Cayman
Showing 26851–27000 of 45550 results
-
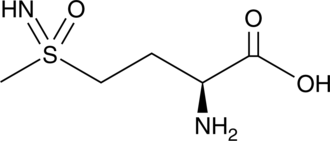
L-Methionine-(S,R)-sulfoximine is an inhibitor of glutamine synthetase and a sulfoximine derivative of L-methionine.{46389} It inhibits pea glutamine synthetase by 31 to 64% when used at concentrations ranging from 5 to 25 µM following preincubation with L-glutamine, an effect that is absent without L-glutamine preincubation. It also inhibits glutamine synthetase in isolated chick embryo retinas.{46390}
Brand:CaymanSKU:27608 - 1 gAvailable on backorder
L-Methionine-(S,R)-sulfoximine is an inhibitor of glutamine synthetase and a sulfoximine derivative of L-methionine.{46389} It inhibits pea glutamine synthetase by 31 to 64% when used at concentrations ranging from 5 to 25 µM following preincubation with L-glutamine, an effect that is absent without L-glutamine preincubation. It also inhibits glutamine synthetase in isolated chick embryo retinas.{46390}
Brand:CaymanSKU:27608 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
L-Methionine-(S,R)-sulfoximine is an inhibitor of glutamine synthetase and a sulfoximine derivative of L-methionine.{46389} It inhibits pea glutamine synthetase by 31 to 64% when used at concentrations ranging from 5 to 25 µM following preincubation with L-glutamine, an effect that is absent without L-glutamine preincubation. It also inhibits glutamine synthetase in isolated chick embryo retinas.{46390}
Brand:CaymanSKU:27608 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
L-Methionine-(S,R)-sulfoximine is an inhibitor of glutamine synthetase and a sulfoximine derivative of L-methionine.{46389} It inhibits pea glutamine synthetase by 31 to 64% when used at concentrations ranging from 5 to 25 µM following preincubation with L-glutamine, an effect that is absent without L-glutamine preincubation. It also inhibits glutamine synthetase in isolated chick embryo retinas.{46390}
Brand:CaymanSKU:27608 - 500 mgAvailable on backorder
L-Mimosine is a non-protein amino acid that can be isolated from certain plants and fungi. It chelates iron and copper and has been shown to reduce iron overload in animal models.{31870,31871} L-Mimosine inhibits certain enzymes that contain iron or copper, including arginase (IC50 = 3.7 µM), polyphenoloxidase, and dopamine hydroxylase.{31871,31867,31869} It also inhibits the iron-containing enzyme deoxyhypusine hydroxlase, preventing the synthesis of the eukaryotic initiation factor 5A and blocking cell cycling.{31868}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-L-Mimosine is a non-protein amino acid that can be isolated from certain plants and fungi. It chelates iron and copper and has been shown to reduce iron overload in animal models.{31870,31871} L-Mimosine inhibits certain enzymes that contain iron or copper, including arginase (IC50 = 3.7 µM), polyphenoloxidase, and dopamine hydroxylase.{31871,31867,31869} It also inhibits the iron-containing enzyme deoxyhypusine hydroxlase, preventing the synthesis of the eukaryotic initiation factor 5A and blocking cell cycling.{31868}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-L-Mimosine is a non-protein amino acid that can be isolated from certain plants and fungi. It chelates iron and copper and has been shown to reduce iron overload in animal models.{31870,31871} L-Mimosine inhibits certain enzymes that contain iron or copper, including arginase (IC50 = 3.7 µM), polyphenoloxidase, and dopamine hydroxylase.{31871,31867,31869} It also inhibits the iron-containing enzyme deoxyhypusine hydroxlase, preventing the synthesis of the eukaryotic initiation factor 5A and blocking cell cycling.{31868}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-L-Mimosine is a non-protein amino acid that can be isolated from certain plants and fungi. It chelates iron and copper and has been shown to reduce iron overload in animal models.{31870,31871} L-Mimosine inhibits certain enzymes that contain iron or copper, including arginase (IC50 = 3.7 µM), polyphenoloxidase, and dopamine hydroxylase.{31871,31867,31869} It also inhibits the iron-containing enzyme deoxyhypusine hydroxlase, preventing the synthesis of the eukaryotic initiation factor 5A and blocking cell cycling.{31868}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Ins(1,4,5)P3 is an isomer of the biologically important D-myo-inositol-1,4,5-triphosphate. Unlike its isomer, Ins(1,4,5)P3 does not evoke a rise in intracellular calcium when added to cells.{17407} It is not known if Ins(1,4,5)P3 can act as a competitive inhibitor of biologically-active inositol phosphates.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008426 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Ins(1,4,5)P3 is an isomer of the biologically important D-myo-inositol-1,4,5-triphosphate. Unlike its isomer, Ins(1,4,5)P3 does not evoke a rise in intracellular calcium when added to cells.{17407} It is not known if Ins(1,4,5)P3 can act as a competitive inhibitor of biologically-active inositol phosphates.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008426 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Ins(1,4,5)P3 is an isomer of the biologically important D-myo-inositol-1,4,5-triphosphate. Unlike its isomer, Ins(1,4,5)P3 does not evoke a rise in intracellular calcium when added to cells.{17407} It is not known if Ins(1,4,5)P3 can act as a competitive inhibitor of biologically-active inositol phosphates.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008426 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
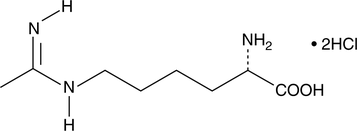
