N-Acetyl-DL-penicillamine (3 mmol/kg per day, p.o.) reduces the biological half-life of mercury and decreases liver, kidney, brain, and blood mercury levels, as well as increases urinary excretion of mercury in a concentration-dependent manner, in mice when administered following injection of methyl mercuric chloride. It decreases mercuric chloride-induced mortality in mice when administered orally at a dose of 1.6 mmol/kg.{45969} N-Acetyl-DL-penicillamine is also an analog of SNAP (Item No. 82250) that does not generate nitric oxide and has been used as a negative control in experiments using SNAP.{45970,45971}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10010404 - 250 mgAvailable on backorder
-
N-Acetyl-DL-penicillamine is a chelating agent.{45968,45972,45969} It inhibits the binding of methyl mercury to isolated human erythrocytes by 50% and removes 50% of methyl mercury ions from methyl mercury-loaded blood cells when used at a concentration of 1 mM.{45968,45972} N-Acetyl-DL-penicillamine (3 mmol/kg per day, p.o.) reduces the biological half-life of mercury and decreases liver, kidney, brain, and blood mercury levels, as well as increases urinary excretion of mercury in a concentration-dependent manner, in mice when administered following injection of methyl mercuric chloride. It decreases mercuric chloride-induced mortality in mice when administered orally at a dose of 1.6 mmol/kg.{45969} N-Acetyl-DL-penicillamine is also an analog of SNAP (Item No. 82250) that does not generate nitric oxide and has been used as a negative control in experiments using SNAP.{45970,45971}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10010404 - 5 gAvailable on backorder
-
N-Acetyl-DL-penicillamine is a chelating agent.{45968,45972,45969} It inhibits the binding of methyl mercury to isolated human erythrocytes by 50% and removes 50% of methyl mercury ions from methyl mercury-loaded blood cells when used at a concentration of 1 mM.{45968,45972} N-Acetyl-DL-penicillamine (3 mmol/kg per day, p.o.) reduces the biological half-life of mercury and decreases liver, kidney, brain, and blood mercury levels, as well as increases urinary excretion of mercury in a concentration-dependent manner, in mice when administered following injection of methyl mercuric chloride. It decreases mercuric chloride-induced mortality in mice when administered orally at a dose of 1.6 mmol/kg.{45969} N-Acetyl-DL-penicillamine is also an analog of SNAP (Item No. 82250) that does not generate nitric oxide and has been used as a negative control in experiments using SNAP.{45970,45971}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10010404 - 500 mgAvailable on backorder
-
N-acetyl-L-Carnosine is a dipeptide and acetylated form of L-carnosine (Item No. 29825) that has been found in heart and skeletal muscle and has antioxidant and anticataract activities.{30665,57282} It reduces iron- and ascorbate-induced malondialdehyde (MDA) accumulation in liposomes when used at concentrations of 10 and 20 mM.{30665} Topical administration of N-acetyl-L-carnosine (1% v/v) reduces cortical opacities in a canine model of age-related cataracts.{57282}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
-
N-acetyl-L-Carnosine is a dipeptide and acetylated form of L-carnosine (Item No. 29825) that has been found in heart and skeletal muscle and has antioxidant and anticataract activities.{30665,57282} It reduces iron- and ascorbate-induced malondialdehyde (MDA) accumulation in liposomes when used at concentrations of 10 and 20 mM.{30665} Topical administration of N-acetyl-L-carnosine (1% v/v) reduces cortical opacities in a canine model of age-related cataracts.{57282}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
-
N-acetyl-L-Carnosine is a dipeptide and acetylated form of L-carnosine (Item No. 29825) that has been found in heart and skeletal muscle and has antioxidant and anticataract activities.{30665,57282} It reduces iron- and ascorbate-induced malondialdehyde (MDA) accumulation in liposomes when used at concentrations of 10 and 20 mM.{30665} Topical administration of N-acetyl-L-carnosine (1% v/v) reduces cortical opacities in a canine model of age-related cataracts.{57282}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
-
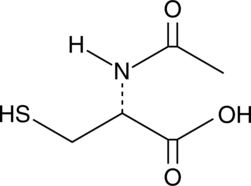
N-Acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC) is an antioxidant and precursor of glutathione that has multiple effects in cells and animals. As an antioxidant, NAC scavenges hydrogen peroxide, hydroxyl radical, and hypochlorous acid.{32379,32381} NAC may be deacetylated to cysteine, which can be combined with glutamate and glycine to produce reduced glutathione (Item No. 10007461), which serves to reduce hydroperoxides and detoxify xenobiotics.{32379,32381} The free sulfhydryl group of NAC can also hydrolyze disulfide bonds of mucins and other proteins, thus facilitating clearance of mucus.{32384} Through these actions, NAC inhibits DNA adduct formation, limits hepatotoxic effects of acetaminophen, and provides diverse cytoprotective effects in vivo.{32378,32379,32380,32381,32384,32385}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20261 -Available on backorder
-
N-Acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC) is an antioxidant and precursor of glutathione that has multiple effects in cells and animals. As an antioxidant, NAC scavenges hydrogen peroxide, hydroxyl radical, and hypochlorous acid.{32379,32381} NAC may be deacetylated to cysteine, which can be combined with glutamate and glycine to produce reduced glutathione (Item No. 10007461), which serves to reduce hydroperoxides and detoxify xenobiotics.{32379,32381} The free sulfhydryl group of NAC can also hydrolyze disulfide bonds of mucins and other proteins, thus facilitating clearance of mucus.{32384} Through these actions, NAC inhibits DNA adduct formation, limits hepatotoxic effects of acetaminophen, and provides diverse cytoprotective effects in vivo.{32378,32379,32380,32381,32384,32385}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20261 -Available on backorder
-
N-Acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC) is an antioxidant and precursor of glutathione that has multiple effects in cells and animals. As an antioxidant, NAC scavenges hydrogen peroxide, hydroxyl radical, and hypochlorous acid.{32379,32381} NAC may be deacetylated to cysteine, which can be combined with glutamate and glycine to produce reduced glutathione (Item No. 10007461), which serves to reduce hydroperoxides and detoxify xenobiotics.{32379,32381} The free sulfhydryl group of NAC can also hydrolyze disulfide bonds of mucins and other proteins, thus facilitating clearance of mucus.{32384} Through these actions, NAC inhibits DNA adduct formation, limits hepatotoxic effects of acetaminophen, and provides diverse cytoprotective effects in vivo.{32378,32379,32380,32381,32384,32385}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20261 -Available on backorder
-
N-Acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC) is an antioxidant and precursor of glutathione that has multiple effects in cells and animals. As an antioxidant, NAC scavenges hydrogen peroxide, hydroxyl radical, and hypochlorous acid.{32379,32381} NAC may be deacetylated to cysteine, which can be combined with glutamate and glycine to produce reduced glutathione (Item No. 10007461), which serves to reduce hydroperoxides and detoxify xenobiotics.{32379,32381} The free sulfhydryl group of NAC can also hydrolyze disulfide bonds of mucins and other proteins, thus facilitating clearance of mucus.{32384} Through these actions, NAC inhibits DNA adduct formation, limits hepatotoxic effects of acetaminophen, and provides diverse cytoprotective effects in vivo.{32378,32379,32380,32381,32384,32385}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20261 -Available on backorder
-
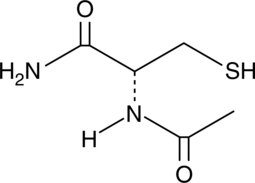
N-acetyl-L-Cysteine amide (NACA) is an antioxidant.{48071,48072} It is the amide form of N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC; Item No. 20261) and has increased cellular membrane and blood-brain barrier permeability compared to NAC. NACA (750 μM) inhibits glutamate-induced cytotoxicity, decreases in intracellular glutathione (GSH) levels, and increases in intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels in PC12 cells.{48073} It reduces cortical tissue damage and decreases the distance traveled to the platform in the Morris water maze in a rat model of traumatic brain injury.{48072} NACA (60 and 120 mg/kg) also inhibits ovalbumin-induced decreases in GSH, increases in nuclear NF-κB p65 and HIF-1α, and increases in IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 levels in mouse lung tissue.{48074}
