Cayman
Showing 30751–30900 of 45550 results
-
Myristoyl-L-carnitine-d3 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of myristoyl-L-carnitine (Item No. 26559) by GC- or LC-MS. Myristoyl-L-carnitine is a naturally occurring long-chain acylcarnitine.{42563} Plasma levels of myristoyl-L-carnitine are decreased in patients with chronic fatigue syndrome and increased in patients with end-stage renal disease.{42563,42564}
Brand:CaymanSKU:26581 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Myristoyl-L-carnitine-d3 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of myristoyl-L-carnitine (Item No. 26559) by GC- or LC-MS. Myristoyl-L-carnitine is a naturally occurring long-chain acylcarnitine.{42563} Plasma levels of myristoyl-L-carnitine are decreased in patients with chronic fatigue syndrome and increased in patients with end-stage renal disease.{42563,42564}
Brand:CaymanSKU:26581 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Myrothecine A is a trichothecene mycotoxin that has been found in M. roridum and has anticancer activities.{48753,48754} It inhibits proliferation of A549, MCF-7, HepG2, and SMMC-7721 cancer cells (IC50s = 95, 70, 60, and 25 µM, respectively).{48753} Myrothecine A (50 µM) induces G1 cell cycle arrest in HepG2 cells, as well as increases Bax and cleaved caspase-3, -5, and -8 levels and induces apoptosis in SMMC-7721 cells.{48753,48754}
Brand:CaymanSKU:28193 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Myrtillin is a natural anthocyanin found in plants. It is the 3-glucoside of delphinidin. Anthocyanins, including myrtillin, are potent antioxidants.{26210,26209,23825}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Myrtillin is a natural anthocyanin found in plants. It is the 3-glucoside of delphinidin. Anthocyanins, including myrtillin, are potent antioxidants.{26210,26209,23825}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Myrtillin is a natural anthocyanin found in plants. It is the 3-glucoside of delphinidin. Anthocyanins, including myrtillin, are potent antioxidants.{26210,26209,23825}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Myrtillin is a natural anthocyanin found in plants. It is the 3-glucoside of delphinidin. Anthocyanins, including myrtillin, are potent antioxidants.{26210,26209,23825}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Myxochelin A is a microbial metabolite that has been found in A. disciformis and has diverse biological activities.{53609} It is active against Gram-positive bacteria, including B. cereus, S. aureus, and M. luteus, but not Gram-negative bacteria or fungi in an agar diffusion assay when used at a concentration of 80 µg/disc. Myxochelin A inhibits 5-lipoxygenase (5-LO) activity with an IC50 value of 1.9 µM for the recombinant human enzyme.{53610} It is cytotoxic to 26-L5 colon cancer cells when used at a concentration of 3 µg/ml.{53611}
Brand:CaymanSKU:26422 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
MZ1 is a hybrid compound that drives the selective proteasomal degradation of bromodomain-containing protein 4 (BRD4).{33482} It is characterized as a proteolysis-targeting chimera (PROTAC) and contains JQ-1, which binds bromo- and extra-terminal (BET) proteins, linked to a ligand for the E3 ubiquitin ligase VHL. MZ1 induces the selective degradation of BRD4 in HeLa cells when used at 0.1-0.5 µM.{33482} At concentrations of 2-10 µM, MZ1 causes the removal of BRD2, BRD3, and BRD4.{33482} BRD protein removal is evident within four hours of adding MZ1 and persists for at least 48 hours, unless MZ1 is removed.{33482}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21622 -Out of stock
MZ1 is a hybrid compound that drives the selective proteasomal degradation of bromodomain-containing protein 4 (BRD4).{33482} It is characterized as a proteolysis-targeting chimera (PROTAC) and contains JQ-1, which binds bromo- and extra-terminal (BET) proteins, linked to a ligand for the E3 ubiquitin ligase VHL. MZ1 induces the selective degradation of BRD4 in HeLa cells when used at 0.1-0.5 µM.{33482} At concentrations of 2-10 µM, MZ1 causes the removal of BRD2, BRD3, and BRD4.{33482} BRD protein removal is evident within four hours of adding MZ1 and persists for at least 48 hours, unless MZ1 is removed.{33482}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21622 -Out of stock
MZ1 is a hybrid compound that drives the selective proteasomal degradation of bromodomain-containing protein 4 (BRD4).{33482} It is characterized as a proteolysis-targeting chimera (PROTAC) and contains JQ-1, which binds bromo- and extra-terminal (BET) proteins, linked to a ligand for the E3 ubiquitin ligase VHL. MZ1 induces the selective degradation of BRD4 in HeLa cells when used at 0.1-0.5 µM.{33482} At concentrations of 2-10 µM, MZ1 causes the removal of BRD2, BRD3, and BRD4.{33482} BRD protein removal is evident within four hours of adding MZ1 and persists for at least 48 hours, unless MZ1 is removed.{33482}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21622 -Out of stock
N-(1-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)propan-2-yl)oleamide binds to the cannabinoid 1 (CB1) receptor with a Ki value of 365 nM in a radioligand binding assay using rat brain homogenate.{36053} It has an EC50 value of 698 nM for the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARα) in a luciferase reporter assay and, in rats, it decreases food intake. It does not inhibit fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH).
Brand:CaymanSKU:9002954 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
N-(1-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)propan-2-yl)oleamide binds to the cannabinoid 1 (CB1) receptor with a Ki value of 365 nM in a radioligand binding assay using rat brain homogenate.{36053} It has an EC50 value of 698 nM for the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARα) in a luciferase reporter assay and, in rats, it decreases food intake. It does not inhibit fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH).
Brand:CaymanSKU:9002954 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
N-(1-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)propan-2-yl)oleamide binds to the cannabinoid 1 (CB1) receptor with a Ki value of 365 nM in a radioligand binding assay using rat brain homogenate.{36053} It has an EC50 value of 698 nM for the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARα) in a luciferase reporter assay and, in rats, it decreases food intake. It does not inhibit fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH).