L-NAME requires hydrolysis of the methyl ester by cellular esterases to become a fully functional inhibitor (L-NNA).{5433} L-NNA exhibits some selectivity for inhibition of neuronal and endothelial isoforms. It exhibits Ki values of 15 nM, 39 nM, and 4.4 µM for nNOS (bovine), eNOS (human), and iNOS (mouse), respectively.{5344,1857,5648} The reported Ki value for the inhibition of iNOS ranges from 4-65 µM.{1857,1901} L-NAME inhibits cGMP formation in endothelial cells with an IC50 of 3.1 µM (in the presence of 30 µM arginine) and reverses the vasodilation effects of acetylcholine in rat aorta rings with an EC50 of 0.54 µM.{1211,1855}
Brand:CaymanSKU:80210 - 1 gAvailable on backorder
L-NAME requires hydrolysis of the methyl ester by cellular esterases to become a fully functional inhibitor (L-NNA).{5433} L-NNA exhibits some selectivity for inhibition of neuronal and endothelial isoforms. It exhibits Ki values of 15 nM, 39 nM, and 4.4 µM for nNOS (bovine), eNOS (human), and iNOS (mouse), respectively.{5344,1857,5648} The reported Ki value for the inhibition of iNOS ranges from 4-65 µM.{1857,1901} L-NAME inhibits cGMP formation in endothelial cells with an IC50 of 3.1 µM (in the presence of 30 µM arginine) and reverses the vasodilation effects of acetylcholine in rat aorta rings with an EC50 of 0.54 µM.{1211,1855}
Brand:CaymanSKU:80210 - 10 gAvailable on backorder
L-NAME requires hydrolysis of the methyl ester by cellular esterases to become a fully functional inhibitor (L-NNA).{5433} L-NNA exhibits some selectivity for inhibition of neuronal and endothelial isoforms. It exhibits Ki values of 15 nM, 39 nM, and 4.4 µM for nNOS (bovine), eNOS (human), and iNOS (mouse), respectively.{5344,1857,5648} The reported Ki value for the inhibition of iNOS ranges from 4-65 µM.{1857,1901} L-NAME inhibits cGMP formation in endothelial cells with an IC50 of 3.1 µM (in the presence of 30 µM arginine) and reverses the vasodilation effects of acetylcholine in rat aorta rings with an EC50 of 0.54 µM.{1211,1855}
Brand:CaymanSKU:80210 - 5 gAvailable on backorder
L-NAME requires hydrolysis of the methyl ester by cellular esterases to become a fully functional inhibitor (L-NNA).{5433} L-NNA exhibits some selectivity for inhibition of neuronal and endothelial isoforms. It exhibits Ki values of 15 nM, 39 nM, and 4.4 µM for nNOS (bovine), eNOS (human), and iNOS (mouse), respectively.{5344,1857,5648} The reported Ki value for the inhibition of iNOS ranges from 4-65 µM.{1857,1901} L-NAME inhibits cGMP formation in endothelial cells with an IC50 of 3.1 µM (in the presence of 30 µM arginine) and reverses the vasodilation effects of acetylcholine in rat aorta rings with an EC50 of 0.54 µM.{1211,1855}
Brand:CaymanSKU:80210 - 50 gAvailable on backorder
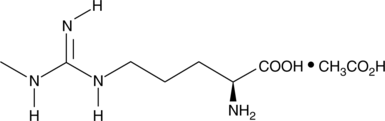
L-NIL is a relatively selective inhibitor of iNOS. It exhibits IC50 values of 0.4-3.3 µM for iNOS as opposed to 8-38 and 17-92 µM for eNOS and nNOS, respectively.{1259,8620,26945} L-NIL effectively inhibits iNOS both in vitro and in vivo.{8487,3731,26945} L-NIL has been used to demonstrate a critical role for iNOS in the immune response to infection by the protozoan L. major.{26945,26947}
Brand:CaymanSKU:80310 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
L-NIL is a relatively selective inhibitor of iNOS. It exhibits IC50 values of 0.4-3.3 µM for iNOS as opposed to 8-38 and 17-92 µM for eNOS and nNOS, respectively.{1259,8620,26945} L-NIL effectively inhibits iNOS both in vitro and in vivo.{8487,3731,26945} L-NIL has been used to demonstrate a critical role for iNOS in the immune response to infection by the protozoan L. major.{26945,26947}
Brand:CaymanSKU:80310 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
L-NIL is a relatively selective inhibitor of iNOS. It exhibits IC50 values of 0.4-3.3 µM for iNOS as opposed to 8-38 and 17-92 µM for eNOS and nNOS, respectively.{1259,8620,26945} L-NIL effectively inhibits iNOS both in vitro and in vivo.{8487,3731,26945} L-NIL has been used to demonstrate a critical role for iNOS in the immune response to infection by the protozoan L. major.{26945,26947}
Brand:CaymanSKU:80310 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
L-NIL is a relatively selective inhibitor of iNOS. It exhibits IC50 values of 0.4-3.3 µM for iNOS as opposed to 8-38 and 17-92 µM for eNOS and nNOS, respectively.{1259,8620,26945} L-NIL effectively inhibits iNOS both in vitro and in vivo.{8487,3731,26945} L-NIL has been used to demonstrate a critical role for iNOS in the immune response to infection by the protozoan L. major.{26945,26947}
Brand:CaymanSKU:80310 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
L-NIO is a non-selective inhibitor of all NOS isoforms. The Ki values for nNOS (rat), eNOS (bovine), and iNOS (mouse) are 1.7, 3.9, and 3.9 µM, respectively.{6358} L-NIO inhibits endothelial-dependent relaxation induced by acetylcholine in rat aortic rings and hypotensive responses to acetylcholine and bradykinin.{1211}
Brand:CaymanSKU:80320 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
L-NIO is a non-selective inhibitor of all NOS isoforms. The Ki values for nNOS (rat), eNOS (bovine), and iNOS (mouse) are 1.7, 3.9, and 3.9 µM, respectively.{6358} L-NIO inhibits endothelial-dependent relaxation induced by acetylcholine in rat aortic rings and hypotensive responses to acetylcholine and bradykinin.{1211}
Brand:CaymanSKU:80320 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
L-NIO is a non-selective inhibitor of all NOS isoforms. The Ki values for nNOS (rat), eNOS (bovine), and iNOS (mouse) are 1.7, 3.9, and 3.9 µM, respectively.{6358} L-NIO inhibits endothelial-dependent relaxation induced by acetylcholine in rat aortic rings and hypotensive responses to acetylcholine and bradykinin.{1211}