Brand:CaymanSKU:25866 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
-
N-acetyl-L-Cysteine amide (NACA) is an antioxidant.{48071,48072} It is the amide form of N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC; Item No. 20261) and has increased cellular membrane and blood-brain barrier permeability compared to NAC. NACA (750 μM) inhibits glutamate-induced cytotoxicity, decreases in intracellular glutathione (GSH) levels, and increases in intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels in PC12 cells.{48073} It reduces cortical tissue damage and decreases the distance traveled to the platform in the Morris water maze in a rat model of traumatic brain injury.{48072} NACA (60 and 120 mg/kg) also inhibits ovalbumin-induced decreases in GSH, increases in nuclear NF-κB p65 and HIF-1α, and increases in IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 levels in mouse lung tissue.{48074}
Brand:CaymanSKU:25866 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
-
N-acetyl-L-Cysteine amide (NACA) is an antioxidant.{48071,48072} It is the amide form of N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC; Item No. 20261) and has increased cellular membrane and blood-brain barrier permeability compared to NAC. NACA (750 μM) inhibits glutamate-induced cytotoxicity, decreases in intracellular glutathione (GSH) levels, and increases in intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels in PC12 cells.{48073} It reduces cortical tissue damage and decreases the distance traveled to the platform in the Morris water maze in a rat model of traumatic brain injury.{48072} NACA (60 and 120 mg/kg) also inhibits ovalbumin-induced decreases in GSH, increases in nuclear NF-κB p65 and HIF-1α, and increases in IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 levels in mouse lung tissue.{48074}
Brand:CaymanSKU:25866 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
-
N-acetyl-L-Cysteine amide (NACA) is an antioxidant.{48071,48072} It is the amide form of N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC; Item No. 20261) and has increased cellular membrane and blood-brain barrier permeability compared to NAC. NACA (750 μM) inhibits glutamate-induced cytotoxicity, decreases in intracellular glutathione (GSH) levels, and increases in intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels in PC12 cells.{48073} It reduces cortical tissue damage and decreases the distance traveled to the platform in the Morris water maze in a rat model of traumatic brain injury.{48072} NACA (60 and 120 mg/kg) also inhibits ovalbumin-induced decreases in GSH, increases in nuclear NF-κB p65 and HIF-1α, and increases in IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 levels in mouse lung tissue.{48074}
Brand:CaymanSKU:25866 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
-
N-acetyl-L-Cysteine ethyl ester is an esterified form of N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC; Item No. 20261). It has enhanced cell permeability in isolated perfused rat liver compared to NAC.{53848} N-acetyl-L-Cysteine ethyl ester (1 mM) prevents tert-butyl hydroperoxide-induced formation of methemoglobin in isolated human red blood cells. It increases glutathione levels in rat liver, kidney, heart, testis, and brain when administered at a dose of 50 mg/kg twice per day for two weeks. N-acetyl-L-Cysteine ethyl ester reduces increases in plasma aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) levels induced by paracetamol (acetaminophen; Item No. 10024) in rats.
Brand:CaymanSKU:30299 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
-
N-acetyl-L-Cysteine ethyl ester is an esterified form of N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC; Item No. 20261). It has enhanced cell permeability in isolated perfused rat liver compared to NAC.{53848} N-acetyl-L-Cysteine ethyl ester (1 mM) prevents tert-butyl hydroperoxide-induced formation of methemoglobin in isolated human red blood cells. It increases glutathione levels in rat liver, kidney, heart, testis, and brain when administered at a dose of 50 mg/kg twice per day for two weeks. N-acetyl-L-Cysteine ethyl ester reduces increases in plasma aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) levels induced by paracetamol (acetaminophen; Item No. 10024) in rats.
Brand:CaymanSKU:30299 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
-
N-acetyl-L-Cysteine ethyl ester is an esterified form of N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC; Item No. 20261). It has enhanced cell permeability in isolated perfused rat liver compared to NAC.{53848} N-acetyl-L-Cysteine ethyl ester (1 mM) prevents tert-butyl hydroperoxide-induced formation of methemoglobin in isolated human red blood cells. It increases glutathione levels in rat liver, kidney, heart, testis, and brain when administered at a dose of 50 mg/kg twice per day for two weeks. N-acetyl-L-Cysteine ethyl ester reduces increases in plasma aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) levels induced by paracetamol (acetaminophen; Item No. 10024) in rats.
Brand:CaymanSKU:30299 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
-
N-acetyl-L-Cysteine ethyl ester is an esterified form of N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC; Item No. 20261). It has enhanced cell permeability in isolated perfused rat liver compared to NAC.{53848} N-acetyl-L-Cysteine ethyl ester (1 mM) prevents tert-butyl hydroperoxide-induced formation of methemoglobin in isolated human red blood cells. It increases glutathione levels in rat liver, kidney, heart, testis, and brain when administered at a dose of 50 mg/kg twice per day for two weeks. N-acetyl-L-Cysteine ethyl ester reduces increases in plasma aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) levels induced by paracetamol (acetaminophen; Item No. 10024) in rats.
Brand:CaymanSKU:30299 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
-
L-Deoxyalliin (Item No. 14014), also known as S-allyl-L-cysteine, is a water soluble organosulfur compound derived from garlic that has neuroprotective and antioxidative activities.{21895,21907} N-Acetyl-S-allyl-L-cysteine is a principal metabolite of L-deoxyalliin in humans, mice, rats, and dogs.{28672,28673,28671} It is readily detected in plasma and urine. The conversion of L-deoxyalliin to N-acetyl-S-allyl-L-cysteine appears to be mediated by a family of flavin-containing monooxygenases.{28673,28674}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
-
L-Deoxyalliin (Item No. 14014), also known as S-allyl-L-cysteine, is a water soluble organosulfur compound derived from garlic that has neuroprotective and antioxidative activities.{21895,21907} N-Acetyl-S-allyl-L-cysteine is a principal metabolite of L-deoxyalliin in humans, mice, rats, and dogs.{28672,28673,28671} It is readily detected in plasma and urine. The conversion of L-deoxyalliin to N-acetyl-S-allyl-L-cysteine appears to be mediated by a family of flavin-containing monooxygenases.{28673,28674}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
-
L-Deoxyalliin (Item No. 14014), also known as S-allyl-L-cysteine, is a water soluble organosulfur compound derived from garlic that has neuroprotective and antioxidative activities.{21895,21907} N-Acetyl-S-allyl-L-cysteine is a principal metabolite of L-deoxyalliin in humans, mice, rats, and dogs.{28672,28673,28671} It is readily detected in plasma and urine. The conversion of L-deoxyalliin to N-acetyl-S-allyl-L-cysteine appears to be mediated by a family of flavin-containing monooxygenases.{28673,28674}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
-
N-acetyl-S-farnesyl-L-Cysteine is a synthetic substrate for the isoprenylated protein methyltransferase (also known as S-adenosylmethionine-dependent methyltransferase).{2306,2304} Because it is able to serve as a substrate for the methyltransferase, it effectively functions as an inhibitor of methylation of endogenous isoprenylated proteins.