Brand:CaymanSKU:9002954 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
N-(2-Aminoethyl)maleimide is a thiol-reactive cross-linking agent.{52503,52504} It has been used in the synthesis of maleimide-functionalized heparin hydrogels in the development of growth factor delivery systems and radiotracers for thiol-mediated protein labelling.
Brand:CaymanSKU:30530 - 1 gAvailable on backorder
N-(2-Aminoethyl)maleimide is a thiol-reactive cross-linking agent.{52503,52504} It has been used in the synthesis of maleimide-functionalized heparin hydrogels in the development of growth factor delivery systems and radiotracers for thiol-mediated protein labelling.
Brand:CaymanSKU:30530 - 250 mgAvailable on backorder
N-(2-Aminoethyl)maleimide is a thiol-reactive cross-linking agent.{52503,52504} It has been used in the synthesis of maleimide-functionalized heparin hydrogels in the development of growth factor delivery systems and radiotracers for thiol-mediated protein labelling.
Brand:CaymanSKU:30530 - 500 mgAvailable on backorder
N-(2-Fluorophenethyl)-5-(2-methoxyphenyl)picolinamide is an inhibitor of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF-1) signaling (IC50 = 0.32 μM in a cell-based hypoxia responsive element (HRE) reporter assay under hypoxic conditions).{50774} It inhibits hypoxia-induced increases in HIF-1α levels in MDA-MB-231, SKOV3, and HeLa cells in a concentration-dependent manner. N-(2-Fluorophenethyl)-5-(2-methoxyphenyl)picolinamide also inhibits hypoxia-induced VEGF expression and capillary-like tube formation in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) and inhibits migration and invasion of MDA-MB-231 cells in wound healing and transwell assays under hypoxic conditions. It also reduces lung metastasis in an MDA-MB-231 mouse xenograft model when administered at doses of 15 and 30 mg/kg every other day.
Brand:CaymanSKU:29740 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
N-(2-Fluorophenethyl)-5-(2-methoxyphenyl)picolinamide is an inhibitor of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF-1) signaling (IC50 = 0.32 μM in a cell-based hypoxia responsive element (HRE) reporter assay under hypoxic conditions).{50774} It inhibits hypoxia-induced increases in HIF-1α levels in MDA-MB-231, SKOV3, and HeLa cells in a concentration-dependent manner. N-(2-Fluorophenethyl)-5-(2-methoxyphenyl)picolinamide also inhibits hypoxia-induced VEGF expression and capillary-like tube formation in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) and inhibits migration and invasion of MDA-MB-231 cells in wound healing and transwell assays under hypoxic conditions. It also reduces lung metastasis in an MDA-MB-231 mouse xenograft model when administered at doses of 15 and 30 mg/kg every other day.
Brand:CaymanSKU:29740 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
N-(2-Fluorophenethyl)-5-(2-methoxyphenyl)picolinamide is an inhibitor of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF-1) signaling (IC50 = 0.32 μM in a cell-based hypoxia responsive element (HRE) reporter assay under hypoxic conditions).{50774} It inhibits hypoxia-induced increases in HIF-1α levels in MDA-MB-231, SKOV3, and HeLa cells in a concentration-dependent manner. N-(2-Fluorophenethyl)-5-(2-methoxyphenyl)picolinamide also inhibits hypoxia-induced VEGF expression and capillary-like tube formation in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) and inhibits migration and invasion of MDA-MB-231 cells in wound healing and transwell assays under hypoxic conditions. It also reduces lung metastasis in an MDA-MB-231 mouse xenograft model when administered at doses of 15 and 30 mg/kg every other day.
Brand:CaymanSKU:29740 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-Naphthalimide is an N-substituted 1,8-naphthalimide used as a fluorescent probe and as a precursor for protection of amine groups.{28744} It is used to detect nucleic acids and their precursors, which quench the fluorescence of N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-naphthalimide.{41257} Nucleic acids quench the fluorescence most strongly followed by nucleosides and nucleobases, of which purine bases quench more strongly than pyrimidine bases. N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-Naphthalimide is electroactive and forms adducts with 1,3-dihydroxy benzene and 1,3,5-trihydroxybenzene.{28744} N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-Naphthalimide displays excitation spectra of 330-333 and 344-347 nm with emission spectra of 366-378 nm in solvents of varying polarities, with a higher Stokes shift in less polar solvents.{41256}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-Naphthalimide is an N-substituted 1,8-naphthalimide used as a fluorescent probe and as a precursor for protection of amine groups.{28744} It is used to detect nucleic acids and their precursors, which quench the fluorescence of N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-naphthalimide.{41257} Nucleic acids quench the fluorescence most strongly followed by nucleosides and nucleobases, of which purine bases quench more strongly than pyrimidine bases. N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-Naphthalimide is electroactive and forms adducts with 1,3-dihydroxy benzene and 1,3,5-trihydroxybenzene.{28744} N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-Naphthalimide displays excitation spectra of 330-333 and 344-347 nm with emission spectra of 366-378 nm in solvents of varying polarities, with a higher Stokes shift in less polar solvents.{41256}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-Naphthalimide is an N-substituted 1,8-naphthalimide used as a fluorescent probe and as a precursor for protection of amine groups.{28744} It is used to detect nucleic acids and their precursors, which quench the fluorescence of N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-naphthalimide.{41257} Nucleic acids quench the fluorescence most strongly followed by nucleosides and nucleobases, of which purine bases quench more strongly than pyrimidine bases. N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-Naphthalimide is electroactive and forms adducts with 1,3-dihydroxy benzene and 1,3,5-trihydroxybenzene.{28744} N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-Naphthalimide displays excitation spectra of 330-333 and 344-347 nm with emission spectra of 366-378 nm in solvents of varying polarities, with a higher Stokes shift in less polar solvents.{41256}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