Brand:CaymanSKU:80320 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
L-NIO is a non-selective inhibitor of all NOS isoforms. The Ki values for nNOS (rat), eNOS (bovine), and iNOS (mouse) are 1.7, 3.9, and 3.9 µM, respectively.{6358} L-NIO inhibits endothelial-dependent relaxation induced by acetylcholine in rat aortic rings and hypotensive responses to acetylcholine and bradykinin.{1211}
Brand:CaymanSKU:80320 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
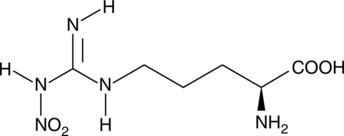
L-NMMA is the archetypal competitive NOS inhibitor to which other inhibitors are often compared.{5433} It is a relatively non-selective inhibitor of all NOS isoforms. The Ki values for nNOS (rat), eNOS (human), and iNOS (mouse) are approximately 0.18, 0.4, and 6 µM, respectively.{1415,5648}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10005031 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
L-NMMA is the archetypal competitive NOS inhibitor to which other inhibitors are often compared.{5433} It is a relatively non-selective inhibitor of all NOS isoforms. The Ki values for nNOS (rat), eNOS (human), and iNOS (mouse) are approximately 0.18, 0.4, and 6 µM, respectively.{1415,5648}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10005031 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
L-NMMA is the archetypal competitive NOS inhibitor to which other inhibitors are often compared.{5433} It is a relatively non-selective inhibitor of all NOS isoforms. The Ki values for nNOS (rat), eNOS (human), and iNOS (mouse) are approximately 0.18, 0.4, and 6 µM, respectively.{1415,5648}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10005031 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
L-NMMA is the archetypal competitive NOS inhibitor to which other inhibitors are often compared.{5433} It is a relatively non-selective inhibitor of all NOS isoforms. The Ki values for nNOS (rat), eNOS (human), and iNOS (mouse) are approximately 0.18, 0.4, and 6 µM, respectively.{1415,5648}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10005031 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
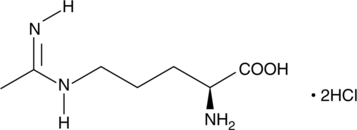
L-NNA is a competitive inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase (NOS) with selectivity for the neuronal and endothelial isoforms of the enzyme. Although L-NAME is much more soluble than L-NNA in aqueous systems, a hydrolysis step is required to “activate” L-NAME, thus adding complexity to an in vivo experiment.{5433} L-NNA inhibits nNOS, eNOS, and iNOS with Ki values of 15 nM (bovine), 39 nM (human), and 4.4 µM (mouse), respectively.{1857,5648}
Brand:CaymanSKU:80220 - 1 gAvailable on backorder
L-NNA is a competitive inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase (NOS) with selectivity for the neuronal and endothelial isoforms of the enzyme. Although L-NAME is much more soluble than L-NNA in aqueous systems, a hydrolysis step is required to “activate” L-NAME, thus adding complexity to an in vivo experiment.{5433} L-NNA inhibits nNOS, eNOS, and iNOS with Ki values of 15 nM (bovine), 39 nM (human), and 4.4 µM (mouse), respectively.{1857,5648}
Brand:CaymanSKU:80220 - 10 gAvailable on backorder
L-NNA is a competitive inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase (NOS) with selectivity for the neuronal and endothelial isoforms of the enzyme. Although L-NAME is much more soluble than L-NNA in aqueous systems, a hydrolysis step is required to “activate” L-NAME, thus adding complexity to an in vivo experiment.{5433} L-NNA inhibits nNOS, eNOS, and iNOS with Ki values of 15 nM (bovine), 39 nM (human), and 4.4 µM (mouse), respectively.{1857,5648}
Brand:CaymanSKU:80220 - 5 gAvailable on backorder
L-NNA is a competitive inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase (NOS) with selectivity for the neuronal and endothelial isoforms of the enzyme. Although L-NAME is much more soluble than L-NNA in aqueous systems, a hydrolysis step is required to “activate” L-NAME, thus adding complexity to an in vivo experiment.{5433} L-NNA inhibits nNOS, eNOS, and iNOS with Ki values of 15 nM (bovine), 39 nM (human), and 4.4 µM (mouse), respectively.{1857,5648}
Brand:CaymanSKU:80220 - 50 gAvailable on backorder
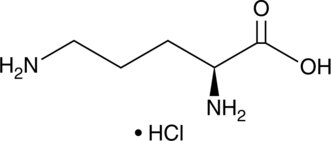
L-Ornithine is an active metabolite of L-arginine (Item No. 23703) and a non-proteinogenic amino acid.{53911} L-Ornithine is formed from arginine by arginase I during the final step of the urea cycle and acts as an alternate precursor to L-glutamate in the biosynthesis of proline. Exogenous administration of L-ornithine (111 mg/kg) delays the onset of ethanol-induced ataxia and decreases ethanol-induced sleeping time in rats.{53912}
Brand:CaymanSKU:30779 - 100 gAvailable on backorder
L-Ornithine is an active metabolite of L-arginine (Item No. 23703) and a non-proteinogenic amino acid.{53911} L-Ornithine is formed from arginine by arginase I during the final step of the urea cycle and acts as an alternate precursor to L-glutamate in the biosynthesis of proline. Exogenous administration of L-ornithine (111 mg/kg) delays the onset of ethanol-induced ataxia and decreases ethanol-induced sleeping time in rats.{53912}
Brand:CaymanSKU:30779 - 250 gAvailable on backorder
L-Ornithine is an active metabolite of L-arginine (Item No. 23703) and a non-proteinogenic amino acid.{53911} L-Ornithine is formed from arginine by arginase I during the final step of the urea cycle and acts as an alternate precursor to L-glutamate in the biosynthesis of proline. Exogenous administration of L-ornithine (111 mg/kg) delays the onset of ethanol-induced ataxia and decreases ethanol-induced sleeping time in rats.{53912}
Brand:CaymanSKU:30779 - 50 gAvailable on backorder