Brand:CaymanSKU:63270 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
-
N-acetyl-S-farnesyl-L-Cysteine is a synthetic substrate for the isoprenylated protein methyltransferase (also known as S-adenosylmethionine-dependent methyltransferase).{2306,2304} Because it is able to serve as a substrate for the methyltransferase, it effectively functions as an inhibitor of methylation of endogenous isoprenylated proteins.
Brand:CaymanSKU:63270 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
-
N-acetyl-S-farnesyl-L-Cysteine is a synthetic substrate for the isoprenylated protein methyltransferase (also known as S-adenosylmethionine-dependent methyltransferase).{2306,2304} Because it is able to serve as a substrate for the methyltransferase, it effectively functions as an inhibitor of methylation of endogenous isoprenylated proteins.
Brand:CaymanSKU:63270 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
-
N-acetyl-S-farnesyl-L-Cysteine is a synthetic substrate for the isoprenylated protein methyltransferase (also known as S-adenosylmethionine-dependent methyltransferase).{2306,2304} Because it is able to serve as a substrate for the methyltransferase, it effectively functions as an inhibitor of methylation of endogenous isoprenylated proteins.
Brand:CaymanSKU:63270 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
-
N-acetyl-S-geranylgeranyl-L-Cysteine is a synthetic substrate for the isoprenylated protein methyltransferase (also known as S-adenosylmethionine-dependent methyltransferase).{2306,2304} Because it is able to serve as a substrate for the methyltransferase, it effectively functions as an inhibitor of methylation of endogenous isoprenylated proteins.
Brand:CaymanSKU:63340 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
-
N-acetyl-S-geranylgeranyl-L-Cysteine is a synthetic substrate for the isoprenylated protein methyltransferase (also known as S-adenosylmethionine-dependent methyltransferase).{2306,2304} Because it is able to serve as a substrate for the methyltransferase, it effectively functions as an inhibitor of methylation of endogenous isoprenylated proteins.
Brand:CaymanSKU:63340 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
-
N-acetyl-S-geranylgeranyl-L-Cysteine is a synthetic substrate for the isoprenylated protein methyltransferase (also known as S-adenosylmethionine-dependent methyltransferase).{2306,2304} Because it is able to serve as a substrate for the methyltransferase, it effectively functions as an inhibitor of methylation of endogenous isoprenylated proteins.
Brand:CaymanSKU:63340 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
-
N-acetyl-S-geranylgeranyl-L-Cysteine is a synthetic substrate for the isoprenylated protein methyltransferase (also known as S-adenosylmethionine-dependent methyltransferase).{2306,2304} Because it is able to serve as a substrate for the methyltransferase, it effectively functions as an inhibitor of methylation of endogenous isoprenylated proteins.
Brand:CaymanSKU:63340 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
-
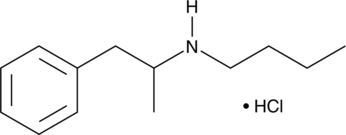
N-Acetylmethamphetamine (Item No. 27889) is an analytical reference standard categorized as an amphetamine. N-Acetylmethamphetamine is a by-product formed in the synthesis of methamphetamine from pseudoephedrine.{35847} It can also be formed as an analytical artifact in the injector during GC-MS analysis. This product is intended for research and forensic applications.
Brand:CaymanSKU:27889 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
-
N-Acetylmethamphetamine (Item No. 27889) is an analytical reference standard categorized as an amphetamine. N-Acetylmethamphetamine is a by-product formed in the synthesis of methamphetamine from pseudoephedrine.{35847} It can also be formed as an analytical artifact in the injector during GC-MS analysis. This product is intended for research and forensic applications.
Brand:CaymanSKU:27889 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
-
N-Acetylmuramic acid (MurNAc) is a component of the glycan strands in bacterial peptidoglycan.{59328} It is linked to N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) by β-1,4 linkages in an alternating pattern, as well as to the peptide side chains via its lactyl side chain, in native peptidoglycan.
Brand:CaymanSKU:31330 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
-
N-Acetylmuramic acid (MurNAc) is a component of the glycan strands in bacterial peptidoglycan.{59328} It is linked to N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) by β-1,4 linkages in an alternating pattern, as well as to the peptide side chains via its lactyl side chain, in native peptidoglycan.
Brand:CaymanSKU:31330 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
-
N-Acetylmuramic acid (MurNAc) is a component of the glycan strands in bacterial peptidoglycan.{59328} It is linked to N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) by β-1,4 linkages in an alternating pattern, as well as to the peptide side chains via its lactyl side chain, in native peptidoglycan.
Brand:CaymanSKU:31330 - 250 mgAvailable on backorder
-
N-Acetylmuramic acid (MurNAc) is a component of the glycan strands in bacterial peptidoglycan.{59328} It is linked to N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) by β-1,4 linkages in an alternating pattern, as well as to the peptide side chains via its lactyl side chain, in native peptidoglycan.
Brand:CaymanSKU:31330 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
-
Salic acids are nine-carbon carbohydrate α-keto acids that have many important biological functions, including cell-cell recognition and host-pathogen interactions.{26390,6370} N-Acetylneuraminic acid (NANA) is the most abundant sialic acid and is found in bacteria as well as in eukaryotic cells.{26390,26388} The pathways for NANA synthesis and metabolism in bacteria differ from those used in eukaryotic cells.{26388} This sialic acid is an essential component of human brain gangliosides and sialylated glycoproteins.{26389}
Brand:CaymanSKU:- -
Salic acids are nine-carbon carbohydrate α-keto acids that have many important biological functions, including cell-cell recognition and host-pathogen interactions.{26390,6370} N-Acetylneuraminic acid (NANA) is the most abundant sialic acid and is found in bacteria as well as in eukaryotic cells.{26390,26388} The pathways for NANA synthesis and metabolism in bacteria differ from those used in eukaryotic cells.{26388} This sialic acid is an essential component of human brain gangliosides and sialylated glycoproteins.{26389}
Brand:CaymanSKU:- -
Salic acids are nine-carbon carbohydrate α-keto acids that have many important biological functions, including cell-cell recognition and host-pathogen interactions.{26390,6370} N-Acetylneuraminic acid (NANA) is the most abundant sialic acid and is found in bacteria as well as in eukaryotic cells.{26390,26388} The pathways for NANA synthesis and metabolism in bacteria differ from those used in eukaryotic cells.{26388} This sialic acid is an essential component of human brain gangliosides and sialylated glycoproteins.{26389}
Brand:CaymanSKU:- -
Salic acids are nine-carbon carbohydrate α-keto acids that have many important biological functions, including cell-cell recognition and host-pathogen interactions.{26390,6370} N-Acetylneuraminic acid (NANA) is the most abundant sialic acid and is found in bacteria as well as in eukaryotic cells.{26390,26388} The pathways for NANA synthesis and metabolism in bacteria differ from those used in eukaryotic cells.{26388} This sialic acid is an essential component of human brain gangliosides and sialylated glycoproteins.{26389}