N-(2-phenylethyl)-indomethacin amide (N-2PIA) is one of several aromatic amides of indomethacin reported to be potent and selective reversible inhibitors of COX-2.{8243} N-2PIA inhibits human recombinant and ovine COX-2 with IC50 values of 0.06 and 0.125 µM, respectively.{8243,8513} It is over 400 times less potent as an inhibitor of human recombinant and ovine COX-1. N-2PIA shows anti-inflammatory, antiangiogenic, and cancer chemopreventive activity in various experimental models.{8243}
Brand:CaymanSKU:70272 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
N-(2-phenylethyl)-indomethacin amide (N-2PIA) is one of several aromatic amides of indomethacin reported to be potent and selective reversible inhibitors of COX-2.{8243} N-2PIA inhibits human recombinant and ovine COX-2 with IC50 values of 0.06 and 0.125 µM, respectively.{8243,8513} It is over 400 times less potent as an inhibitor of human recombinant and ovine COX-1. N-2PIA shows anti-inflammatory, antiangiogenic, and cancer chemopreventive activity in various experimental models.{8243}
Brand:CaymanSKU:70272 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
N-(2-phenylethyl)-indomethacin amide (N-2PIA) is one of several aromatic amides of indomethacin reported to be potent and selective reversible inhibitors of COX-2.{8243} N-2PIA inhibits human recombinant and ovine COX-2 with IC50 values of 0.06 and 0.125 µM, respectively.{8243,8513} It is over 400 times less potent as an inhibitor of human recombinant and ovine COX-1. N-2PIA shows anti-inflammatory, antiangiogenic, and cancer chemopreventive activity in various experimental models.{8243}
Brand:CaymanSKU:70272 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
N-(2-phenylethyl)-indomethacin amide (N-2PIA) is one of several aromatic amides of indomethacin reported to be potent and selective reversible inhibitors of COX-2.{8243} N-2PIA inhibits human recombinant and ovine COX-2 with IC50 values of 0.06 and 0.125 µM, respectively.{8243,8513} It is over 400 times less potent as an inhibitor of human recombinant and ovine COX-1. N-2PIA shows anti-inflammatory, antiangiogenic, and cancer chemopreventive activity in various experimental models.{8243}
Brand:CaymanSKU:70272 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
Lidocaine is an anesthetic that blocks voltage-gated Na+ channels (IC50 = 128 µM) with selectivity over L-type Ca2+ channels and GABAA receptors.{25312} Lidocaine can also have pronociceptive effects by activating the transient receptor potential (TRP) channel TRPA1.{23938} N-(2,6-Dimethylphenyl)-2-(ethylmethylamino)acetamide is a lidocaine impurity.{29992,29993}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
Lidocaine is an anesthetic that blocks voltage-gated Na+ channels (IC50 = 128 µM) with selectivity over L-type Ca2+ channels and GABAA receptors.{25312} Lidocaine can also have pronociceptive effects by activating the transient receptor potential (TRP) channel TRPA1.{23938} N-(2,6-Dimethylphenyl)-2-(ethylmethylamino)acetamide is a lidocaine impurity.{29992,29993}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
Lidocaine is an anesthetic that blocks voltage-gated Na+ channels (IC50 = 128 µM) with selectivity over L-type Ca2+ channels and GABAA receptors.{25312} Lidocaine can also have pronociceptive effects by activating the transient receptor potential (TRP) channel TRPA1.{23938} N-(2,6-Dimethylphenyl)-2-(ethylmethylamino)acetamide is a lidocaine impurity.{29992,29993}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
N-(3-Aminopropyl)acetamide is a monoacetylated polyamine that can be used as a building block in the synthesis of heterocyclic compounds. Polyamines are promising biochemical markers of cancer and many other pathophysiological conditions, thus their concentrations in biological fluids have been analyzed.{32370}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9002787 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
N-(3-Aminopropyl)acetamide is a monoacetylated polyamine that can be used as a building block in the synthesis of heterocyclic compounds. Polyamines are promising biochemical markers of cancer and many other pathophysiological conditions, thus their concentrations in biological fluids have been analyzed.{32370}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9002787 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
N-(3-Aminopropyl)acetamide is a monoacetylated polyamine that can be used as a building block in the synthesis of heterocyclic compounds. Polyamines are promising biochemical markers of cancer and many other pathophysiological conditions, thus their concentrations in biological fluids have been analyzed.{32370}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9002787 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
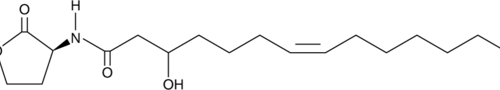
N-(3-hydroxy-7-cis tetradecenoyl)-L-Homoserine lactone is a long-chain N-acyl-homoserine lactone (AHL) produced by some Gram-negative bacteria and is involved in quorum sensing.{33808} Quorum sensing enables bacteria to change gene expression based on cues from nearby bacteria and from eukaryotic hosts about nutrients, environmental conditions, or threats.{15399} Due to the benefit of quorum sensing for bacterial survival, quorum sensing molecules are potential targets for controlling bacterial infections.{13466} In mouse and human leukocyte immunoassays using LPS-stimulated macrophages, N-(3-hydroxy-7-cis tetradecenoyl)-L-homoserine lactone did not have an effect on cytokine or antibody production.{33809}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9002939 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
N-(3-hydroxy-7-cis tetradecenoyl)-L-Homoserine lactone is a long-chain N-acyl-homoserine lactone (AHL) produced by some Gram-negative bacteria and is involved in quorum sensing.{33808} Quorum sensing enables bacteria to change gene expression based on cues from nearby bacteria and from eukaryotic hosts about nutrients, environmental conditions, or threats.{15399} Due to the benefit of quorum sensing for bacterial survival, quorum sensing molecules are potential targets for controlling bacterial infections.{13466} In mouse and human leukocyte immunoassays using LPS-stimulated macrophages, N-(3-hydroxy-7-cis tetradecenoyl)-L-homoserine lactone did not have an effect on cytokine or antibody production.{33809}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9002939 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