L-Ornithine is an active metabolite of L-arginine (Item No. 23703) and a non-proteinogenic amino acid.{53911} L-Ornithine is formed from arginine by arginase I during the final step of the urea cycle and acts as an alternate precursor to L-glutamate in the biosynthesis of proline. Exogenous administration of L-ornithine (111 mg/kg) delays the onset of ethanol-induced ataxia and decreases ethanol-induced sleeping time in rats.{53912}
Brand:CaymanSKU:30779 - 500 gAvailable on backorder
L-Ornithine lactam is a synthetic intermediate.{52853,52857} It has been used in the synthesis of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4) inhibitors, as well as signaling peptides.
Brand:CaymanSKU:31683 - 1 gAvailable on backorder
L-Ornithine lactam is a synthetic intermediate.{52853,52857} It has been used in the synthesis of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4) inhibitors, as well as signaling peptides.
Brand:CaymanSKU:31683 - 250 mgAvailable on backorder
L-Ornithine lactam is a synthetic intermediate.{52853,52857} It has been used in the synthesis of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4) inhibitors, as well as signaling peptides.
Brand:CaymanSKU:31683 - 500 mgAvailable on backorder
Four distinct human isoenzymes of alkaline phosphatase (AP) are known: intestinal (IAP), placental (PLAP), tissue non-specific (NSAP, also known as liver/bone/kidney AP), and germ cell AP (also known as placental-like AP, PLAP-like).{30380} L-p-Bromotetramisole is a cell-permeable inhibitor of all four human AP isoenzymes (Kis =18 and 56 µM for PLAP and NSAP, respectively).{30380,30384,30383,30381} While PLAP is strongly inhibited by L-p-bromotetramisole, a second AP, possibly PLAP-like, shows only partial inhibition.{30383} L-p-Bromotetramisole has been shown to inhibit a tyrosine phosphatase from Drosophila and, as a result, is also used as a tyrosine phosphatase inhibitor.{30382,30385}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
Four distinct human isoenzymes of alkaline phosphatase (AP) are known: intestinal (IAP), placental (PLAP), tissue non-specific (NSAP, also known as liver/bone/kidney AP), and germ cell AP (also known as placental-like AP, PLAP-like).{30380} L-p-Bromotetramisole is a cell-permeable inhibitor of all four human AP isoenzymes (Kis =18 and 56 µM for PLAP and NSAP, respectively).{30380,30384,30383,30381} While PLAP is strongly inhibited by L-p-bromotetramisole, a second AP, possibly PLAP-like, shows only partial inhibition.{30383} L-p-Bromotetramisole has been shown to inhibit a tyrosine phosphatase from Drosophila and, as a result, is also used as a tyrosine phosphatase inhibitor.{30382,30385}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
Four distinct human isoenzymes of alkaline phosphatase (AP) are known: intestinal (IAP), placental (PLAP), tissue non-specific (NSAP, also known as liver/bone/kidney AP), and germ cell AP (also known as placental-like AP, PLAP-like).{30380} L-p-Bromotetramisole is a cell-permeable inhibitor of all four human AP isoenzymes (Kis =18 and 56 µM for PLAP and NSAP, respectively).{30380,30384,30383,30381} While PLAP is strongly inhibited by L-p-bromotetramisole, a second AP, possibly PLAP-like, shows only partial inhibition.{30383} L-p-Bromotetramisole has been shown to inhibit a tyrosine phosphatase from Drosophila and, as a result, is also used as a tyrosine phosphatase inhibitor.{30382,30385}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
Four distinct human isoenzymes of alkaline phosphatase (AP) are known: intestinal (IAP), placental (PLAP), tissue non-specific (NSAP, also known as liver/bone/kidney AP), and germ cell AP (also known as placental-like AP, PLAP-like).{30380} L-p-Bromotetramisole is a cell-permeable inhibitor of all four human AP isoenzymes (Kis =18 and 56 µM for PLAP and NSAP, respectively).{30380,30384,30383,30381} While PLAP is strongly inhibited by L-p-bromotetramisole, a second AP, possibly PLAP-like, shows only partial inhibition.{30383} L-p-Bromotetramisole has been shown to inhibit a tyrosine phosphatase from Drosophila and, as a result, is also used as a tyrosine phosphatase inhibitor.{30382,30385}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
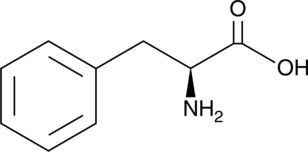
L-Phenylalanine is an essential amino acid.{54554,54556,54555} Blood and brain levels of L-phenylalanine are increased and associated with progressive cognitive impairments, seizures, motor deficits, and autism in patients with phenylketonuria, an inborn error of metabolism characterized by mutations in the gene encoding phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH). L-Phenylalanine inhibits NMDA-induced currents in primary rat hippocampal neurons (IC50 = 1.71 mM).{54554} It also assembles into fibrils in vitro that are cytotoxic to PC12 and CHO cells when used at concentrations ranging from 1.16 to 15 mM.{54556}
Brand:CaymanSKU:31498 - 100 gAvailable on backorder
L-Phenylalanine is an essential amino acid.{54554,54556,54555} Blood and brain levels of L-phenylalanine are increased and associated with progressive cognitive impairments, seizures, motor deficits, and autism in patients with phenylketonuria, an inborn error of metabolism characterized by mutations in the gene encoding phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH). L-Phenylalanine inhibits NMDA-induced currents in primary rat hippocampal neurons (IC50 = 1.71 mM).{54554} It also assembles into fibrils in vitro that are cytotoxic to PC12 and CHO cells when used at concentrations ranging from 1.16 to 15 mM.{54556}
Brand:CaymanSKU:31498 - 250 gAvailable on backorder