Brand:CaymanSKU:- -
N-Acetylpuromycin is a non-ribotoxic form of the antibiotic puromycin (Item No. 13884) that is formed in puromycin-resistant S. alboniger that endogenously express puromycin-acetyltransferase.{37780} In AD293(Pr) cells that express puromycin-N-acetyltransferase, the enzyme responsible for the biosynthesis of N-acetylpuromycin, puromycin application induces downregulation of the negative regulators of TGF-β signalling SnoN and Ski without activating MAPK or inhibition of protein synthesis.{37781}
Brand:CaymanSKU:25335 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
-
N-Acetylpuromycin is a non-ribotoxic form of the antibiotic puromycin (Item No. 13884) that is formed in puromycin-resistant S. alboniger that endogenously express puromycin-acetyltransferase.{37780} In AD293(Pr) cells that express puromycin-N-acetyltransferase, the enzyme responsible for the biosynthesis of N-acetylpuromycin, puromycin application induces downregulation of the negative regulators of TGF-β signalling SnoN and Ski without activating MAPK or inhibition of protein synthesis.{37781}
Brand:CaymanSKU:25335 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
-
N-Acetylpuromycin is a non-ribotoxic form of the antibiotic puromycin (Item No. 13884) that is formed in puromycin-resistant S. alboniger that endogenously express puromycin-acetyltransferase.{37780} In AD293(Pr) cells that express puromycin-N-acetyltransferase, the enzyme responsible for the biosynthesis of N-acetylpuromycin, puromycin application induces downregulation of the negative regulators of TGF-β signalling SnoN and Ski without activating MAPK or inhibition of protein synthesis.{37781}
Brand:CaymanSKU:25335 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
-
N-Acetylpuromycin is a non-ribotoxic form of the antibiotic puromycin (Item No. 13884) that is formed in puromycin-resistant S. alboniger that endogenously express puromycin-acetyltransferase.{37780} In AD293(Pr) cells that express puromycin-N-acetyltransferase, the enzyme responsible for the biosynthesis of N-acetylpuromycin, puromycin application induces downregulation of the negative regulators of TGF-β signalling SnoN and Ski without activating MAPK or inhibition of protein synthesis.{37781}
Brand:CaymanSKU:25335 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
-
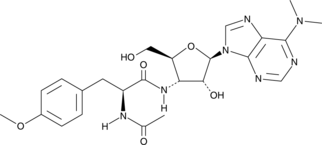
N-Acetylserotonin (NAS) is the immediate precursor of melatonin (Item No. 14427). It is produced from serotonin by the enzyme aralkylamine N-acetyltransferase and is converted to melatonin by acetylserotonin O-methyltransferase.{23138} Like melatonin, NAS is considered to be a neurotransmitter and acts as an agonist at the melatonin receptors MT1, MT2, and MT3.{23139} NAS may also have unique central effects since it is distributed in specific brain areas separate from serotonin and melatonin.{23139}
Brand:CaymanSKU:- -
N-Acetylserotonin (NAS) is the immediate precursor of melatonin (Item No. 14427). It is produced from serotonin by the enzyme aralkylamine N-acetyltransferase and is converted to melatonin by acetylserotonin O-methyltransferase.{23138} Like melatonin, NAS is considered to be a neurotransmitter and acts as an agonist at the melatonin receptors MT1, MT2, and MT3.{23139} NAS may also have unique central effects since it is distributed in specific brain areas separate from serotonin and melatonin.{23139}
Brand:CaymanSKU:- -
N-Acetylserotonin (NAS) is the immediate precursor of melatonin (Item No. 14427). It is produced from serotonin by the enzyme aralkylamine N-acetyltransferase and is converted to melatonin by acetylserotonin O-methyltransferase.{23138} Like melatonin, NAS is considered to be a neurotransmitter and acts as an agonist at the melatonin receptors MT1, MT2, and MT3.{23139} NAS may also have unique central effects since it is distributed in specific brain areas separate from serotonin and melatonin.{23139}
Brand:CaymanSKU:- -
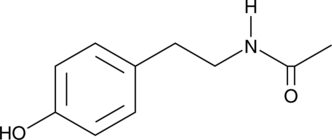
N-acetyltyramine is a metabolite of the biogenic amine tyramine (Item No. 18601).{43167} It enhances cytotoxicity of doxorubicin (Item No. 15007) in resistant P388 murine leukemia cells with an IC50 value of 0.13 μg/ml compared with an IC50 value of 0.48 µg/ml for doxorubicin alone.
Brand:CaymanSKU:9001373 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
-
N-acetyltyramine is a metabolite of the biogenic amine tyramine (Item No. 18601).{43167} It enhances cytotoxicity of doxorubicin (Item No. 15007) in resistant P388 murine leukemia cells with an IC50 value of 0.13 μg/ml compared with an IC50 value of 0.48 µg/ml for doxorubicin alone.
Brand:CaymanSKU:9001373 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
-
N-Arachidonoyl dopamine (NADA) is an arachidonoyl amino acid and cannabinoid (CB) receptor 1 agonist (Ki = 250 nM in rat brain membranes, which highly express CB1 receptors).{9213} It is selective for CB1 over CB2 receptors (Ki = >12,000 nM in rat spleen membranes, which highly express CB2 receptors). NADA induces intracellular calcium mobilization in N18TG2 neuroblastoma cells (EC50 = 0.7 µM). It inhibits the proliferation of MCF-7 breast cancer cells (IC50 = 0.25 µM), an effect that can be reversed by the CB1 receptor antagonist SR141716A (rimonabant; Item No. 9000484). NADA (10 mg/kg) induces hypothermia, catalepsy, hypolocomotion, and analgesia in mice.
Brand:CaymanSKU:90057 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
-
N-Arachidonoyl dopamine (NADA) is an arachidonoyl amino acid and cannabinoid (CB) receptor 1 agonist (Ki = 250 nM in rat brain membranes, which highly express CB1 receptors).{9213} It is selective for CB1 over CB2 receptors (Ki = >12,000 nM in rat spleen membranes, which highly express CB2 receptors). NADA induces intracellular calcium mobilization in N18TG2 neuroblastoma cells (EC50 = 0.7 µM). It inhibits the proliferation of MCF-7 breast cancer cells (IC50 = 0.25 µM), an effect that can be reversed by the CB1 receptor antagonist SR141716A (rimonabant; Item No. 9000484). NADA (10 mg/kg) induces hypothermia, catalepsy, hypolocomotion, and analgesia in mice.
Brand:CaymanSKU:90057 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
-
N-Arachidonoyl dopamine (NADA) is an arachidonoyl amino acid and cannabinoid (CB) receptor 1 agonist (Ki = 250 nM in rat brain membranes, which highly express CB1 receptors).{9213} It is selective for CB1 over CB2 receptors (Ki = >12,000 nM in rat spleen membranes, which highly express CB2 receptors). NADA induces intracellular calcium mobilization in N18TG2 neuroblastoma cells (EC50 = 0.7 µM). It inhibits the proliferation of MCF-7 breast cancer cells (IC50 = 0.25 µM), an effect that can be reversed by the CB1 receptor antagonist SR141716A (rimonabant; Item No. 9000484). NADA (10 mg/kg) induces hypothermia, catalepsy, hypolocomotion, and analgesia in mice.
Brand:CaymanSKU:90057 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
-
N-Arachidonoyl dopamine (NADA) is an arachidonoyl amino acid and cannabinoid (CB) receptor 1 agonist (Ki = 250 nM in rat brain membranes, which highly express CB1 receptors).{9213} It is selective for CB1 over CB2 receptors (Ki = >12,000 nM in rat spleen membranes, which highly express CB2 receptors). NADA induces intracellular calcium mobilization in N18TG2 neuroblastoma cells (EC50 = 0.7 µM). It inhibits the proliferation of MCF-7 breast cancer cells (IC50 = 0.25 µM), an effect that can be reversed by the CB1 receptor antagonist SR141716A (rimonabant; Item No. 9000484). NADA (10 mg/kg) induces hypothermia, catalepsy, hypolocomotion, and analgesia in mice.