N-(3-hydroxy-7-cis tetradecenoyl)-L-Homoserine lactone is a long-chain N-acyl-homoserine lactone (AHL) produced by some Gram-negative bacteria and is involved in quorum sensing.{33808} Quorum sensing enables bacteria to change gene expression based on cues from nearby bacteria and from eukaryotic hosts about nutrients, environmental conditions, or threats.{15399} Due to the benefit of quorum sensing for bacterial survival, quorum sensing molecules are potential targets for controlling bacterial infections.{13466} In mouse and human leukocyte immunoassays using LPS-stimulated macrophages, N-(3-hydroxy-7-cis tetradecenoyl)-L-homoserine lactone did not have an effect on cytokine or antibody production.{33809}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9002939 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
N-(3-hydroxy-7-cis tetradecenoyl)-L-Homoserine lactone is a long-chain N-acyl-homoserine lactone (AHL) produced by some Gram-negative bacteria and is involved in quorum sensing.{33808} Quorum sensing enables bacteria to change gene expression based on cues from nearby bacteria and from eukaryotic hosts about nutrients, environmental conditions, or threats.{15399} Due to the benefit of quorum sensing for bacterial survival, quorum sensing molecules are potential targets for controlling bacterial infections.{13466} In mouse and human leukocyte immunoassays using LPS-stimulated macrophages, N-(3-hydroxy-7-cis tetradecenoyl)-L-homoserine lactone did not have an effect on cytokine or antibody production.{33809}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9002939 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
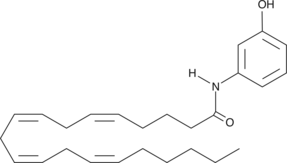
N-(3-hydroxyphenyl)-Arachidonoyl amide (3-HPA) is an analog of AM404 (N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-arachidonoyl amide), which is a selective inhibitor of carrier-mediated transport of arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA).{4894} 3-HPA is metabolized by both cyclooxygenase-1 (COX-1) and COX-2 and was found to selectively and irreversibly inhibit COX-2 with an IC50 value of 2 µM.{14589}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007704 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
N-(3-hydroxyphenyl)-Arachidonoyl amide (3-HPA) is an analog of AM404 (N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-arachidonoyl amide), which is a selective inhibitor of carrier-mediated transport of arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA).{4894} 3-HPA is metabolized by both cyclooxygenase-1 (COX-1) and COX-2 and was found to selectively and irreversibly inhibit COX-2 with an IC50 value of 2 µM.{14589}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007704 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
N-(3-hydroxyphenyl)-Arachidonoyl amide (3-HPA) is an analog of AM404 (N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-arachidonoyl amide), which is a selective inhibitor of carrier-mediated transport of arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA).{4894} 3-HPA is metabolized by both cyclooxygenase-1 (COX-1) and COX-2 and was found to selectively and irreversibly inhibit COX-2 with an IC50 value of 2 µM.{14589}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007704 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
N-(3-hydroxyphenyl)-Arachidonoyl amide (3-HPA) is an analog of AM404 (N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-arachidonoyl amide), which is a selective inhibitor of carrier-mediated transport of arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA).{4894} 3-HPA is metabolized by both cyclooxygenase-1 (COX-1) and COX-2 and was found to selectively and irreversibly inhibit COX-2 with an IC50 value of 2 µM.{14589}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007704 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
N-(3-pyridyl)-indomethacin amide (N-3PyIA) is one of several aromatic amides of indomethacin reported to be potent and selective reversible inhibitors of COX-2.{8243} N-3PyIA selectively inhibits human recombinant COX-2 with an IC50 of 0.052 µM. It is about 1,300 times less potent as an inhibitor of ovine recombinant COX-1.{8243} However, N-3PyIA is not selective as an inhibitor of ovine seminal vesicular COX-1 and ovine placental COX-2. The IC50 values for ovine COX-1 and -2 are 75 and 50 µM, respectively.{8513}
Brand:CaymanSKU:70274 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
N-(3-pyridyl)-indomethacin amide (N-3PyIA) is one of several aromatic amides of indomethacin reported to be potent and selective reversible inhibitors of COX-2.{8243} N-3PyIA selectively inhibits human recombinant COX-2 with an IC50 of 0.052 µM. It is about 1,300 times less potent as an inhibitor of ovine recombinant COX-1.{8243} However, N-3PyIA is not selective as an inhibitor of ovine seminal vesicular COX-1 and ovine placental COX-2. The IC50 values for ovine COX-1 and -2 are 75 and 50 µM, respectively.{8513}
Brand:CaymanSKU:70274 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
N-(3-pyridyl)-indomethacin amide (N-3PyIA) is one of several aromatic amides of indomethacin reported to be potent and selective reversible inhibitors of COX-2.{8243} N-3PyIA selectively inhibits human recombinant COX-2 with an IC50 of 0.052 µM. It is about 1,300 times less potent as an inhibitor of ovine recombinant COX-1.{8243} However, N-3PyIA is not selective as an inhibitor of ovine seminal vesicular COX-1 and ovine placental COX-2. The IC50 values for ovine COX-1 and -2 are 75 and 50 µM, respectively.{8513}
Brand:CaymanSKU:70274 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
N-(3-pyridyl)-indomethacin amide (N-3PyIA) is one of several aromatic amides of indomethacin reported to be potent and selective reversible inhibitors of COX-2.{8243} N-3PyIA selectively inhibits human recombinant COX-2 with an IC50 of 0.052 µM. It is about 1,300 times less potent as an inhibitor of ovine recombinant COX-1.{8243} However, N-3PyIA is not selective as an inhibitor of ovine seminal vesicular COX-1 and ovine placental COX-2. The IC50 values for ovine COX-1 and -2 are 75 and 50 µM, respectively.{8513}
Brand:CaymanSKU:70274 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
N-(4-acetamidophenyl)-indomethacin amide (N-4-AIA) is one of several aromatic amides of indomethacin reported to be potent and selective reversible inhibitors of COX-2.{8243} N-4-AIA inhibits human recombinant and ovine COX-2 with IC50 values of 0.12 and 0.625 µM, respectively.{8243,8513} It is about 400 times less potent as an inhibitor of human recombinant COX-1 and 80 times less potent as an inhibitor of ovine COX-1 than ovine COX-2.