L-Phenylalanine is an essential amino acid.{54554,54556,54555} Blood and brain levels of L-phenylalanine are increased and associated with progressive cognitive impairments, seizures, motor deficits, and autism in patients with phenylketonuria, an inborn error of metabolism characterized by mutations in the gene encoding phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH). L-Phenylalanine inhibits NMDA-induced currents in primary rat hippocampal neurons (IC50 = 1.71 mM).{54554} It also assembles into fibrils in vitro that are cytotoxic to PC12 and CHO cells when used at concentrations ranging from 1.16 to 15 mM.{54556}
Brand:CaymanSKU:31498 - 50 gAvailable on backorder
L-Phenylalanine is an essential amino acid.{54554,54556,54555} Blood and brain levels of L-phenylalanine are increased and associated with progressive cognitive impairments, seizures, motor deficits, and autism in patients with phenylketonuria, an inborn error of metabolism characterized by mutations in the gene encoding phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH). L-Phenylalanine inhibits NMDA-induced currents in primary rat hippocampal neurons (IC50 = 1.71 mM).{54554} It also assembles into fibrils in vitro that are cytotoxic to PC12 and CHO cells when used at concentrations ranging from 1.16 to 15 mM.{54556}
Brand:CaymanSKU:31498 - 500 gAvailable on backorder
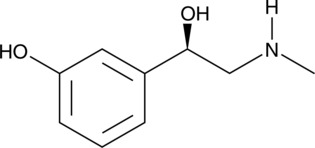
L-Phenylephrine is an adrenergic α1A receptor agonist (Ki = 1.4 µM) that demonstrates selectivity against the α1B and α1C receptor subtypes (Kis = 23.9 and 47.8 µM, respectively).{28120} By stimulating adrenergic α1 receptors, L-phenylephrine can induce aortic smooth muscle contractions, although reported relative affinity and potency values in rabbit are 5-fold weaker compared to that of L-norepinephrine.{28119} This compound is frequently used to precontract smooth muscle in preparations designed to study the properties of various vasodilator agents.{28121,28122} Because L-phenylephrine acts on adrenergic α1 receptors in the arterioles of the nasal mucosa to produce constriction, it has been examined clinically as an oral decongestant.{28123}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
L-Phenylephrine is an adrenergic α1A receptor agonist (Ki = 1.4 µM) that demonstrates selectivity against the α1B and α1C receptor subtypes (Kis = 23.9 and 47.8 µM, respectively).{28120} By stimulating adrenergic α1 receptors, L-phenylephrine can induce aortic smooth muscle contractions, although reported relative affinity and potency values in rabbit are 5-fold weaker compared to that of L-norepinephrine.{28119} This compound is frequently used to precontract smooth muscle in preparations designed to study the properties of various vasodilator agents.{28121,28122} Because L-phenylephrine acts on adrenergic α1 receptors in the arterioles of the nasal mucosa to produce constriction, it has been examined clinically as an oral decongestant.{28123}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
L-Phenylephrine is an adrenergic α1A receptor agonist (Ki = 1.4 µM) that demonstrates selectivity against the α1B and α1C receptor subtypes (Kis = 23.9 and 47.8 µM, respectively).{28120} By stimulating adrenergic α1 receptors, L-phenylephrine can induce aortic smooth muscle contractions, although reported relative affinity and potency values in rabbit are 5-fold weaker compared to that of L-norepinephrine.{28119} This compound is frequently used to precontract smooth muscle in preparations designed to study the properties of various vasodilator agents.{28121,28122} Because L-phenylephrine acts on adrenergic α1 receptors in the arterioles of the nasal mucosa to produce constriction, it has been examined clinically as an oral decongestant.{28123}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
L-Phenylephrine is an adrenergic α1A receptor agonist (Ki = 1.4 µM) that demonstrates selectivity against the α1B and α1C receptor subtypes (Kis = 23.9 and 47.8 µM, respectively).{28120} By stimulating adrenergic α1 receptors, L-phenylephrine can induce aortic smooth muscle contractions, although reported relative affinity and potency values in rabbit are 5-fold weaker compared to that of L-norepinephrine.{28119} This compound is frequently used to precontract smooth muscle in preparations designed to study the properties of various vasodilator agents.{28121,28122} Because L-phenylephrine acts on adrenergic α1 receptors in the arterioles of the nasal mucosa to produce constriction, it has been examined clinically as an oral decongestant.{28123}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
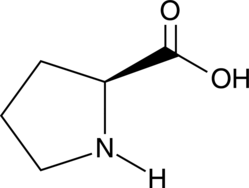
L-Proline is a nonessential amino acid.{54262} It contains a pyrrolidine ring, which contains the α-amino nitrogen, and is highly rigid, properties that affect protein conformation and folding and can cause kinks and turns in protein secondary structure.{54262,54263} It is a substrate for the proton-coupled amino acid transporter 1 (PAT1) and an inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase (AChE; Ki = 86 µM).{54264,54265} L-Proline accumulates in plants under environmental stress and is important for environmental stress tolerance through its involvement in protein synthesis, redox balance maintenance, osmoprotection, and signaling.{54266}
Brand:CaymanSKU:30772 - 1 kgAvailable on backorder
L-Proline is a nonessential amino acid.{54262} It contains a pyrrolidine ring, which contains the α-amino nitrogen, and is highly rigid, properties that affect protein conformation and folding and can cause kinks and turns in protein secondary structure.{54262,54263} It is a substrate for the proton-coupled amino acid transporter 1 (PAT1) and an inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase (AChE; Ki = 86 µM).{54264,54265} L-Proline accumulates in plants under environmental stress and is important for environmental stress tolerance through its involvement in protein synthesis, redox balance maintenance, osmoprotection, and signaling.{54266}