Brand:CaymanSKU:90057 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
-
N-Arachidonoyl dopamine-d8 contains eight deuterium atoms at the 5, 6, 8, 9, 11, 12, 14, and 15 positions. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of N-arachidonoyl dopamine by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. Several different arachidonoyl amino acids, including NADA, have been isolated and characterized from bovine brain.{9589} NADA is the amide of the neurotransmitter dopamine and arachidonic acid. NADA is a CB1-selective cannabinoid agonist, inducing the typical tetrad of hypothermia, analgesia, catalepsy, and hypomotility in rats which exceeds that of anandamide (AEA).{9213} NADA is a full agonist at the vanilloid receptor 1, but is inactive on the dopaminergic D1 and D2 receptors. NADA is also a potent inhibitor (IC50 = 0.25 µM) of the proliferation of MCF-7 breast carcinoma cells. Recent reports of NADA’s endothelium-dependent vasodilation indicate that some of its cannabinergic activities antagonized by SR141716A may be non-CB1/CB2 dependent.{11224}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007431 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
-
N-Arachidonoyl dopamine-d8 contains eight deuterium atoms at the 5, 6, 8, 9, 11, 12, 14, and 15 positions. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of N-arachidonoyl dopamine by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. Several different arachidonoyl amino acids, including NADA, have been isolated and characterized from bovine brain.{9589} NADA is the amide of the neurotransmitter dopamine and arachidonic acid. NADA is a CB1-selective cannabinoid agonist, inducing the typical tetrad of hypothermia, analgesia, catalepsy, and hypomotility in rats which exceeds that of anandamide (AEA).{9213} NADA is a full agonist at the vanilloid receptor 1, but is inactive on the dopaminergic D1 and D2 receptors. NADA is also a potent inhibitor (IC50 = 0.25 µM) of the proliferation of MCF-7 breast carcinoma cells. Recent reports of NADA’s endothelium-dependent vasodilation indicate that some of its cannabinergic activities antagonized by SR141716A may be non-CB1/CB2 dependent.{11224}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007431 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
-
N-Arachidonoyl dopamine-d8 contains eight deuterium atoms at the 5, 6, 8, 9, 11, 12, 14, and 15 positions. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of N-arachidonoyl dopamine by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. Several different arachidonoyl amino acids, including NADA, have been isolated and characterized from bovine brain.{9589} NADA is the amide of the neurotransmitter dopamine and arachidonic acid. NADA is a CB1-selective cannabinoid agonist, inducing the typical tetrad of hypothermia, analgesia, catalepsy, and hypomotility in rats which exceeds that of anandamide (AEA).{9213} NADA is a full agonist at the vanilloid receptor 1, but is inactive on the dopaminergic D1 and D2 receptors. NADA is also a potent inhibitor (IC50 = 0.25 µM) of the proliferation of MCF-7 breast carcinoma cells. Recent reports of NADA’s endothelium-dependent vasodilation indicate that some of its cannabinergic activities antagonized by SR141716A may be non-CB1/CB2 dependent.{11224}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007431 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
-
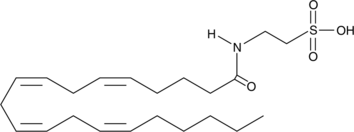
N-Arachidonoyl taurine is an arachidonoyl amino acid.{16245} It is oxygenated by 12(S)- and 15(S)-lipoxygenase and is converted to 12-HETE-taurine (12-HETE-T) in murine resident peritoneal macrophages.{46067} N-Arachidonoyl taurine is an activator of the transient receptor potential vanilloid (TRPV) channels TRPV1 and TRPV4 (EC50s = 28 and 21 µM, respectively).{16245} It increases calcium flux in HIT-T15 pancreatic β-cells and INS-1 rat islet cells when used at a concentration of 10 µM and increases insulin secretion from 832/13 INS-1 pancreatic β-cells.{46068} The levels of N-arachidonoyl taurine are changed in mouse brain following administration of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC).{46069}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10005537 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
-
N-Arachidonoyl taurine is an arachidonoyl amino acid.{16245} It is oxygenated by 12(S)- and 15(S)-lipoxygenase and is converted to 12-HETE-taurine (12-HETE-T) in murine resident peritoneal macrophages.{46067} N-Arachidonoyl taurine is an activator of the transient receptor potential vanilloid (TRPV) channels TRPV1 and TRPV4 (EC50s = 28 and 21 µM, respectively).{16245} It increases calcium flux in HIT-T15 pancreatic β-cells and INS-1 rat islet cells when used at a concentration of 10 µM and increases insulin secretion from 832/13 INS-1 pancreatic β-cells.{46068} The levels of N-arachidonoyl taurine are changed in mouse brain following administration of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC).{46069}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10005537 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
-
N-Arachidonoyl taurine is an arachidonoyl amino acid.{16245} It is oxygenated by 12(S)- and 15(S)-lipoxygenase and is converted to 12-HETE-taurine (12-HETE-T) in murine resident peritoneal macrophages.{46067} N-Arachidonoyl taurine is an activator of the transient receptor potential vanilloid (TRPV) channels TRPV1 and TRPV4 (EC50s = 28 and 21 µM, respectively).{16245} It increases calcium flux in HIT-T15 pancreatic β-cells and INS-1 rat islet cells when used at a concentration of 10 µM and increases insulin secretion from 832/13 INS-1 pancreatic β-cells.{46068} The levels of N-arachidonoyl taurine are changed in mouse brain following administration of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC).{46069}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10005537 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
-
N-Arachidonoyl taurine is an arachidonoyl amino acid.{16245} It is oxygenated by 12(S)- and 15(S)-lipoxygenase and is converted to 12-HETE-taurine (12-HETE-T) in murine resident peritoneal macrophages.{46067} N-Arachidonoyl taurine is an activator of the transient receptor potential vanilloid (TRPV) channels TRPV1 and TRPV4 (EC50s = 28 and 21 µM, respectively).{16245} It increases calcium flux in HIT-T15 pancreatic β-cells and INS-1 rat islet cells when used at a concentration of 10 µM and increases insulin secretion from 832/13 INS-1 pancreatic β-cells.{46068} The levels of N-arachidonoyl taurine are changed in mouse brain following administration of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC).{46069}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10005537 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
-
Several different arachidonoyl amino acids, including N-arachidonoyl-3-hydroxy-γ-aminobutyric acid (NAG-3H-ABA), have been isolated and characterized from bovine brain.{9589} The glycine congener (NAGly; Item No. 90051) was further characterized and found to suppress formalin-induced pain in rats. NAG-3H-ABA was also found in rat brain by LC-MS techniques, but has not been fully characterized to date. Most arachidonoyl amino acids are poor ligands for the CB1 receptor.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10158 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
-
Several different arachidonoyl amino acids, including N-arachidonoyl-3-hydroxy-γ-aminobutyric acid (NAG-3H-ABA), have been isolated and characterized from bovine brain.{9589} The glycine congener (NAGly; Item No. 90051) was further characterized and found to suppress formalin-induced pain in rats. NAG-3H-ABA was also found in rat brain by LC-MS techniques, but has not been fully characterized to date. Most arachidonoyl amino acids are poor ligands for the CB1 receptor.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10158 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
-
Several different arachidonoyl amino acids, including N-arachidonoyl-3-hydroxy-γ-aminobutyric acid (NAG-3H-ABA), have been isolated and characterized from bovine brain.{9589} The glycine congener (NAGly; Item No. 90051) was further characterized and found to suppress formalin-induced pain in rats. NAG-3H-ABA was also found in rat brain by LC-MS techniques, but has not been fully characterized to date. Most arachidonoyl amino acids are poor ligands for the CB1 receptor.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10158 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
-
Several different arachidonoyl amino acids, including N-arachidonoyl-3-hydroxy-γ-aminobutyric acid (NAG-3H-ABA), have been isolated and characterized from bovine brain.{9589} The glycine congener (NAGly; Item No. 90051) was further characterized and found to suppress formalin-induced pain in rats. NAG-3H-ABA was also found in rat brain by LC-MS techniques, but has not been fully characterized to date. Most arachidonoyl amino acids are poor ligands for the CB1 receptor.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10158 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
-
Several different arachidonoyl amino acids, including N-arachidonoyl-L-alanine (NALA), have been isolated and characterized from bovine brain.{9589} The glycine congener (NAGly) was further characterized and found to suppress formalin-induced pain in rats. NALA may have activity at cannabinoid receptor and/or VR1, but has not been fully characterized to date.