Brand:CaymanSKU:70278 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
N-(4-acetamidophenyl)-indomethacin amide (N-4-AIA) is one of several aromatic amides of indomethacin reported to be potent and selective reversible inhibitors of COX-2.{8243} N-4-AIA inhibits human recombinant and ovine COX-2 with IC50 values of 0.12 and 0.625 µM, respectively.{8243,8513} It is about 400 times less potent as an inhibitor of human recombinant COX-1 and 80 times less potent as an inhibitor of ovine COX-1 than ovine COX-2.
Brand:CaymanSKU:70278 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
N-(4-acetamidophenyl)-indomethacin amide (N-4-AIA) is one of several aromatic amides of indomethacin reported to be potent and selective reversible inhibitors of COX-2.{8243} N-4-AIA inhibits human recombinant and ovine COX-2 with IC50 values of 0.12 and 0.625 µM, respectively.{8243,8513} It is about 400 times less potent as an inhibitor of human recombinant COX-1 and 80 times less potent as an inhibitor of ovine COX-1 than ovine COX-2.
Brand:CaymanSKU:70278 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
N-(4-acetamidophenyl)-indomethacin amide (N-4-AIA) is one of several aromatic amides of indomethacin reported to be potent and selective reversible inhibitors of COX-2.{8243} N-4-AIA inhibits human recombinant and ovine COX-2 with IC50 values of 0.12 and 0.625 µM, respectively.{8243,8513} It is about 400 times less potent as an inhibitor of human recombinant COX-1 and 80 times less potent as an inhibitor of ovine COX-1 than ovine COX-2.
Brand:CaymanSKU:70278 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
N-(8Z-Heptadecen-1-yl)-O-(3-pyridylmethyl)carbamate is a synthetic analog of the long-chain fatty acid amides (macamides or macaenes) isolated from the maca (L. meyenii) plant, which are structurally related to cannabinoids.{28386} Nineteen macamides have currently been identified and many are recognized as potent inhibitors of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) and demonstrate selective antiproliferative activity against diverse cancer cell lines.{28386,28387} N-(8Z-Heptadecen-1-yl)-O-(3-pyridylmethyl)carbamate irreversibly inhibits FAAH with an IC50 value of 0.153 µM.{28386}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9002365 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
N-(8Z-Heptadecen-1-yl)-O-(3-pyridylmethyl)carbamate is a synthetic analog of the long-chain fatty acid amides (macamides or macaenes) isolated from the maca (L. meyenii) plant, which are structurally related to cannabinoids.{28386} Nineteen macamides have currently been identified and many are recognized as potent inhibitors of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) and demonstrate selective antiproliferative activity against diverse cancer cell lines.{28386,28387} N-(8Z-Heptadecen-1-yl)-O-(3-pyridylmethyl)carbamate irreversibly inhibits FAAH with an IC50 value of 0.153 µM.{28386}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9002365 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
N-(8Z-Heptadecen-1-yl)-O-(3-pyridylmethyl)carbamate is a synthetic analog of the long-chain fatty acid amides (macamides or macaenes) isolated from the maca (L. meyenii) plant, which are structurally related to cannabinoids.{28386} Nineteen macamides have currently been identified and many are recognized as potent inhibitors of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) and demonstrate selective antiproliferative activity against diverse cancer cell lines.{28386,28387} N-(8Z-Heptadecen-1-yl)-O-(3-pyridylmethyl)carbamate irreversibly inhibits FAAH with an IC50 value of 0.153 µM.{28386}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9002365 - 250 mgAvailable on backorder
N-(8Z-Heptadecen-1-yl)-O-(3-pyridylmethyl)carbamate is a synthetic analog of the long-chain fatty acid amides (macamides or macaenes) isolated from the maca (L. meyenii) plant, which are structurally related to cannabinoids.{28386} Nineteen macamides have currently been identified and many are recognized as potent inhibitors of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) and demonstrate selective antiproliferative activity against diverse cancer cell lines.{28386,28387} N-(8Z-Heptadecen-1-yl)-O-(3-pyridylmethyl)carbamate irreversibly inhibits FAAH with an IC50 value of 0.153 µM.{28386}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9002365 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
N-(diphenylmethylene) Glycine benzyl ester is a synthetic intermediate useful for pharmaceutical synthesis.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007089 - 1 gAvailable on backorder
N-(diphenylmethylene) Glycine benzyl ester is a synthetic intermediate useful for pharmaceutical synthesis.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007089 - 10 gAvailable on backorder
N-(diphenylmethylene) Glycine benzyl ester is a synthetic intermediate useful for pharmaceutical synthesis.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007089 - 5 gAvailable on backorder
N-(diphenylmethylene) Glycine benzyl ester is a synthetic intermediate useful for pharmaceutical synthesis.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007089 - 500 mgAvailable on backorder
N-(n-Butyl)deoxygalactonojirimycin (NB-DGJ) is an inhibitor of the glycolipid biosynthesis enzyme glucosylceramide synthase and the glycolipid catabolic enzymes glucocerebrosidase (GBA) and β-glucosidase 2 (GBA2).{31624,49490,49491,49492,50926} It also inhibits acid α-glucosidase, sucrase, maltase, and lactase.{49492} NB-DGJ (0.5-500 µM) reduces glycolipid levels in HL-60 and WEHI-3B cells.{31624} It decreases brain ganglioside levels in a Glb1-/- neonatal mouse model of GM1 gangliosidosis when administered intraperitoneally at doses of 600 and 1,200 mg/kg four times per day for three days.{31622} NB-DGJ (1-1,200 mg/kg per day for 35 days) increases testicular glucosylceramide levels in mice.{49490} NB-DGJ induces abnormal spermatid and acrosome formation, as well as reduces motility, in isolated mouse epididymal sperm when administered at doses of 15, 25, and 50 mg/kg per day.{50926} It also induces infertility, an effect that is reversed by withdrawal, in the same model.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