Brand:CaymanSKU:30772 - 100 gAvailable on backorder
L-Proline is a nonessential amino acid.{54262} It contains a pyrrolidine ring, which contains the α-amino nitrogen, and is highly rigid, properties that affect protein conformation and folding and can cause kinks and turns in protein secondary structure.{54262,54263} It is a substrate for the proton-coupled amino acid transporter 1 (PAT1) and an inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase (AChE; Ki = 86 µM).{54264,54265} L-Proline accumulates in plants under environmental stress and is important for environmental stress tolerance through its involvement in protein synthesis, redox balance maintenance, osmoprotection, and signaling.{54266}
Brand:CaymanSKU:30772 - 250 gAvailable on backorder
L-Proline is a nonessential amino acid.{54262} It contains a pyrrolidine ring, which contains the α-amino nitrogen, and is highly rigid, properties that affect protein conformation and folding and can cause kinks and turns in protein secondary structure.{54262,54263} It is a substrate for the proton-coupled amino acid transporter 1 (PAT1) and an inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase (AChE; Ki = 86 µM).{54264,54265} L-Proline accumulates in plants under environmental stress and is important for environmental stress tolerance through its involvement in protein synthesis, redox balance maintenance, osmoprotection, and signaling.{54266}
Brand:CaymanSKU:30772 - 500 gAvailable on backorder
L-Pyrohomoglutamic acid is an amino acid building block.{59326,59327} It has been used in the synthesis of ligands for FK506-binding proteins (FKBPs) and histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors.
Brand:CaymanSKU:31694 - 1 gAvailable on backorder
L-Pyrohomoglutamic acid is an amino acid building block.{59326,59327} It has been used in the synthesis of ligands for FK506-binding proteins (FKBPs) and histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors.
Brand:CaymanSKU:31694 - 5 gAvailable on backorder
L-Pyrohomoglutamic acid is an amino acid building block.{59326,59327} It has been used in the synthesis of ligands for FK506-binding proteins (FKBPs) and histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors.
Brand:CaymanSKU:31694 - 500 mgAvailable on backorder
L-Quisqualic acid is a natural analog of glutamate that acts as an agonist at AMPA-selective and metabotropic glutamate receptors (EC50s = 170, 10, 40, and 29 nM at GluR-A, mGluR1, mGluR3, and mGluR5, respectively), as well as the ionotropic kainate receptor (GRIK4; Ki = 6.43 nM).{21635,24138,33255,33256,23341,33260} L-Quisqualic acid is used to study receptor dynamics and as an excitotoxin to selectively destroy neurons in the brain or spinal cord.{33257,33258}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20211 -Available on backorder
L-Quisqualic acid is a natural analog of glutamate that acts as an agonist at AMPA-selective and metabotropic glutamate receptors (EC50s = 170, 10, 40, and 29 nM at GluR-A, mGluR1, mGluR3, and mGluR5, respectively), as well as the ionotropic kainate receptor (GRIK4; Ki = 6.43 nM).{21635,24138,33255,33256,23341,33260} L-Quisqualic acid is used to study receptor dynamics and as an excitotoxin to selectively destroy neurons in the brain or spinal cord.{33257,33258}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20211 -Available on backorder
L-Quisqualic acid is a natural analog of glutamate that acts as an agonist at AMPA-selective and metabotropic glutamate receptors (EC50s = 170, 10, 40, and 29 nM at GluR-A, mGluR1, mGluR3, and mGluR5, respectively), as well as the ionotropic kainate receptor (GRIK4; Ki = 6.43 nM).{21635,24138,33255,33256,23341,33260} L-Quisqualic acid is used to study receptor dynamics and as an excitotoxin to selectively destroy neurons in the brain or spinal cord.{33257,33258}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20211 -Available on backorder
L-Quisqualic acid is a natural analog of glutamate that acts as an agonist at AMPA-selective and metabotropic glutamate receptors (EC50s = 170, 10, 40, and 29 nM at GluR-A, mGluR1, mGluR3, and mGluR5, respectively), as well as the ionotropic kainate receptor (GRIK4; Ki = 6.43 nM).{21635,24138,33255,33256,23341,33260} L-Quisqualic acid is used to study receptor dynamics and as an excitotoxin to selectively destroy neurons in the brain or spinal cord.{33257,33258}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20211 -Available on backorder
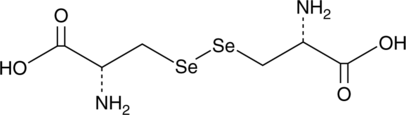
L-Selenocystine is a diselenide-bridged amino acid that may be confused with selenocysteine (Sec), which is a rare amino acid featuring a single selenium atom. L-Selenocystine is a redox-active selenium compound that has both anti- and pro-oxidant actions.{29926,29925} This compound can be reduced by low molecular thiols and disulfide reductases to Sec. It is reduced to Sec by mammalian thioredoxin reductase (apparent Km = 6.0 µM), and this property can be used to assay thioredoxin reductase activity.{29925,29924} L-Selenocystine induces an unfolded protein response, ER stress, and large cytoplasmic vacuolization in HeLa cells and has cytostatic effects in a range of cancer cell types.{29925,29927}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