Brand:CaymanSKU:90065 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
-
Several different arachidonoyl amino acids, including N-arachidonoyl-L-alanine (NALA), have been isolated and characterized from bovine brain.{9589} The glycine congener (NAGly) was further characterized and found to suppress formalin-induced pain in rats. NALA may have activity at cannabinoid receptor and/or VR1, but has not been fully characterized to date.
Brand:CaymanSKU:90065 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
-
Several different arachidonoyl amino acids, including N-arachidonoyl-L-alanine (NALA), have been isolated and characterized from bovine brain.{9589} The glycine congener (NAGly) was further characterized and found to suppress formalin-induced pain in rats. NALA may have activity at cannabinoid receptor and/or VR1, but has not been fully characterized to date.
Brand:CaymanSKU:90065 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
-
Several different arachidonoyl amino acids, including N-arachidonoyl-L-alanine (NALA), have been isolated and characterized from bovine brain.{9589} The glycine congener (NAGly) was further characterized and found to suppress formalin-induced pain in rats. NALA may have activity at cannabinoid receptor and/or VR1, but has not been fully characterized to date.
Brand:CaymanSKU:90065 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
-
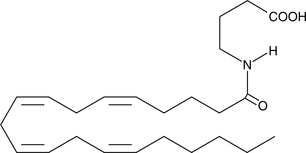
Arachidonoyl amides of both amino acids and neurotransmitters such as dopamine have been previously reported in the literature.{9213} N-Arachidonoyl-L-serine (ARA-S) is one such recently isolated endocannabinoid with an unusual activity profile. ARA-S does not bind to central cannabinoid (CB1) and peripheral cannabinoid (CB2) receptors or vanilloid receptor 1 (VR1). Like cannabidiol, ARA-S (5 mg/kg) antagonizes the hypotensive effects of a 10 mg/kg IV bolus of abnormal cannabidiol (Abn-CBD) in an anesthetized rat blood pressure model.{11984} However, similar to Abn-CBD, ARA-S relaxes isolated rat mesenteric arteries and abdominal aorta as well as increases phosphorylation of Akt and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) in HUVEC.{14066} The precise mechanisms of action by ARA-S and Abn-DBD in various vascular preparations appears to be different and requires further investigation.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10005455 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
-
Arachidonoyl amides of both amino acids and neurotransmitters such as dopamine have been previously reported in the literature.{9213} N-Arachidonoyl-L-serine (ARA-S) is one such recently isolated endocannabinoid with an unusual activity profile. ARA-S does not bind to central cannabinoid (CB1) and peripheral cannabinoid (CB2) receptors or vanilloid receptor 1 (VR1). Like cannabidiol, ARA-S (5 mg/kg) antagonizes the hypotensive effects of a 10 mg/kg IV bolus of abnormal cannabidiol (Abn-CBD) in an anesthetized rat blood pressure model.{11984} However, similar to Abn-CBD, ARA-S relaxes isolated rat mesenteric arteries and abdominal aorta as well as increases phosphorylation of Akt and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) in HUVEC.{14066} The precise mechanisms of action by ARA-S and Abn-DBD in various vascular preparations appears to be different and requires further investigation.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10005455 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
-
Arachidonoyl amides of both amino acids and neurotransmitters such as dopamine have been previously reported in the literature.{9213} N-Arachidonoyl-L-serine (ARA-S) is one such recently isolated endocannabinoid with an unusual activity profile. ARA-S does not bind to central cannabinoid (CB1) and peripheral cannabinoid (CB2) receptors or vanilloid receptor 1 (VR1). Like cannabidiol, ARA-S (5 mg/kg) antagonizes the hypotensive effects of a 10 mg/kg IV bolus of abnormal cannabidiol (Abn-CBD) in an anesthetized rat blood pressure model.{11984} However, similar to Abn-CBD, ARA-S relaxes isolated rat mesenteric arteries and abdominal aorta as well as increases phosphorylation of Akt and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) in HUVEC.{14066} The precise mechanisms of action by ARA-S and Abn-DBD in various vascular preparations appears to be different and requires further investigation.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10005455 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
-
Arachidonoyl amides of both amino acids and neurotransmitters such as dopamine have been previously reported in the literature.{9213} N-Arachidonoyl-L-serine (ARA-S) is one such recently isolated endocannabinoid with an unusual activity profile. ARA-S does not bind to central cannabinoid (CB1) and peripheral cannabinoid (CB2) receptors or vanilloid receptor 1 (VR1). Like cannabidiol, ARA-S (5 mg/kg) antagonizes the hypotensive effects of a 10 mg/kg IV bolus of abnormal cannabidiol (Abn-CBD) in an anesthetized rat blood pressure model.{11984} However, similar to Abn-CBD, ARA-S relaxes isolated rat mesenteric arteries and abdominal aorta as well as increases phosphorylation of Akt and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) in HUVEC.{14066} The precise mechanisms of action by ARA-S and Abn-DBD in various vascular preparations appears to be different and requires further investigation.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10005455 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
-
Several different arachidonoyl amino acids, including N-Arachidonoyl-γ-aminobutyric acid (NAGABA), have been isolated and characterized from bovine brain.The glycine congener (NAGly) was further characterized and found to suppress formalin-induced pain in rats. NAGABA was also found to suppress normal responses to pain, but has not been fully characterized to date.{9589}
Brand:CaymanSKU:90067 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
-
Several different arachidonoyl amino acids, including N-Arachidonoyl-γ-aminobutyric acid (NAGABA), have been isolated and characterized from bovine brain.The glycine congener (NAGly) was further characterized and found to suppress formalin-induced pain in rats. NAGABA was also found to suppress normal responses to pain, but has not been fully characterized to date.{9589}
Brand:CaymanSKU:90067 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
-
Several different arachidonoyl amino acids, including N-Arachidonoyl-γ-aminobutyric acid (NAGABA), have been isolated and characterized from bovine brain.The glycine congener (NAGly) was further characterized and found to suppress formalin-induced pain in rats. NAGABA was also found to suppress normal responses to pain, but has not been fully characterized to date.{9589}
Brand:CaymanSKU:90067 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
-
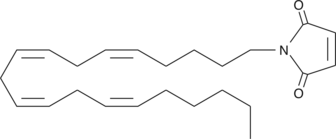
2-Arachidonoyl glycerol (2-AG) is an endogenous agonist of the central cannabinoid (CB1) and peripheral cannabinoid (CB2) receptors.{7183,7182,9610} 2-AG is present at relatively high levels in the central nervous system and is the most abundant molecular species of monoacylglycerol found in rat brain.{7183,6819} Monoacylglycerol lipase (MGL) hydrolyzes 2-AG to arachidonic acid and glycerol, thereby terminating its biological actions.{11364} N-Arachidonyl maleimide (NAM) is a potent, irreversible inhibitor of monoacylglycerol lipase (MGL) or MGL-like activity in rat cerebellar membranes, exhibiting an IC50 value of 140 nM.{13255} Inhibition of MGL by the sulfhydryl-reactive maleimide group of NAM suggests a critical cysteine residue is present in the substrate-binding site of the enzyme.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007517 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
-
2-Arachidonoyl glycerol (2-AG) is an endogenous agonist of the central cannabinoid (CB1) and peripheral cannabinoid (CB2) receptors.{7183,7182,9610} 2-AG is present at relatively high levels in the central nervous system and is the most abundant molecular species of monoacylglycerol found in rat brain.{7183,6819} Monoacylglycerol lipase (MGL) hydrolyzes 2-AG to arachidonic acid and glycerol, thereby terminating its biological actions.{11364} N-Arachidonyl maleimide (NAM) is a potent, irreversible inhibitor of monoacylglycerol lipase (MGL) or MGL-like activity in rat cerebellar membranes, exhibiting an IC50 value of 140 nM.{13255} Inhibition of MGL by the sulfhydryl-reactive maleimide group of NAM suggests a critical cysteine residue is present in the substrate-binding site of the enzyme.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007517 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
-
2-Arachidonoyl glycerol (2-AG) is an endogenous agonist of the central cannabinoid (CB1) and peripheral cannabinoid (CB2) receptors.{7183,7182,9610} 2-AG is present at relatively high levels in the central nervous system and is the most abundant molecular species of monoacylglycerol found in rat brain.{7183,6819} Monoacylglycerol lipase (MGL) hydrolyzes 2-AG to arachidonic acid and glycerol, thereby terminating its biological actions.{11364} N-Arachidonyl maleimide (NAM) is a potent, irreversible inhibitor of monoacylglycerol lipase (MGL) or MGL-like activity in rat cerebellar membranes, exhibiting an IC50 value of 140 nM.{13255} Inhibition of MGL by the sulfhydryl-reactive maleimide group of NAM suggests a critical cysteine residue is present in the substrate-binding site of the enzyme.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007517 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
-
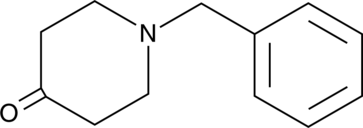
N-Benzyl-4-piperidone (Item No. 21962) is an analytical reference standard that is structurally categorized as a piperidine. It is a starting material that is used in the synthesis of fentanyl (Item Nos. ISO60197 | 14719) and related compounds. The physiological and toxicological properties of this compound are not known. This product is intended for research and forensic applications.