N-(n-Butyl)deoxygalactonojirimycin (NB-DGJ) is an inhibitor of the glycolipid biosynthesis enzyme glucosylceramide synthase and the glycolipid catabolic enzymes glucocerebrosidase (GBA) and β-glucosidase 2 (GBA2).{31624,49490,49491,49492,50926} It also inhibits acid α-glucosidase, sucrase, maltase, and lactase.{49492} NB-DGJ (0.5-500 µM) reduces glycolipid levels in HL-60 and WEHI-3B cells.{31624} It decreases brain ganglioside levels in a Glb1-/- neonatal mouse model of GM1 gangliosidosis when administered intraperitoneally at doses of 600 and 1,200 mg/kg four times per day for three days.{31622} NB-DGJ (1-1,200 mg/kg per day for 35 days) increases testicular glucosylceramide levels in mice.{49490} NB-DGJ induces abnormal spermatid and acrosome formation, as well as reduces motility, in isolated mouse epididymal sperm when administered at doses of 15, 25, and 50 mg/kg per day.{50926} It also induces infertility, an effect that is reversed by withdrawal, in the same model.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
N-(n-Butyl)deoxygalactonojirimycin (NB-DGJ) is an inhibitor of the glycolipid biosynthesis enzyme glucosylceramide synthase and the glycolipid catabolic enzymes glucocerebrosidase (GBA) and β-glucosidase 2 (GBA2).{31624,49490,49491,49492,50926} It also inhibits acid α-glucosidase, sucrase, maltase, and lactase.{49492} NB-DGJ (0.5-500 µM) reduces glycolipid levels in HL-60 and WEHI-3B cells.{31624} It decreases brain ganglioside levels in a Glb1-/- neonatal mouse model of GM1 gangliosidosis when administered intraperitoneally at doses of 600 and 1,200 mg/kg four times per day for three days.{31622} NB-DGJ (1-1,200 mg/kg per day for 35 days) increases testicular glucosylceramide levels in mice.{49490} NB-DGJ induces abnormal spermatid and acrosome formation, as well as reduces motility, in isolated mouse epididymal sperm when administered at doses of 15, 25, and 50 mg/kg per day.{50926} It also induces infertility, an effect that is reversed by withdrawal, in the same model.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
N-(p-amylcinnamoyl) Anthranilic acid (ACA) is a channel blocker that acts on several transient receptor potential (TRP) channels, including TRPM2, TRPM8, and TRPC6 (IC50 = 1.7, 3.8, and 2.3 μM, respectively).{24045,24047} It is a weak inhibitor of TRPV1.{24047} ACA is also an inhibitor of phospholipase A2, blocking the release of arachidonic acid when given at 50 μM.{24044,24046}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-N-(p-amylcinnamoyl) Anthranilic acid (ACA) is a channel blocker that acts on several transient receptor potential (TRP) channels, including TRPM2, TRPM8, and TRPC6 (IC50 = 1.7, 3.8, and 2.3 μM, respectively).{24045,24047} It is a weak inhibitor of TRPV1.{24047} ACA is also an inhibitor of phospholipase A2, blocking the release of arachidonic acid when given at 50 μM.{24044,24046}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-N-(p-amylcinnamoyl) Anthranilic acid (ACA) is a channel blocker that acts on several transient receptor potential (TRP) channels, including TRPM2, TRPM8, and TRPC6 (IC50 = 1.7, 3.8, and 2.3 μM, respectively).{24045,24047} It is a weak inhibitor of TRPV1.{24047} ACA is also an inhibitor of phospholipase A2, blocking the release of arachidonic acid when given at 50 μM.{24044,24046}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-N-(p-amylcinnamoyl) Anthranilic acid (ACA) is a channel blocker that acts on several transient receptor potential (TRP) channels, including TRPM2, TRPM8, and TRPC6 (IC50 = 1.7, 3.8, and 2.3 μM, respectively).{24045,24047} It is a weak inhibitor of TRPV1.{24047} ACA is also an inhibitor of phospholipase A2, blocking the release of arachidonic acid when given at 50 μM.{24044,24046}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-N-(p-Coumaroyl) serotonin is an antioxidative phenolic naturally found in plants, including safflower seed and millet grain.{29000,29005} It ameliorates atherosclerosis in vivo, reducing lesion area in mice and rabbits.{29000,29002} N-(p-Coumaroyl) serotonin also suppresses inflammatory cytokine generation by human monocytes, augments fibroblast proliferation, and promotes relaxation of vascular smooth muscle cells in vitro.{29001,29003,29004}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
N-(p-Coumaroyl) serotonin is an antioxidative phenolic naturally found in plants, including safflower seed and millet grain.{29000,29005} It ameliorates atherosclerosis in vivo, reducing lesion area in mice and rabbits.{29000,29002} N-(p-Coumaroyl) serotonin also suppresses inflammatory cytokine generation by human monocytes, augments fibroblast proliferation, and promotes relaxation of vascular smooth muscle cells in vitro.{29001,29003,29004}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
N-(p-Coumaroyl) serotonin is an antioxidative phenolic naturally found in plants, including safflower seed and millet grain.{29000,29005} It ameliorates atherosclerosis in vivo, reducing lesion area in mice and rabbits.{29000,29002} N-(p-Coumaroyl) serotonin also suppresses inflammatory cytokine generation by human monocytes, augments fibroblast proliferation, and promotes relaxation of vascular smooth muscle cells in vitro.{29001,29003,29004}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
N-(p-Coumaroyl) serotonin is an antioxidative phenolic naturally found in plants, including safflower seed and millet grain.{29000,29005} It ameliorates atherosclerosis in vivo, reducing lesion area in mice and rabbits.{29000,29002} N-(p-Coumaroyl) serotonin also suppresses inflammatory cytokine generation by human monocytes, augments fibroblast proliferation, and promotes relaxation of vascular smooth muscle cells in vitro.{29001,29003,29004}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
N-(p-Tosyl)-GPR-pNA is a colorimetric substrate for thrombin.{48594} Thrombin preferentially binds to and cleaves the Gly-Pro-Arg (GPR) peptide sequence to release p-nitroanilide (pNA), which can be quantified by colorimetric detection at 405 nm as a measure of thrombin activity.
Brand:CaymanSKU:27568 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
N-(p-Tosyl)-GPR-pNA is a colorimetric substrate for thrombin.{48594} Thrombin preferentially binds to and cleaves the Gly-Pro-Arg (GPR) peptide sequence to release p-nitroanilide (pNA), which can be quantified by colorimetric detection at 405 nm as a measure of thrombin activity.
Brand:CaymanSKU:27568 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
N-(p-Tosyl)-GPR-pNA is a colorimetric substrate for thrombin.{48594} Thrombin preferentially binds to and cleaves the Gly-Pro-Arg (GPR) peptide sequence to release p-nitroanilide (pNA), which can be quantified by colorimetric detection at 405 nm as a measure of thrombin activity.
Brand:CaymanSKU:27568 - 250 mgAvailable on backorder
N-(p-Tosyl)-GPR-pNA is a colorimetric substrate for thrombin.{48594} Thrombin preferentially binds to and cleaves the Gly-Pro-Arg (GPR) peptide sequence to release p-nitroanilide (pNA), which can be quantified by colorimetric detection at 405 nm as a measure of thrombin activity.
Brand:CaymanSKU:27568 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
Certain chronic neurologic disorders, such as Parkinson’s disease, are caused by an insufficiency of the neurotransmitter dopamine secondary to the degeneration of substantia nigra dopaminergic neurons.{7161} N-(α-Linolenoyl) tyrosine (NALT) is a simple α-amide conjugate between the ω-3 essential fatty acid α-linolenate and the amino acid tyrosine. α-Linolenate is an important precursor to docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), a prominent brain polyunsaturated fatty acid, while tyrosine is the metabolic precursor for neuronal dopamine synthesis. NALT was prepared as a method for enhancing central nervous system (CNS) dopamine content by facilitated transport of the tyrosine precursor across the blood-brain barrier.{10323} In experimental rat models of dopamine insufficiency, NALT increased CNS dopamine levels and exhibited an activity profile consistent with an anti-Parkinson’s therapeutic agent.{10323}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10032 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Certain chronic neurologic disorders, such as Parkinson’s disease, are caused by an insufficiency of the neurotransmitter dopamine secondary to the degeneration of substantia nigra dopaminergic neurons.{7161} N-(α-Linolenoyl) tyrosine (NALT) is a simple α-amide conjugate between the ω-3 essential fatty acid α-linolenate and the amino acid tyrosine. α-Linolenate is an important precursor to docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), a prominent brain polyunsaturated fatty acid, while tyrosine is the metabolic precursor for neuronal dopamine synthesis. NALT was prepared as a method for enhancing central nervous system (CNS) dopamine content by facilitated transport of the tyrosine precursor across the blood-brain barrier.{10323} In experimental rat models of dopamine insufficiency, NALT increased CNS dopamine levels and exhibited an activity profile consistent with an anti-Parkinson’s therapeutic agent.{10323}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10032 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
Certain chronic neurologic disorders, such as Parkinson’s disease, are caused by an insufficiency of the neurotransmitter dopamine secondary to the degeneration of substantia nigra dopaminergic neurons.{7161} N-(α-Linolenoyl) tyrosine (NALT) is a simple α-amide conjugate between the ω-3 essential fatty acid α-linolenate and the amino acid tyrosine. α-Linolenate is an important precursor to docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), a prominent brain polyunsaturated fatty acid, while tyrosine is the metabolic precursor for neuronal dopamine synthesis. NALT was prepared as a method for enhancing central nervous system (CNS) dopamine content by facilitated transport of the tyrosine precursor across the blood-brain barrier.{10323} In experimental rat models of dopamine insufficiency, NALT increased CNS dopamine levels and exhibited an activity profile consistent with an anti-Parkinson’s therapeutic agent.{10323}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10032 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Certain chronic neurologic disorders, such as Parkinson’s disease, are caused by an insufficiency of the neurotransmitter dopamine secondary to the degeneration of substantia nigra dopaminergic neurons.{7161} N-(α-Linolenoyl) tyrosine (NALT) is a simple α-amide conjugate between the ω-3 essential fatty acid α-linolenate and the amino acid tyrosine. α-Linolenate is an important precursor to docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), a prominent brain polyunsaturated fatty acid, while tyrosine is the metabolic precursor for neuronal dopamine synthesis. NALT was prepared as a method for enhancing central nervous system (CNS) dopamine content by facilitated transport of the tyrosine precursor across the blood-brain barrier.{10323} In experimental rat models of dopamine insufficiency, NALT increased CNS dopamine levels and exhibited an activity profile consistent with an anti-Parkinson’s therapeutic agent.{10323}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10032 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density.{15370} This regulatory process manifests itself with a variety of phenotypes including biofilm formation and virulence factor production.{13434} Coordinated gene expression is achieved by the production, release, and detection of small diffusible signal molecules called autoinducers. The N-acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) comprise one such class of autoinducers, each of which generally consists of a fatty acid coupled with homoserine lactone (HSL). Regulation of bacterial quorum sensing signaling systems to inhibit pathogenesis represents a new approach to antimicrobial therapy in the treatment of infectious diseases.{15369} AHLs vary in acyl group length (C4-C18), in the substitution of C3 (hydrogen, hydroxyl, or oxo group), and in the presence or absence of one or more carbon-carbon double bonds in the fatty acid chain. These differences confer signal specificity through the affinity of transcriptional regulators of the LuxR family.{15398} In one of the most-studied quorum-sensing systems in gram-negative bacteria, the LuxI AHL synthase catalyzes the production of N-(β-ketocaproyl)-L-homoserine lactone utilizing S-adenosylmethionine and hexanoyl-acyl carrier protein as reaction substrates in the marine bioluminescence bacterium V. fischeri.{16881} At increased populations of the bacteria, localized higher concentrations of 3-O-C6-HSL, an endogenous ligand to transcriptional factor LuxR, leads to increased production of both the AHL synthase and proteins responsible for bioluminescence.{15370} Numerous other species of bacteria also employ N-(β-ketocaproyl)-L-homoserine lactone in cell-to-cell communication.{16800,15932,16767,15399}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10011207 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density.{15370} This regulatory process manifests itself with a variety of phenotypes including biofilm formation and virulence factor production.{13434} Coordinated gene expression is achieved by the production, release, and detection of small diffusible signal molecules called autoinducers. The N-acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) comprise one such class of autoinducers, each of which generally consists of a fatty acid coupled with homoserine lactone (HSL). Regulation of bacterial quorum sensing signaling systems to inhibit pathogenesis represents a new approach to antimicrobial therapy in the treatment of infectious diseases.{15369} AHLs vary in acyl group length (C4-C18), in the substitution of C3 (hydrogen, hydroxyl, or oxo group), and in the presence or absence of one or more carbon-carbon double bonds in the fatty acid chain. These differences confer signal specificity through the affinity of transcriptional regulators of the LuxR family.{15398} In one of the most-studied quorum-sensing systems in gram-negative bacteria, the LuxI AHL synthase catalyzes the production of N-(β-ketocaproyl)-L-homoserine lactone utilizing S-adenosylmethionine and hexanoyl-acyl carrier protein as reaction substrates in the marine bioluminescence bacterium V. fischeri.{16881} At increased populations of the bacteria, localized higher concentrations of 3-O-C6-HSL, an endogenous ligand to transcriptional factor LuxR, leads to increased production of both the AHL synthase and proteins responsible for bioluminescence.{15370} Numerous other species of bacteria also employ N-(β-ketocaproyl)-L-homoserine lactone in cell-to-cell communication.{16800,15932,16767,15399}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10011207 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density.{15370} This regulatory process manifests itself with a variety of phenotypes including biofilm formation and virulence factor production.{13434} Coordinated gene expression is achieved by the production, release, and detection of small diffusible signal molecules called autoinducers. The N-acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) comprise one such class of autoinducers, each of which generally consists of a fatty acid coupled with homoserine lactone (HSL). Regulation of bacterial quorum sensing signaling systems to inhibit pathogenesis represents a new approach to antimicrobial therapy in the treatment of infectious diseases.{15369} AHLs vary in acyl group length (C4-C18), in the substitution of C3 (hydrogen, hydroxyl, or oxo group), and in the presence or absence of one or more carbon-carbon double bonds in the fatty acid chain. These differences confer signal specificity through the affinity of transcriptional regulators of the LuxR family.{15398} In one of the most-studied quorum-sensing systems in gram-negative bacteria, the LuxI AHL synthase catalyzes the production of N-(β-ketocaproyl)-L-homoserine lactone utilizing S-adenosylmethionine and hexanoyl-acyl carrier protein as reaction substrates in the marine bioluminescence bacterium V. fischeri.{16881} At increased populations of the bacteria, localized higher concentrations of 3-O-C6-HSL, an endogenous ligand to transcriptional factor LuxR, leads to increased production of both the AHL synthase and proteins responsible for bioluminescence.{15370} Numerous other species of bacteria also employ N-(β-ketocaproyl)-L-homoserine lactone in cell-to-cell communication.{16800,15932,16767,15399}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10011207 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density.{15370} This regulatory process manifests itself with a variety of phenotypes including biofilm formation and virulence factor production.{13434} Coordinated gene expression is achieved by the production, release, and detection of small diffusible signal molecules called autoinducers. The N-acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) comprise one such class of autoinducers, each of which generally consists of a fatty acid coupled with homoserine lactone (HSL). Regulation of bacterial quorum sensing signaling systems to inhibit pathogenesis represents a new approach to antimicrobial therapy in the treatment of infectious diseases.{15369} AHLs vary in acyl group length (C4-C18), in the substitution of C3 (hydrogen, hydroxyl, or oxo group), and in the presence or absence of one or more carbon-carbon double bonds in the fatty acid chain. These differences confer signal specificity through the affinity of transcriptional regulators of the LuxR family.{15398} In one of the most-studied quorum-sensing systems in gram-negative bacteria, the LuxI AHL synthase catalyzes the production of N-(β-ketocaproyl)-L-homoserine lactone utilizing S-adenosylmethionine and hexanoyl-acyl carrier protein as reaction substrates in the marine bioluminescence bacterium V. fischeri.{16881} At increased populations of the bacteria, localized higher concentrations of 3-O-C6-HSL, an endogenous ligand to transcriptional factor LuxR, leads to increased production of both the AHL synthase and proteins responsible for bioluminescence.{15370} Numerous other species of bacteria also employ N-(β-ketocaproyl)-L-homoserine lactone in cell-to-cell communication.{16800,15932,16767,15399}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10011207 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
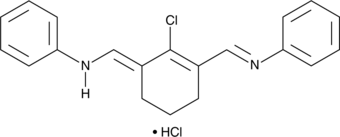
N-[(3-(Anilinomethylene)-2-chloro-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)methylene]aniline is a building block.{53717,53718} It has been used in the synthesis of various cyanine-containing dyes.
Brand:CaymanSKU:30560 - 1 gAvailable on backorder