L-Selenocystine is a diselenide-bridged amino acid that may be confused with selenocysteine (Sec), which is a rare amino acid featuring a single selenium atom. L-Selenocystine is a redox-active selenium compound that has both anti- and pro-oxidant actions.{29926,29925} This compound can be reduced by low molecular thiols and disulfide reductases to Sec. It is reduced to Sec by mammalian thioredoxin reductase (apparent Km = 6.0 µM), and this property can be used to assay thioredoxin reductase activity.{29925,29924} L-Selenocystine induces an unfolded protein response, ER stress, and large cytoplasmic vacuolization in HeLa cells and has cytostatic effects in a range of cancer cell types.{29925,29927}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
L-Selenocystine is a diselenide-bridged amino acid that may be confused with selenocysteine (Sec), which is a rare amino acid featuring a single selenium atom. L-Selenocystine is a redox-active selenium compound that has both anti- and pro-oxidant actions.{29926,29925} This compound can be reduced by low molecular thiols and disulfide reductases to Sec. It is reduced to Sec by mammalian thioredoxin reductase (apparent Km = 6.0 µM), and this property can be used to assay thioredoxin reductase activity.{29925,29924} L-Selenocystine induces an unfolded protein response, ER stress, and large cytoplasmic vacuolization in HeLa cells and has cytostatic effects in a range of cancer cell types.{29925,29927}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
L-Selenocystine is a diselenide-bridged amino acid that may be confused with selenocysteine (Sec), which is a rare amino acid featuring a single selenium atom. L-Selenocystine is a redox-active selenium compound that has both anti- and pro-oxidant actions.{29926,29925} This compound can be reduced by low molecular thiols and disulfide reductases to Sec. It is reduced to Sec by mammalian thioredoxin reductase (apparent Km = 6.0 µM), and this property can be used to assay thioredoxin reductase activity.{29925,29924} L-Selenocystine induces an unfolded protein response, ER stress, and large cytoplasmic vacuolization in HeLa cells and has cytostatic effects in a range of cancer cell types.{29925,29927}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
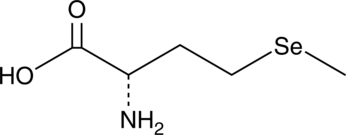
L-Selenomethionine (SeMet), a naturally occurring amino acid, is the predominant form of selenium found in Brazil nuts, grains, soy beans, and legumes.{25988} It promotes cell cycle progression and is known to elevate the expression of the antioxidant enzymes thioredoxin reductase, glutathione reductase, and glutathione peroxidase.{25990,25986,25987} At 5 µM, SeMet has been shown to selectively induce apoptosis in LNCaP prostate cancer cells without affecting non-cancerous cells.{25989}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-L-Selenomethionine (SeMet), a naturally occurring amino acid, is the predominant form of selenium found in Brazil nuts, grains, soy beans, and legumes.{25988} It promotes cell cycle progression and is known to elevate the expression of the antioxidant enzymes thioredoxin reductase, glutathione reductase, and glutathione peroxidase.{25990,25986,25987} At 5 µM, SeMet has been shown to selectively induce apoptosis in LNCaP prostate cancer cells without affecting non-cancerous cells.{25989}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-L-Selenomethionine (SeMet), a naturally occurring amino acid, is the predominant form of selenium found in Brazil nuts, grains, soy beans, and legumes.{25988} It promotes cell cycle progression and is known to elevate the expression of the antioxidant enzymes thioredoxin reductase, glutathione reductase, and glutathione peroxidase.{25990,25986,25987} At 5 µM, SeMet has been shown to selectively induce apoptosis in LNCaP prostate cancer cells without affecting non-cancerous cells.{25989}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-L-Sulforaphane is an isothiocyanate derived from the natural compound glucoraphanin, which is abundant in cruciferous vegetables, including broccoli.{23486} It has powerful antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-carcinogenic effects.{23486,23487} L-Sulforaphane, at 40 µM, activates nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2- (Nrf2) mediated gene expression by disrupting its association with Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (Keap1), allowing Nrf2 to enter the nucleus to alter transcription.{21883,21473} In this way, sulforaphane induces the expression of phase II detoxification enzymes, which in turn provide diverse beneficial effects.{21884,23486}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-L-Sulforaphane is an isothiocyanate derived from the natural compound glucoraphanin, which is abundant in cruciferous vegetables, including broccoli.{23486} It has powerful antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-carcinogenic effects.{23486,23487} L-Sulforaphane, at 40 µM, activates nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2- (Nrf2) mediated gene expression by disrupting its association with Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (Keap1), allowing Nrf2 to enter the nucleus to alter transcription.{21883,21473} In this way, sulforaphane induces the expression of phase II detoxification enzymes, which in turn provide diverse beneficial effects.{21884,23486}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-L-Sulforaphane is an isothiocyanate derived from the natural compound glucoraphanin, which is abundant in cruciferous vegetables, including broccoli.{23486} It has powerful antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-carcinogenic effects.{23486,23487} L-Sulforaphane, at 40 µM, activates nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2- (Nrf2) mediated gene expression by disrupting its association with Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (Keap1), allowing Nrf2 to enter the nucleus to alter transcription.{21883,21473} In this way, sulforaphane induces the expression of phase II detoxification enzymes, which in turn provide diverse beneficial effects.{21884,23486}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-L-Sulforaphane is an isothiocyanate derived from the natural compound glucoraphanin, which is abundant in cruciferous vegetables, including broccoli.{23486} It has powerful antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-carcinogenic effects.{23486,23487} L-Sulforaphane, at 40 µM, activates nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2- (Nrf2) mediated gene expression by disrupting its association with Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (Keap1), allowing Nrf2 to enter the nucleus to alter transcription.{21883,21473} In this way, sulforaphane induces the expression of phase II detoxification enzymes, which in turn provide diverse beneficial effects.{21884,23486}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-L-Sulforaphene is a natural isothiocyanate found in cruciferous vegetables. Like the related compound L-sulforaphane (Item No. 14797), it has antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-carcinogenic effects.{28035,28034} Radish root extract, which contains L-sulforaphene, induces apoptosis in a p53-independent manner.{28034}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
L-Sulforaphene is a natural isothiocyanate found in cruciferous vegetables. Like the related compound L-sulforaphane (Item No. 14797), it has antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-carcinogenic effects.{28035,28034} Radish root extract, which contains L-sulforaphene, induces apoptosis in a p53-independent manner.{28034}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
L-Sulforaphene is a natural isothiocyanate found in cruciferous vegetables. Like the related compound L-sulforaphane (Item No. 14797), it has antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-carcinogenic effects.{28035,28034} Radish root extract, which contains L-sulforaphene, induces apoptosis in a p53-independent manner.{28034}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
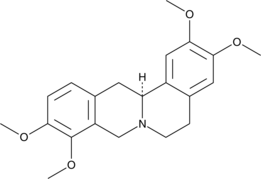
L-Tetrahydropalmatine is an alkaloid that can be found in Corydalis yanhusuo root, which is used as an herbal remedy for pain. L-Tetrahydropalmatine has been found to have diverse effects in animals, including antagonizing the supraspinal dopamine 2 receptor and reducing stress-induced anxiety in rats.{32267,32268} L-Tetrahydropalmatine also protects against ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats.{32266}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20535 -Available on backorder
L-Tetrahydropalmatine is an alkaloid that can be found in Corydalis yanhusuo root, which is used as an herbal remedy for pain. L-Tetrahydropalmatine has been found to have diverse effects in animals, including antagonizing the supraspinal dopamine 2 receptor and reducing stress-induced anxiety in rats.{32267,32268} L-Tetrahydropalmatine also protects against ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats.{32266}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20535 -Available on backorder
L-Tetrahydropalmatine is an alkaloid that can be found in Corydalis yanhusuo root, which is used as an herbal remedy for pain. L-Tetrahydropalmatine has been found to have diverse effects in animals, including antagonizing the supraspinal dopamine 2 receptor and reducing stress-induced anxiety in rats.{32267,32268} L-Tetrahydropalmatine also protects against ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats.{32266}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20535 -Available on backorder
L-Tetrahydropalmatine is an alkaloid that can be found in Corydalis yanhusuo root, which is used as an herbal remedy for pain. L-Tetrahydropalmatine has been found to have diverse effects in animals, including antagonizing the supraspinal dopamine 2 receptor and reducing stress-induced anxiety in rats.{32267,32268} L-Tetrahydropalmatine also protects against ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats.{32266}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20535 -Available on backorder
L-Theanine is the major amino acid found in Camellia sinensis, the source of green tea.{19534} It is an analog of the excitatory neurotransmitter, glutamate, and thusly, binds to glutamate receptors.{19535} L-Theanine can antagonize various glutamate receptor subtypes as well as inhibit glutamine and glutamate transporters, which has been shown to be neuroprotective in animal models of focal cerebral ischemia.{19535,32452} Further, L-theanine is reported to increase brain levels of dopamine, serotonin, GABA, nerve growth factor, and brain-derived neurotrophic factor.{19535,32452}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20832 -Out of stock
L-Theanine is the major amino acid found in Camellia sinensis, the source of green tea.{19534} It is an analog of the excitatory neurotransmitter, glutamate, and thusly, binds to glutamate receptors.{19535} L-Theanine can antagonize various glutamate receptor subtypes as well as inhibit glutamine and glutamate transporters, which has been shown to be neuroprotective in animal models of focal cerebral ischemia.{19535,32452} Further, L-theanine is reported to increase brain levels of dopamine, serotonin, GABA, nerve growth factor, and brain-derived neurotrophic factor.{19535,32452}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20832 -Out of stock