Brand:CaymanSKU:21962 -Out of stock
-
N-Benzyl-4-piperidone (Item No. 21962) is an analytical reference standard that is structurally categorized as a piperidine. It is a starting material that is used in the synthesis of fentanyl (Item Nos. ISO60197 | 14719) and related compounds. The physiological and toxicological properties of this compound are not known. This product is intended for research and forensic applications.
Brand:CaymanSKU:21962 -Out of stock
-
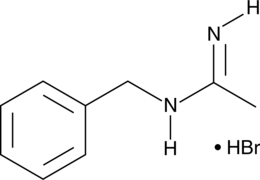
Of the different types of nitric oxide synthases (NOS), the inducible (iNOS) form contributes to inflammation and immune response while the constitutively-expressed endothelial (eNOS) enzyme plays important roles in regulating vascular tone. N-Benzylacetamidine is a potent inhibitor of iNOS (IC50 = 0.20 μM), with over 1,000-fold selectivity compared to eNOS (IC50 = 350 µM).{17417}
Brand:CaymanSKU:- -
Of the different types of nitric oxide synthases (NOS), the inducible (iNOS) form contributes to inflammation and immune response while the constitutively-expressed endothelial (eNOS) enzyme plays important roles in regulating vascular tone. N-Benzylacetamidine is a potent inhibitor of iNOS (IC50 = 0.20 μM), with over 1,000-fold selectivity compared to eNOS (IC50 = 350 µM).{17417}
Brand:CaymanSKU:- -
Of the different types of nitric oxide synthases (NOS), the inducible (iNOS) form contributes to inflammation and immune response while the constitutively-expressed endothelial (eNOS) enzyme plays important roles in regulating vascular tone. N-Benzylacetamidine is a potent inhibitor of iNOS (IC50 = 0.20 μM), with over 1,000-fold selectivity compared to eNOS (IC50 = 350 µM).{17417}
Brand:CaymanSKU:- -
Of the different types of nitric oxide synthases (NOS), the inducible (iNOS) form contributes to inflammation and immune response while the constitutively-expressed endothelial (eNOS) enzyme plays important roles in regulating vascular tone. N-Benzylacetamidine is a potent inhibitor of iNOS (IC50 = 0.20 μM), with over 1,000-fold selectivity compared to eNOS (IC50 = 350 µM).{17417}
Brand:CaymanSKU:- -
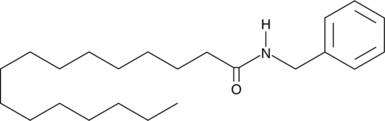
N-Benzylpalmitamide is a long-chain fatty acid amide (macamide or macaene) isolated from the maca (L. meyenii) plant and is structurally related to cannabinoids.{28386} N-Benzylpalmitamide has been the most frequently isolated of the 19 macamides currently identified. While many macamides have been identified as potent inhibitors of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), N-benzylpalmitamide displays only moderate FAAH inhibitory activity (44% inhibition at 500 µM).{28386} Additionally, many members of this family demonstrate selective antiproliferative activity against diverse cancer cell lines.{28387}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9002235 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
-
N-Benzylpalmitamide is a long-chain fatty acid amide (macamide or macaene) isolated from the maca (L. meyenii) plant and is structurally related to cannabinoids.{28386} N-Benzylpalmitamide has been the most frequently isolated of the 19 macamides currently identified. While many macamides have been identified as potent inhibitors of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), N-benzylpalmitamide displays only moderate FAAH inhibitory activity (44% inhibition at 500 µM).{28386} Additionally, many members of this family demonstrate selective antiproliferative activity against diverse cancer cell lines.{28387}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9002235 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
-
N-Benzylpalmitamide is a long-chain fatty acid amide (macamide or macaene) isolated from the maca (L. meyenii) plant and is structurally related to cannabinoids.{28386} N-Benzylpalmitamide has been the most frequently isolated of the 19 macamides currently identified. While many macamides have been identified as potent inhibitors of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), N-benzylpalmitamide displays only moderate FAAH inhibitory activity (44% inhibition at 500 µM).{28386} Additionally, many members of this family demonstrate selective antiproliferative activity against diverse cancer cell lines.{28387}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9002235 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
-
N-Benzylpalmitamide is a long-chain fatty acid amide (macamide or macaene) isolated from the maca (L. meyenii) plant and is structurally related to cannabinoids.{28386} N-Benzylpalmitamide has been the most frequently isolated of the 19 macamides currently identified. While many macamides have been identified as potent inhibitors of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), N-benzylpalmitamide displays only moderate FAAH inhibitory activity (44% inhibition at 500 µM).{28386} Additionally, many members of this family demonstrate selective antiproliferative activity against diverse cancer cell lines.{28387}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9002235 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
-
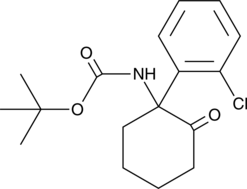
N-Boc Ketamine (Item No. 9003561) is an analytical reference standard categorized as an arylcyclohexylamine. This product is intended for research and forensic applications.
Brand:CaymanSKU:9003561 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
-
N-Boc Ketamine (Item No. 9003561) is an analytical reference standard categorized as an arylcyclohexylamine. This product is intended for research and forensic applications.
Brand:CaymanSKU:9003561 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
-
N-Boc Norketamine (Item No. 9003560) is an analytical reference standard categorized as an arylcyclohexylamine. This product is intended for research and forensic applications.
Brand:CaymanSKU:9003560 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
-
N-Boc Norketamine (Item No. 9003560) is an analytical reference standard categorized as an arylcyclohexylamine. This product is intended for research and forensic applications.
Brand:CaymanSKU:9003560 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
-
N-Boc-L-proline is a synthetic intermediate.{49607,49608} It has been used in the synthesis of enantioselective catalysts for aldol reactions and hepatitis C virus (HCV) NS5A inhibitors.
Brand:CaymanSKU:30386 - 100 gAvailable on backorder
-
N-Boc-L-proline is a synthetic intermediate.{49607,49608} It has been used in the synthesis of enantioselective catalysts for aldol reactions and hepatitis C virus (HCV) NS5A inhibitors.
Brand:CaymanSKU:30386 - 25 gAvailable on backorder
-
N-Boc-L-proline is a synthetic intermediate.{49607,49608} It has been used in the synthesis of enantioselective catalysts for aldol reactions and hepatitis C virus (HCV) NS5A inhibitors.
Brand:CaymanSKU:30386 - 50 gAvailable on backorder
-
N-butyl Amphetamine (hydrochloride) (Item No. 23547) is an analytical reference standard categorized as an amphetamine.{26035} This product is intended for research and forensic applications.
Brand:CaymanSKU:23547 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
-
N-butyl Amphetamine (hydrochloride) (Item No. 23547) is an analytical reference standard categorized as an amphetamine.{26035} This product is intended for research and forensic applications.
Brand:CaymanSKU:23547 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
-
N-butyl Pentylone (hydrochloride) (Item No. 26701) is an analytical reference standard categorized as a cathinone. This product is intended for research and forensic applications.
Brand:CaymanSKU:26701 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
-
N-butyl Pentylone (hydrochloride) (Item No. 26701) is an analytical reference standard categorized as a cathinone. This product is intended for research and forensic applications.
Brand:CaymanSKU:26701 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
-
N-Butyldeoxynojirimycin (NB-DNJ) is an iminosugar that inhibits ceramide-specific glucosyltransferase and β-glucosidase 2 (IC50s = 32 and 81 μM, respectively, for rat recombinant enzymes).{38202} The addition of NB-DNJ to growth medium for COS-7 cells expressing wild-type, S364R, N370S, V15M, or M123T glucocerebrosidase, an enzyme deficient in Spanish populations with the sphingolipid storage disorder Gaucher disease, leads to a 2.1-, 1.3-, 2.3-, 3.6,- or 9.9-fold increase in enzyme activity.{38203} NB-DNJ also inhibits HIV-1 and HIV-2 infection of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) with IC50 values of 282 and 211 μM, respectively.{38204} Formulations containing NB-DNJ have been used for the treatment of Gaucher disease and juvenile Sandhoff disease.{38205}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21065 -Out of stock
-
N-Butyldeoxynojirimycin (NB-DNJ) is an iminosugar that inhibits ceramide-specific glucosyltransferase and β-glucosidase 2 (IC50s = 32 and 81 μM, respectively, for rat recombinant enzymes).{38202} The addition of NB-DNJ to growth medium for COS-7 cells expressing wild-type, S364R, N370S, V15M, or M123T glucocerebrosidase, an enzyme deficient in Spanish populations with the sphingolipid storage disorder Gaucher disease, leads to a 2.1-, 1.3-, 2.3-, 3.6,- or 9.9-fold increase in enzyme activity.{38203} NB-DNJ also inhibits HIV-1 and HIV-2 infection of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) with IC50 values of 282 and 211 μM, respectively.{38204} Formulations containing NB-DNJ have been used for the treatment of Gaucher disease and juvenile Sandhoff disease.{38205}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21065 -Out of stock
-
N-Butyldeoxynojirimycin (NB-DNJ) is an iminosugar that inhibits ceramide-specific glucosyltransferase and β-glucosidase 2 (IC50s = 32 and 81 μM, respectively, for rat recombinant enzymes).{38202} The addition of NB-DNJ to growth medium for COS-7 cells expressing wild-type, S364R, N370S, V15M, or M123T glucocerebrosidase, an enzyme deficient in Spanish populations with the sphingolipid storage disorder Gaucher disease, leads to a 2.1-, 1.3-, 2.3-, 3.6,- or 9.9-fold increase in enzyme activity.{38203} NB-DNJ also inhibits HIV-1 and HIV-2 infection of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) with IC50 values of 282 and 211 μM, respectively.{38204} Formulations containing NB-DNJ have been used for the treatment of Gaucher disease and juvenile Sandhoff disease.{38205}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21065 -Out of stock
-
N-Butyldeoxynojirimycin (NB-DNJ) is an iminosugar that inhibits ceramide-specific glucosyltransferase and β-glucosidase 2 (IC50s = 32 and 81 μM, respectively, for rat recombinant enzymes).{38202} The addition of NB-DNJ to growth medium for COS-7 cells expressing wild-type, S364R, N370S, V15M, or M123T glucocerebrosidase, an enzyme deficient in Spanish populations with the sphingolipid storage disorder Gaucher disease, leads to a 2.1-, 1.3-, 2.3-, 3.6,- or 9.9-fold increase in enzyme activity.{38203} NB-DNJ also inhibits HIV-1 and HIV-2 infection of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) with IC50 values of 282 and 211 μM, respectively.{38204} Formulations containing NB-DNJ have been used for the treatment of Gaucher disease and juvenile Sandhoff disease.{38205}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21065 -Out of stock
-
N-Butylfluorescein is a fluorescent compound that displays excitation/emission maxima of 467/512 nm, respectively.{48518} It has been used in the synthesis of butyl fluorescein myo-inositol phosphate (butyl FLIP), a fluorogenic substrate of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C (PI-PLC).{48519}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20909 -Out of stock
-
N-Butylfluorescein is a fluorescent compound that displays excitation/emission maxima of 467/512 nm, respectively.{48518} It has been used in the synthesis of butyl fluorescein myo-inositol phosphate (butyl FLIP), a fluorogenic substrate of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C (PI-PLC).{48519}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20909 -Out of stock
-
N-Butylfluorescein is a fluorescent compound that displays excitation/emission maxima of 467/512 nm, respectively.{48518} It has been used in the synthesis of butyl fluorescein myo-inositol phosphate (butyl FLIP), a fluorogenic substrate of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C (PI-PLC).{48519}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20909 -Out of stock
-
Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density. Controlling bacterial infections by quenching their quorum sensing systems is a promising field of study. The expression of specific target genes, such as transcriptional regulators belonging to the LuxIR family of proteins, is coordinated by synthesis of diffusible acylhomoserine lactone (AHL) molecules. N-butyryl-L-Homocysteine thio-lactone is an analog of N-butyryl-L-homoserine lactone, the small diffusible signaling molecule involved in quorum sensing, thereby controlling gene expression and cellular metabolism.{16309} N-butyryl-L-Homocysteine thio-lactone induces violacein expression in C. violaceum mutants usually not able to produce AHLs.{16309,16308}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10011204 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
-
Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density. Controlling bacterial infections by quenching their quorum sensing systems is a promising field of study. The expression of specific target genes, such as transcriptional regulators belonging to the LuxIR family of proteins, is coordinated by synthesis of diffusible acylhomoserine lactone (AHL) molecules. N-butyryl-L-Homocysteine thio-lactone is an analog of N-butyryl-L-homoserine lactone, the small diffusible signaling molecule involved in quorum sensing, thereby controlling gene expression and cellular metabolism.{16309} N-butyryl-L-Homocysteine thio-lactone induces violacein expression in C. violaceum mutants usually not able to produce AHLs.{16309,16308}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10011204 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder