Cayman
Showing 26701–26850 of 45550 results
-
L-826,266 is a potent and selective competitive antagonist of the prostaglandin E2 receptor subtype EP3 (Ki = 0.8 nM).{9826} It also binds to the EP4 receptor (Ki = 715 nM) but does not bind to EP1 or EP2 receptors up to a concentration of 5,000 nM. L-826,266 inhibits vasoconstriction induced by the EP3 agonist sulprostone (Item No. 14765) in a concentration-dependent manner (EC50s = 0.45-24.5 µM in isolated human pulmonary arteries).{40626} It also inhibits sulprostone-induced norepinephrine and serotonin release in rat cortex and norepinephrine release in rat vas deferens (pA2s = 7.56, 7.67, and 7.87, respectively).{40635}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
L-826,266 is a potent and selective competitive antagonist of the prostaglandin E2 receptor subtype EP3 (Ki = 0.8 nM).{9826} It also binds to the EP4 receptor (Ki = 715 nM) but does not bind to EP1 or EP2 receptors up to a concentration of 5,000 nM. L-826,266 inhibits vasoconstriction induced by the EP3 agonist sulprostone (Item No. 14765) in a concentration-dependent manner (EC50s = 0.45-24.5 µM in isolated human pulmonary arteries).{40626} It also inhibits sulprostone-induced norepinephrine and serotonin release in rat cortex and norepinephrine release in rat vas deferens (pA2s = 7.56, 7.67, and 7.87, respectively).{40635}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
L-826,266 is a potent and selective competitive antagonist of the prostaglandin E2 receptor subtype EP3 (Ki = 0.8 nM).{9826} It also binds to the EP4 receptor (Ki = 715 nM) but does not bind to EP1 or EP2 receptors up to a concentration of 5,000 nM. L-826,266 inhibits vasoconstriction induced by the EP3 agonist sulprostone (Item No. 14765) in a concentration-dependent manner (EC50s = 0.45-24.5 µM in isolated human pulmonary arteries).{40626} It also inhibits sulprostone-induced norepinephrine and serotonin release in rat cortex and norepinephrine release in rat vas deferens (pA2s = 7.56, 7.67, and 7.87, respectively).{40635}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
L-826,266 is a potent and selective competitive antagonist of the prostaglandin E2 receptor subtype EP3 (Ki = 0.8 nM).{9826} It also binds to the EP4 receptor (Ki = 715 nM) but does not bind to EP1 or EP2 receptors up to a concentration of 5,000 nM. L-826,266 inhibits vasoconstriction induced by the EP3 agonist sulprostone (Item No. 14765) in a concentration-dependent manner (EC50s = 0.45-24.5 µM in isolated human pulmonary arteries).{40626} It also inhibits sulprostone-induced norepinephrine and serotonin release in rat cortex and norepinephrine release in rat vas deferens (pA2s = 7.56, 7.67, and 7.87, respectively).{40635}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
L-858,051 is a water-soluble analog of forskolin (Item No. 11018), a cell-permeant activator of adenylate cyclase.{34032} L-858,051 activates adenylate cyclase (EC50 = 3 µM), inhibits glucose transport, and blocks cytochalasin B (Item No. 11328) binding in rat adipocyte membranes.{34031} L-858,051 is used to activate adenylate cyclase and initiate signaling through elevated cAMP synthesis in a variety of cell types in culture.{34030,34033,34034}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21206 -Out of stock
L-858,051 is a water-soluble analog of forskolin (Item No. 11018), a cell-permeant activator of adenylate cyclase.{34032} L-858,051 activates adenylate cyclase (EC50 = 3 µM), inhibits glucose transport, and blocks cytochalasin B (Item No. 11328) binding in rat adipocyte membranes.{34031} L-858,051 is used to activate adenylate cyclase and initiate signaling through elevated cAMP synthesis in a variety of cell types in culture.{34030,34033,34034}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21206 -Out of stock
L-858,051 is a water-soluble analog of forskolin (Item No. 11018), a cell-permeant activator of adenylate cyclase.{34032} L-858,051 activates adenylate cyclase (EC50 = 3 µM), inhibits glucose transport, and blocks cytochalasin B (Item No. 11328) binding in rat adipocyte membranes.{34031} L-858,051 is used to activate adenylate cyclase and initiate signaling through elevated cAMP synthesis in a variety of cell types in culture.{34030,34033,34034}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21206 -Out of stock
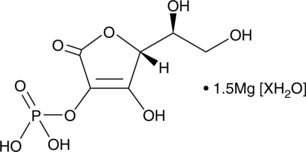
Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) activates four E prostanoid (EP) receptors, EP1-4. EP4 is a Gs protein-coupled receptor that, by elevating the second messenger cAMP, plays important roles in bone formation and resorption, cancer, and atherosclerosis.{16772,16773,16619} L-902,688 is a highly potent agonist of the human PGE2 receptor, EP4. It demonstrates a Ki value of 0.38 nM and an EC50 value of 0.6 nM and is >4,000-fold selective for EP4 over other EP and prostanoid receptors.{17923} L-902,688 induces thermal hyperalgesia when injected into guinea pig forepaw and increases vasodilation of human pulmonary vein.{18105,16074}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007712 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) activates four E prostanoid (EP) receptors, EP1-4. EP4 is a Gs protein-coupled receptor that, by elevating the second messenger cAMP, plays important roles in bone formation and resorption, cancer, and atherosclerosis.{16772,16773,16619} L-902,688 is a highly potent agonist of the human PGE2 receptor, EP4. It demonstrates a Ki value of 0.38 nM and an EC50 value of 0.6 nM and is >4,000-fold selective for EP4 over other EP and prostanoid receptors.{17923} L-902,688 induces thermal hyperalgesia when injected into guinea pig forepaw and increases vasodilation of human pulmonary vein.{18105,16074}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007712 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) activates four E prostanoid (EP) receptors, EP1-4. EP4 is a Gs protein-coupled receptor that, by elevating the second messenger cAMP, plays important roles in bone formation and resorption, cancer, and atherosclerosis.{16772,16773,16619} L-902,688 is a highly potent agonist of the human PGE2 receptor, EP4. It demonstrates a Ki value of 0.38 nM and an EC50 value of 0.6 nM and is >4,000-fold selective for EP4 over other EP and prostanoid receptors.{17923} L-902,688 induces thermal hyperalgesia when injected into guinea pig forepaw and increases vasodilation of human pulmonary vein.{18105,16074}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007712 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) activates four E prostanoid (EP) receptors, EP1-4. EP4 is a Gs protein-coupled receptor that, by elevating the second messenger cAMP, plays important roles in bone formation and resorption, cancer, and atherosclerosis.{16772,16773,16619} L-902,688 is a highly potent agonist of the human PGE2 receptor, EP4. It demonstrates a Ki value of 0.38 nM and an EC50 value of 0.6 nM and is >4,000-fold selective for EP4 over other EP and prostanoid receptors.{17923} L-902,688 induces thermal hyperalgesia when injected into guinea pig forepaw and increases vasodilation of human pulmonary vein.{18105,16074}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007712 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
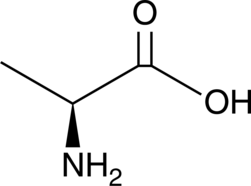
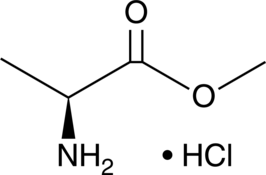
L-Alanine is a non-essential amino acid.{52287} It is produced by direct β-decarboxylation of L-aspartate by L-aspartate β-decarboxylase or transamination of pyruvate in the glucose-alanine cycle and is a precursor for gluconeogenesis.{52288} Dysregulation of L-alanine metabolism is associated with various disease states, including diabetes, metabolic syndrome, ketotic hypoglycemia, and acquired acute lactic acidosis.
Brand:CaymanSKU:29757 - 100 gAvailable on backorder
L-Alanine is a non-essential amino acid.{52287} It is produced by direct β-decarboxylation of L-aspartate by L-aspartate β-decarboxylase or transamination of pyruvate in the glucose-alanine cycle and is a precursor for gluconeogenesis.{52288} Dysregulation of L-alanine metabolism is associated with various disease states, including diabetes, metabolic syndrome, ketotic hypoglycemia, and acquired acute lactic acidosis.
Brand:CaymanSKU:29757 - 250 gAvailable on backorder
L-Alanine is a non-essential amino acid.{52287} It is produced by direct β-decarboxylation of L-aspartate by L-aspartate β-decarboxylase or transamination of pyruvate in the glucose-alanine cycle and is a precursor for gluconeogenesis.{52288} Dysregulation of L-alanine metabolism is associated with various disease states, including diabetes, metabolic syndrome, ketotic hypoglycemia, and acquired acute lactic acidosis.
Brand:CaymanSKU:29757 - 50 gAvailable on backorder
L-Alanine is a non-essential amino acid.{52287} It is produced by direct β-decarboxylation of L-aspartate by L-aspartate β-decarboxylase or transamination of pyruvate in the glucose-alanine cycle and is a precursor for gluconeogenesis.{52288} Dysregulation of L-alanine metabolism is associated with various disease states, including diabetes, metabolic syndrome, ketotic hypoglycemia, and acquired acute lactic acidosis.
Brand:CaymanSKU:29757 - 500 gAvailable on backorder
L-Alanine methyl ester is an amino acid-containing building block.{46897,46898} It has been used in the synthesis of azidothymidine (AZT) nucleotides with anti-HIV activity, as well as anticancer agents.
Brand:CaymanSKU:30527 - 10 gAvailable on backorder
L-Alanine methyl ester is an amino acid-containing building block.{46897,46898} It has been used in the synthesis of azidothymidine (AZT) nucleotides with anti-HIV activity, as well as anticancer agents.
Brand:CaymanSKU:30527 - 25 gAvailable on backorder
L-Alanine methyl ester is an amino acid-containing building block.{46897,46898} It has been used in the synthesis of azidothymidine (AZT) nucleotides with anti-HIV activity, as well as anticancer agents.
Brand:CaymanSKU:30527 - 50 gAvailable on backorder
L-Alanosine is an antibiotic derived from bacterium S. alanosinicus with antineoplastic activity in cells deficient in methylthioadenosine phosphorylase (MTAP) (mean IC50 = 4.8 μM and 10 μM in T-ALL and CAK-1 cells, respectively).{34433,34434} L-Alanosine inhibits adenylosuccinate synthetase to disrupt de novo purine biosynthesis, inhibiting cellular metabolism in MTAP-deficient tumor cells.{34435,34436,34437}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
L-Alanosine is an antibiotic derived from bacterium S. alanosinicus with antineoplastic activity in cells deficient in methylthioadenosine phosphorylase (MTAP) (mean IC50 = 4.8 μM and 10 μM in T-ALL and CAK-1 cells, respectively).{34433,34434} L-Alanosine inhibits adenylosuccinate synthetase to disrupt de novo purine biosynthesis, inhibiting cellular metabolism in MTAP-deficient tumor cells.{34435,34436,34437}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
L-Alanosine is an antibiotic derived from bacterium S. alanosinicus with antineoplastic activity in cells deficient in methylthioadenosine phosphorylase (MTAP) (mean IC50 = 4.8 μM and 10 μM in T-ALL and CAK-1 cells, respectively).{34433,34434} L-Alanosine inhibits adenylosuccinate synthetase to disrupt de novo purine biosynthesis, inhibiting cellular metabolism in MTAP-deficient tumor cells.{34435,34436,34437}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
L-Alanosine is an antibiotic derived from bacterium S. alanosinicus with antineoplastic activity in cells deficient in methylthioadenosine phosphorylase (MTAP) (mean IC50 = 4.8 μM and 10 μM in T-ALL and CAK-1 cells, respectively).{34433,34434} L-Alanosine inhibits adenylosuccinate synthetase to disrupt de novo purine biosynthesis, inhibiting cellular metabolism in MTAP-deficient tumor cells.{34435,34436,34437}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
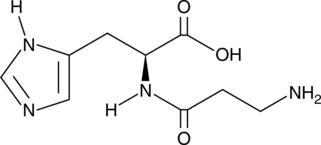
L-Alanyl-L-glutamine is a synthetic glutamine dipeptide that can attenuate oxidative stress in rodent models when administered at doses of 0.75-1.5 mg/kg.{34399,34398,34396,34394} In vivo, the parenteral administration of L-alanyl-L-glutamine to Swiss mice yields higher plasma glutamine levels compared to enteral administration.{34393} In vitro, the addition of this dipeptide (50 mM) to cultures of antibody-producing CHO cells reduces apoptosis and promotes antibody production.{34397} Treatment of insulin-secreting BRIN-BD11 β-cells with L-alanyl-L-glutamine (2 mM) protects against the inflammatory effects of exposure to lipopolysaccharide-treated primary macrophages.{34395}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21809 -Out of stock
L-Alanyl-L-glutamine is a synthetic glutamine dipeptide that can attenuate oxidative stress in rodent models when administered at doses of 0.75-1.5 mg/kg.{34399,34398,34396,34394} In vivo, the parenteral administration of L-alanyl-L-glutamine to Swiss mice yields higher plasma glutamine levels compared to enteral administration.{34393} In vitro, the addition of this dipeptide (50 mM) to cultures of antibody-producing CHO cells reduces apoptosis and promotes antibody production.{34397} Treatment of insulin-secreting BRIN-BD11 β-cells with L-alanyl-L-glutamine (2 mM) protects against the inflammatory effects of exposure to lipopolysaccharide-treated primary macrophages.{34395}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21809 -Out of stock
L-Alanyl-L-glutamine is a synthetic glutamine dipeptide that can attenuate oxidative stress in rodent models when administered at doses of 0.75-1.5 mg/kg.{34399,34398,34396,34394} In vivo, the parenteral administration of L-alanyl-L-glutamine to Swiss mice yields higher plasma glutamine levels compared to enteral administration.{34393} In vitro, the addition of this dipeptide (50 mM) to cultures of antibody-producing CHO cells reduces apoptosis and promotes antibody production.{34397} Treatment of insulin-secreting BRIN-BD11 β-cells with L-alanyl-L-glutamine (2 mM) protects against the inflammatory effects of exposure to lipopolysaccharide-treated primary macrophages.{34395}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21809 -Out of stock
L-Alanyl-L-glutamine is a synthetic glutamine dipeptide that can attenuate oxidative stress in rodent models when administered at doses of 0.75-1.5 mg/kg.{34399,34398,34396,34394} In vivo, the parenteral administration of L-alanyl-L-glutamine to Swiss mice yields higher plasma glutamine levels compared to enteral administration.{34393} In vitro, the addition of this dipeptide (50 mM) to cultures of antibody-producing CHO cells reduces apoptosis and promotes antibody production.{34397} Treatment of insulin-secreting BRIN-BD11 β-cells with L-alanyl-L-glutamine (2 mM) protects against the inflammatory effects of exposure to lipopolysaccharide-treated primary macrophages.{34395}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21809 -Out of stock
L-Allylglycine is an amino acid derivative that reduces glutamate decarboxylase (GAD) activity by 60% when administered at a dose of 39.8 μmol/g per hour ex vivo in mouse brain preparations.{36239} L-Allylglycine (1.2 mmol/kg, i.p.) induces convulsions and decreases GABA concentration throughout the cerebellum, pons, medulla, striatum, cortex, and hippocampus in mice.{36240} Chronic administration (3.2 μg/0.5 μl per hour for 13 days) of L-allylglycine in rats increases locomotor activity in an open field test and impairs attention in the 5-choice serial reaction time task (5CSRTT).{36241} In vitro, L-allylglycine inhibits GAD only when used at high concentrations (1-80 mM). The more potent in vivo activity can be attributed to metabolic conversion of L-allylglycine to 2-keto-4-pentanoic acid, a more potent convulsant and GAD inhibitor.
Brand:CaymanSKU:23348 - 1 gAvailable on backorder
L-Allylglycine is an amino acid derivative that reduces glutamate decarboxylase (GAD) activity by 60% when administered at a dose of 39.8 μmol/g per hour ex vivo in mouse brain preparations.{36239} L-Allylglycine (1.2 mmol/kg, i.p.) induces convulsions and decreases GABA concentration throughout the cerebellum, pons, medulla, striatum, cortex, and hippocampus in mice.{36240} Chronic administration (3.2 μg/0.5 μl per hour for 13 days) of L-allylglycine in rats increases locomotor activity in an open field test and impairs attention in the 5-choice serial reaction time task (5CSRTT).{36241} In vitro, L-allylglycine inhibits GAD only when used at high concentrations (1-80 mM). The more potent in vivo activity can be attributed to metabolic conversion of L-allylglycine to 2-keto-4-pentanoic acid, a more potent convulsant and GAD inhibitor.
Brand:CaymanSKU:23348 - 250 mgAvailable on backorder
L-Allylglycine is an amino acid derivative that reduces glutamate decarboxylase (GAD) activity by 60% when administered at a dose of 39.8 μmol/g per hour ex vivo in mouse brain preparations.{36239} L-Allylglycine (1.2 mmol/kg, i.p.) induces convulsions and decreases GABA concentration throughout the cerebellum, pons, medulla, striatum, cortex, and hippocampus in mice.{36240} Chronic administration (3.2 μg/0.5 μl per hour for 13 days) of L-allylglycine in rats increases locomotor activity in an open field test and impairs attention in the 5-choice serial reaction time task (5CSRTT).{36241} In vitro, L-allylglycine inhibits GAD only when used at high concentrations (1-80 mM). The more potent in vivo activity can be attributed to metabolic conversion of L-allylglycine to 2-keto-4-pentanoic acid, a more potent convulsant and GAD inhibitor.
Brand:CaymanSKU:23348 - 5 gAvailable on backorder
L-Allylglycine is an amino acid derivative that reduces glutamate decarboxylase (GAD) activity by 60% when administered at a dose of 39.8 μmol/g per hour ex vivo in mouse brain preparations.{36239} L-Allylglycine (1.2 mmol/kg, i.p.) induces convulsions and decreases GABA concentration throughout the cerebellum, pons, medulla, striatum, cortex, and hippocampus in mice.{36240} Chronic administration (3.2 μg/0.5 μl per hour for 13 days) of L-allylglycine in rats increases locomotor activity in an open field test and impairs attention in the 5-choice serial reaction time task (5CSRTT).{36241} In vitro, L-allylglycine inhibits GAD only when used at high concentrations (1-80 mM). The more potent in vivo activity can be attributed to metabolic conversion of L-allylglycine to 2-keto-4-pentanoic acid, a more potent convulsant and GAD inhibitor.
Brand:CaymanSKU:23348 - 500 mgAvailable on backorder
L-ANAP is an unnatural amino acid with intrinsic fluorescence that can be genetically encoded into proteins.{28417} This technology allows incorporation of L-ANAP into virtually any site on a protein, providing a unique method for imaging biological processes in vivo.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-L-ANAP is an unnatural amino acid with intrinsic fluorescence that can be genetically encoded into proteins.{28417} This technology allows incorporation of L-ANAP into virtually any site on a protein, providing a unique method for imaging biological processes in vivo.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-L-ANAP is an unnatural amino acid with intrinsic fluorescence that can be genetically encoded into proteins.{28417} This technology allows incorporation of L-ANAP into virtually any site on a protein, providing a unique method for imaging biological processes in vivo.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluR) function to modulate excitatory synaptic transmission in the brain. Eight subtypes (1-8) and multiple splice variants of the mGluR have been identified and grouped based on their pharmacological properties. Group I mGluRs (subtypes 1 and 5) activate the phosphatidyl inositol pathway, while Group II (2 and 3) and Group III (4, 6, 7, and 8) inhibit adenylyl cyclase. L-AP4, an analog of L-glutamic acid, is a selective Group III mGluR agonist that functions presynaptically to suppress glutamate release (IC50 = 2.5 μM).{22831,22827,21634} L-AP4 has been shown to depress synaptic transmission in glutamatergic pathways in the hippocampus, olfactory bulb, and retina as well as act as an agonist at the quisqualate-sensitized AP6 site in hippocampus.{22831}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluR) function to modulate excitatory synaptic transmission in the brain. Eight subtypes (1-8) and multiple splice variants of the mGluR have been identified and grouped based on their pharmacological properties. Group I mGluRs (subtypes 1 and 5) activate the phosphatidyl inositol pathway, while Group II (2 and 3) and Group III (4, 6, 7, and 8) inhibit adenylyl cyclase. L-AP4, an analog of L-glutamic acid, is a selective Group III mGluR agonist that functions presynaptically to suppress glutamate release (IC50 = 2.5 μM).{22831,22827,21634} L-AP4 has been shown to depress synaptic transmission in glutamatergic pathways in the hippocampus, olfactory bulb, and retina as well as act as an agonist at the quisqualate-sensitized AP6 site in hippocampus.{22831}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluR) function to modulate excitatory synaptic transmission in the brain. Eight subtypes (1-8) and multiple splice variants of the mGluR have been identified and grouped based on their pharmacological properties. Group I mGluRs (subtypes 1 and 5) activate the phosphatidyl inositol pathway, while Group II (2 and 3) and Group III (4, 6, 7, and 8) inhibit adenylyl cyclase. L-AP4, an analog of L-glutamic acid, is a selective Group III mGluR agonist that functions presynaptically to suppress glutamate release (IC50 = 2.5 μM).{22831,22827,21634} L-AP4 has been shown to depress synaptic transmission in glutamatergic pathways in the hippocampus, olfactory bulb, and retina as well as act as an agonist at the quisqualate-sensitized AP6 site in hippocampus.{22831}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluR) function to modulate excitatory synaptic transmission in the brain. Eight subtypes (1-8) and multiple splice variants of the mGluR have been identified and grouped based on their pharmacological properties. Group I mGluRs (subtypes 1 and 5) activate the phosphatidyl inositol pathway, while Group II (2 and 3) and Group III (4, 6, 7, and 8) inhibit adenylyl cyclase. L-AP4, an analog of L-glutamic acid, is a selective Group III mGluR agonist that functions presynaptically to suppress glutamate release (IC50 = 2.5 μM).{22831,22827,21634} L-AP4 has been shown to depress synaptic transmission in glutamatergic pathways in the hippocampus, olfactory bulb, and retina as well as act as an agonist at the quisqualate-sensitized AP6 site in hippocampus.{22831}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-L-Arginine is an amino acid and precursor of nitric oxide (NO).{41250} L-Arginine is a substrate for NO synthase that is oxidized to form NO and L-citrulline. It enhances NO release in porcine aortic endothelial cells treated with bradykinin (Item No. 15539) or A23187 (Item No. 11016).{41249} L-Arginine (30 and 300 mg/kg, i.v.) induces dilation of pial arterioles and increases cerebral blood flow in normotensive and spontaneously hypertensive rats.{41248} It also reduces infarct size by 35 and 28% in normotensive and spontaneously hypertensive rats, respectively, following middle cerebral artery occlusion.
Brand:CaymanSKU:23703 - 100 gAvailable on backorder
L-Arginine is an amino acid and precursor of nitric oxide (NO).{41250} L-Arginine is a substrate for NO synthase that is oxidized to form NO and L-citrulline. It enhances NO release in porcine aortic endothelial cells treated with bradykinin (Item No. 15539) or A23187 (Item No. 11016).{41249} L-Arginine (30 and 300 mg/kg, i.v.) induces dilation of pial arterioles and increases cerebral blood flow in normotensive and spontaneously hypertensive rats.{41248} It also reduces infarct size by 35 and 28% in normotensive and spontaneously hypertensive rats, respectively, following middle cerebral artery occlusion.
Brand:CaymanSKU:23703 - 25 gAvailable on backorder
L-Arginine is an amino acid and precursor of nitric oxide (NO).{41250} L-Arginine is a substrate for NO synthase that is oxidized to form NO and L-citrulline. It enhances NO release in porcine aortic endothelial cells treated with bradykinin (Item No. 15539) or A23187 (Item No. 11016).{41249} L-Arginine (30 and 300 mg/kg, i.v.) induces dilation of pial arterioles and increases cerebral blood flow in normotensive and spontaneously hypertensive rats.{41248} It also reduces infarct size by 35 and 28% in normotensive and spontaneously hypertensive rats, respectively, following middle cerebral artery occlusion.
Brand:CaymanSKU:23703 - 50 gAvailable on backorder
L-Ascorbic acid is a naturally occurring electron donor and therefore serves as a reducing agent.{18457} It is synthesized from glucose in the liver of most mammalian species, excluding humans, non-human primates, or guinea pigs who must obtain it through dietary consumption. In humans, L-Ascorbic acid acts as an electron donor for eight different enzymes, including those related to collagen hydroxylation, carnitine synthesis (which aids in the generation of adenosine triphosphate), norepinephrine synthesis, tyrosine metabolism, and amidating peptides.{18461,18452,18453,18454,18456} L-Ascorbic acid demonstrates antioxidant activity that may be of some benefit for reducing the risk of developing chronic diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular disease, and cataracts.{18457}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-L-Ascorbic acid is a naturally occurring electron donor and therefore serves as a reducing agent.{18457} It is synthesized from glucose in the liver of most mammalian species, excluding humans, non-human primates, or guinea pigs who must obtain it through dietary consumption. In humans, L-Ascorbic acid acts as an electron donor for eight different enzymes, including those related to collagen hydroxylation, carnitine synthesis (which aids in the generation of adenosine triphosphate), norepinephrine synthesis, tyrosine metabolism, and amidating peptides.{18461,18452,18453,18454,18456} L-Ascorbic acid demonstrates antioxidant activity that may be of some benefit for reducing the risk of developing chronic diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular disease, and cataracts.{18457}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-L-Ascorbic acid is a naturally occurring electron donor and therefore serves as a reducing agent.{18457} It is synthesized from glucose in the liver of most mammalian species, excluding humans, non-human primates, or guinea pigs who must obtain it through dietary consumption. In humans, L-Ascorbic acid acts as an electron donor for eight different enzymes, including those related to collagen hydroxylation, carnitine synthesis (which aids in the generation of adenosine triphosphate), norepinephrine synthesis, tyrosine metabolism, and amidating peptides.{18461,18452,18453,18454,18456} L-Ascorbic acid demonstrates antioxidant activity that may be of some benefit for reducing the risk of developing chronic diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular disease, and cataracts.{18457}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-L-Ascorbic acid (vitamin C; Item No. 14656) is essential for the synthesis of collagen, with deficiency resulting in scurvy.{18461} Notably, humans and other primates, guinea pigs, and certain other animals lack an enzyme necessary for vitamin C synthesis.{18461} L-Ascorbic acid 2-phosphate (AA2P) is a long-acting ascorbic acid derivative that stimulates collagen expression and formation and is used in human cell culture.{26913,26914} It may be included in media to enhance the survival of human embryonic stem cells or increase the growth and replicative lifespan of human corneal endothelial cells.{26910,26911} AA2P is also used to drive osteogenic differentiation in human adipose stem cells and in human mesenchymal stromal/stem cells.{26912,26916,26915}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
L-Ascorbic acid (vitamin C; Item No. 14656) is essential for the synthesis of collagen, with deficiency resulting in scurvy.{18461} Notably, humans and other primates, guinea pigs, and certain other animals lack an enzyme necessary for vitamin C synthesis.{18461} L-Ascorbic acid 2-phosphate (AA2P) is a long-acting ascorbic acid derivative that stimulates collagen expression and formation and is used in human cell culture.{26913,26914} It may be included in media to enhance the survival of human embryonic stem cells or increase the growth and replicative lifespan of human corneal endothelial cells.{26910,26911} AA2P is also used to drive osteogenic differentiation in human adipose stem cells and in human mesenchymal stromal/stem cells.{26912,26916,26915}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
L-Ascorbic acid (vitamin C; Item No. 14656) is essential for the synthesis of collagen, with deficiency resulting in scurvy.{18461} Notably, humans and other primates, guinea pigs, and certain other animals lack an enzyme necessary for vitamin C synthesis.{18461} L-Ascorbic acid 2-phosphate (AA2P) is a long-acting ascorbic acid derivative that stimulates collagen expression and formation and is used in human cell culture.{26913,26914} It may be included in media to enhance the survival of human embryonic stem cells or increase the growth and replicative lifespan of human corneal endothelial cells.{26910,26911} AA2P is also used to drive osteogenic differentiation in human adipose stem cells and in human mesenchymal stromal/stem cells.{26912,26916,26915}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
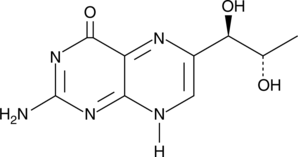
L-Biopterin is the oxidized form of tetrahydro-L-biopterin (BH4), a nitric oxide synthase (NOS) cofactor. L-Biopterin can be reduced to BH4 via thioredoxin reductase followed by dihydropteridine reductase or reduced glutathione. It is extremely toxic to human melanocytes in culture (IC50 = 0.2 µM after 48 hrs).{15034} L-Biopterin is rarely found under physiological conditions except in the epidermis of patients with the depigmentation disorder Vitiligo.{15033}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007662 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
L-Biopterin is the oxidized form of tetrahydro-L-biopterin (BH4), a nitric oxide synthase (NOS) cofactor. L-Biopterin can be reduced to BH4 via thioredoxin reductase followed by dihydropteridine reductase or reduced glutathione. It is extremely toxic to human melanocytes in culture (IC50 = 0.2 µM after 48 hrs).{15034} L-Biopterin is rarely found under physiological conditions except in the epidermis of patients with the depigmentation disorder Vitiligo.{15033}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007662 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
L-Biopterin is the oxidized form of tetrahydro-L-biopterin (BH4), a nitric oxide synthase (NOS) cofactor. L-Biopterin can be reduced to BH4 via thioredoxin reductase followed by dihydropteridine reductase or reduced glutathione. It is extremely toxic to human melanocytes in culture (IC50 = 0.2 µM after 48 hrs).{15034} L-Biopterin is rarely found under physiological conditions except in the epidermis of patients with the depigmentation disorder Vitiligo.{15033}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007662 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
L-Biopterin is the oxidized form of tetrahydro-L-biopterin (BH4), a nitric oxide synthase (NOS) cofactor. L-Biopterin can be reduced to BH4 via thioredoxin reductase followed by dihydropteridine reductase or reduced glutathione. It is extremely toxic to human melanocytes in culture (IC50 = 0.2 µM after 48 hrs).{15034} L-Biopterin is rarely found under physiological conditions except in the epidermis of patients with the depigmentation disorder Vitiligo.{15033}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007662 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
L-Buthionine-(S,R)-sulfoximine is an irreversible inhibitor of γ-glutamylcysteine synthetase (Ki <100 μM), the rate-limiting enzyme for L-glutathione (GSH) synthesis, that induces oxidative stress in cells by depleting GSH.{22905,22906} Administration of L-buthionine-(S,R)-sulfoximine leads to decreased GSH levels in virtually all tissues and is associated with tissue damage and apoptosis.{22908,22904} Whereas elevated glutathione levels are associated with tumor cell resistance, L-buthionine-(S,R)-sulfoximine has been shown to enhance the toxicity of various chemotherapeutic agents in drug-resistant tumors.{22907}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-L-Buthionine-(S,R)-sulfoximine is an irreversible inhibitor of γ-glutamylcysteine synthetase (Ki <100 μM), the rate-limiting enzyme for L-glutathione (GSH) synthesis, that induces oxidative stress in cells by depleting GSH.{22905,22906} Administration of L-buthionine-(S,R)-sulfoximine leads to decreased GSH levels in virtually all tissues and is associated with tissue damage and apoptosis.{22908,22904} Whereas elevated glutathione levels are associated with tumor cell resistance, L-buthionine-(S,R)-sulfoximine has been shown to enhance the toxicity of various chemotherapeutic agents in drug-resistant tumors.{22907}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-L-Buthionine-(S,R)-sulfoximine is an irreversible inhibitor of γ-glutamylcysteine synthetase (Ki <100 μM), the rate-limiting enzyme for L-glutathione (GSH) synthesis, that induces oxidative stress in cells by depleting GSH.{22905,22906} Administration of L-buthionine-(S,R)-sulfoximine leads to decreased GSH levels in virtually all tissues and is associated with tissue damage and apoptosis.{22908,22904} Whereas elevated glutathione levels are associated with tumor cell resistance, L-buthionine-(S,R)-sulfoximine has been shown to enhance the toxicity of various chemotherapeutic agents in drug-resistant tumors.{22907}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-L-Canaline is an aminooxy analog of ornithine that irreversibly inhibits aminotransferases (transaminases), including ornithine aminotransferase (Ki = 2 µM).{29314,29315,29317} It forms oximes with α-keto acids and aldehydes, most notably with pyridoxal phosphate, an essential cofactor of aminotransferases.{29317} L-Canaline is naturally found in plants, including legumes, and is involved in the metabolism of L-canavanine, an aminooxy analog of arginine.{29316} It is cytotoxic to a range of organisms, including bacteria, insects, and parasites.{29315,29316,29313}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9002357 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
L-Canaline is an aminooxy analog of ornithine that irreversibly inhibits aminotransferases (transaminases), including ornithine aminotransferase (Ki = 2 µM).{29314,29315,29317} It forms oximes with α-keto acids and aldehydes, most notably with pyridoxal phosphate, an essential cofactor of aminotransferases.{29317} L-Canaline is naturally found in plants, including legumes, and is involved in the metabolism of L-canavanine, an aminooxy analog of arginine.{29316} It is cytotoxic to a range of organisms, including bacteria, insects, and parasites.{29315,29316,29313}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9002357 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
L-Canaline is an aminooxy analog of ornithine that irreversibly inhibits aminotransferases (transaminases), including ornithine aminotransferase (Ki = 2 µM).{29314,29315,29317} It forms oximes with α-keto acids and aldehydes, most notably with pyridoxal phosphate, an essential cofactor of aminotransferases.{29317} L-Canaline is naturally found in plants, including legumes, and is involved in the metabolism of L-canavanine, an aminooxy analog of arginine.{29316} It is cytotoxic to a range of organisms, including bacteria, insects, and parasites.{29315,29316,29313}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9002357 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
L-Canaline is an aminooxy analog of ornithine that irreversibly inhibits aminotransferases (transaminases), including ornithine aminotransferase (Ki = 2 µM).{29314,29315,29317} It forms oximes with α-keto acids and aldehydes, most notably with pyridoxal phosphate, an essential cofactor of aminotransferases.{29317} L-Canaline is naturally found in plants, including legumes, and is involved in the metabolism of L-canavanine, an aminooxy analog of arginine.{29316} It is cytotoxic to a range of organisms, including bacteria, insects, and parasites.{29315,29316,29313}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9002357 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
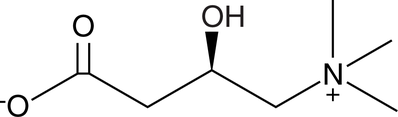
L-Carnitine is an essential metabolite that has diverse roles in metabolism, most notably facilitating the transport of long-chain fatty acids into the mitochondrial matrix for β-oxidation.{27352,27356} L-Carnitine is obtained from dietary sources or by the metabolism of lysine and methionine. It is also important for the maintenance of coenzyme A (CoA; Item No. 16147) stores.
Brand:CaymanSKU:21489 -Out of stock
L-Carnitine is an essential metabolite that has diverse roles in metabolism, most notably facilitating the transport of long-chain fatty acids into the mitochondrial matrix for β-oxidation.{27352,27356} L-Carnitine is obtained from dietary sources or by the metabolism of lysine and methionine. It is also important for the maintenance of coenzyme A (CoA; Item No. 16147) stores.
Brand:CaymanSKU:21489 -Out of stock
L-Carnitine is an essential metabolite that has diverse roles in metabolism, most notably facilitating the transport of long-chain fatty acids into the mitochondrial matrix for β-oxidation.{27352,27356} L-Carnitine is obtained from dietary sources or by the metabolism of lysine and methionine. It is also important for the maintenance of coenzyme A (CoA; Item No. 16147) stores.
Brand:CaymanSKU:21489 -Out of stock
L-Carnitine is an essential metabolite that has diverse roles in metabolism, most notably facilitating the transport of long-chain fatty acids into the mitochondrial matrix for β-oxidation.{27352,27356} L-Carnitine is obtained from dietary sources or by the metabolism of lysine and methionine. It is also important for the maintenance of coenzyme A (CoA; Item No. 16147) stores.
Brand:CaymanSKU:21489 -Out of stock
L-Carnitine-d3 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of L-carnitine (Item No. 21489) by GC- or LC-MS. L-Carnitine is an essential metabolite that has diverse roles in metabolism, most notably facilitating the transport of long-chain fatty acids into the mitochondrial matrix for β-oxidation.{27352,27356} L-Carnitine is obtained from dietary sources or by the metabolism of lysine and methionine. It is also important for the maintenance of coenzyme A (CoA; Item No. 16147) stores.
Brand:CaymanSKU:26565 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
L-Carnitine-d3 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of L-carnitine (Item No. 21489) by GC- or LC-MS. L-Carnitine is an essential metabolite that has diverse roles in metabolism, most notably facilitating the transport of long-chain fatty acids into the mitochondrial matrix for β-oxidation.{27352,27356} L-Carnitine is obtained from dietary sources or by the metabolism of lysine and methionine. It is also important for the maintenance of coenzyme A (CoA; Item No. 16147) stores.
Brand:CaymanSKU:26565 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
L-Carnitine-d3 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of L-carnitine (Item No. 21489) by GC- or LC-MS. L-Carnitine is an essential metabolite that has diverse roles in metabolism, most notably facilitating the transport of long-chain fatty acids into the mitochondrial matrix for β-oxidation.{27352,27356} L-Carnitine is obtained from dietary sources or by the metabolism of lysine and methionine. It is also important for the maintenance of coenzyme A (CoA; Item No. 16147) stores.
Brand:CaymanSKU:26565 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
L-Carnitine-d3 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of L-carnitine (Item No. 21489) by GC- or LC-MS. L-Carnitine is an essential metabolite that has diverse roles in metabolism, most notably facilitating the transport of long-chain fatty acids into the mitochondrial matrix for β-oxidation.{27352,27356} L-Carnitine is obtained from dietary sources or by the metabolism of lysine and methionine. It is also important for the maintenance of coenzyme A (CoA; Item No. 16147) stores.
Brand:CaymanSKU:26565 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
L-Carnosine is a dipeptide composed of β-alanine and L-histidine that has been found in rat olfactory bulb, skeletal muscle, brain, kidney, and spleen tissues, as well as human skeletal muscle, and has diverse biological activities.{53448} It is a metal chelator that forms complexes with copper, cobalt, nickel, cadmium, or zinc. Dietary administration of L-carnosine (60 mg/kg per day) reduces plasma levels of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) in diabetic rats.{53449} It reduces brain edema, blood-brain barrier disruption, microglial activation, and neuronal apoptosis in a rat model of intracerebral hemorrhage when administered at a dose of 1,000 mg/kg.{53450} L-Carnosine (250, 500, and 1,000 mg/kg, i.p.) reduces hepatic protein carbonylation and necrosis in a rat model of cirrhosis induced by bile duct ligation.{53451} It also reduces lung myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity, production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), and TNF-α and IL-6 levels, as well as alveolar hemorrhage, interstitial edema, and pulmonary leukocyte infiltration in a mouse model of LPS-induced lung injury.{53452}
Brand:CaymanSKU:29825 - 10 gAvailable on backorder
L-Carnosine is a dipeptide composed of β-alanine and L-histidine that has been found in rat olfactory bulb, skeletal muscle, brain, kidney, and spleen tissues, as well as human skeletal muscle, and has diverse biological activities.{53448} It is a metal chelator that forms complexes with copper, cobalt, nickel, cadmium, or zinc. Dietary administration of L-carnosine (60 mg/kg per day) reduces plasma levels of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) in diabetic rats.{53449} It reduces brain edema, blood-brain barrier disruption, microglial activation, and neuronal apoptosis in a rat model of intracerebral hemorrhage when administered at a dose of 1,000 mg/kg.{53450} L-Carnosine (250, 500, and 1,000 mg/kg, i.p.) reduces hepatic protein carbonylation and necrosis in a rat model of cirrhosis induced by bile duct ligation.{53451} It also reduces lung myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity, production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), and TNF-α and IL-6 levels, as well as alveolar hemorrhage, interstitial edema, and pulmonary leukocyte infiltration in a mouse model of LPS-induced lung injury.{53452}
Brand:CaymanSKU:29825 - 25 gAvailable on backorder
L-Carnosine is a dipeptide composed of β-alanine and L-histidine that has been found in rat olfactory bulb, skeletal muscle, brain, kidney, and spleen tissues, as well as human skeletal muscle, and has diverse biological activities.{53448} It is a metal chelator that forms complexes with copper, cobalt, nickel, cadmium, or zinc. Dietary administration of L-carnosine (60 mg/kg per day) reduces plasma levels of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) in diabetic rats.{53449} It reduces brain edema, blood-brain barrier disruption, microglial activation, and neuronal apoptosis in a rat model of intracerebral hemorrhage when administered at a dose of 1,000 mg/kg.{53450} L-Carnosine (250, 500, and 1,000 mg/kg, i.p.) reduces hepatic protein carbonylation and necrosis in a rat model of cirrhosis induced by bile duct ligation.{53451} It also reduces lung myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity, production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), and TNF-α and IL-6 levels, as well as alveolar hemorrhage, interstitial edema, and pulmonary leukocyte infiltration in a mouse model of LPS-induced lung injury.{53452}
Brand:CaymanSKU:29825 - 5 gAvailable on backorder
L-Carnosine is a dipeptide composed of β-alanine and L-histidine that has been found in rat olfactory bulb, skeletal muscle, brain, kidney, and spleen tissues, as well as human skeletal muscle, and has diverse biological activities.{53448} It is a metal chelator that forms complexes with copper, cobalt, nickel, cadmium, or zinc. Dietary administration of L-carnosine (60 mg/kg per day) reduces plasma levels of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) in diabetic rats.{53449} It reduces brain edema, blood-brain barrier disruption, microglial activation, and neuronal apoptosis in a rat model of intracerebral hemorrhage when administered at a dose of 1,000 mg/kg.{53450} L-Carnosine (250, 500, and 1,000 mg/kg, i.p.) reduces hepatic protein carbonylation and necrosis in a rat model of cirrhosis induced by bile duct ligation.{53451} It also reduces lung myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity, production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), and TNF-α and IL-6 levels, as well as alveolar hemorrhage, interstitial edema, and pulmonary leukocyte infiltration in a mouse model of LPS-induced lung injury.{53452}
Brand:CaymanSKU:29825 - 50 gAvailable on backorder
L-Cycloserine is a potent inhibitor of serine palmitoyl transferase (SPT), the first enzyme in the sphingolipid synthesis pathway.{39381} It inhibits bacterial SPT activity by 80% at a concentration of 25 µM, which is 100 times more potent than D-cycloserine (Item No. 22194). L-Cycloserine inhibits SPT activity up to 86% in a dose-dependent manner in microsomes prepared from mouse brain following administration of doses ranging from 25-200 mg/kg. It also inhibits SPT in rabbit aorta and several aminotransferases in vitro and in vivo in rat.{39382,39383} L-Cycloserine inhibits the growth of M. tuberculosis through branched chain aminotransferase inactivation, and it does so more rapidly and potently than D-cycloserine (MICs = 0.3 and 2.3 µg/ml, respectively).{39380}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
L-Cycloserine is a potent inhibitor of serine palmitoyl transferase (SPT), the first enzyme in the sphingolipid synthesis pathway.{39381} It inhibits bacterial SPT activity by 80% at a concentration of 25 µM, which is 100 times more potent than D-cycloserine (Item No. 22194). L-Cycloserine inhibits SPT activity up to 86% in a dose-dependent manner in microsomes prepared from mouse brain following administration of doses ranging from 25-200 mg/kg. It also inhibits SPT in rabbit aorta and several aminotransferases in vitro and in vivo in rat.{39382,39383} L-Cycloserine inhibits the growth of M. tuberculosis through branched chain aminotransferase inactivation, and it does so more rapidly and potently than D-cycloserine (MICs = 0.3 and 2.3 µg/ml, respectively).{39380}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
L-Cycloserine is a potent inhibitor of serine palmitoyl transferase (SPT), the first enzyme in the sphingolipid synthesis pathway.{39381} It inhibits bacterial SPT activity by 80% at a concentration of 25 µM, which is 100 times more potent than D-cycloserine (Item No. 22194). L-Cycloserine inhibits SPT activity up to 86% in a dose-dependent manner in microsomes prepared from mouse brain following administration of doses ranging from 25-200 mg/kg. It also inhibits SPT in rabbit aorta and several aminotransferases in vitro and in vivo in rat.{39382,39383} L-Cycloserine inhibits the growth of M. tuberculosis through branched chain aminotransferase inactivation, and it does so more rapidly and potently than D-cycloserine (MICs = 0.3 and 2.3 µg/ml, respectively).{39380}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
L-Cycloserine is a potent inhibitor of serine palmitoyl transferase (SPT), the first enzyme in the sphingolipid synthesis pathway.{39381} It inhibits bacterial SPT activity by 80% at a concentration of 25 µM, which is 100 times more potent than D-cycloserine (Item No. 22194). L-Cycloserine inhibits SPT activity up to 86% in a dose-dependent manner in microsomes prepared from mouse brain following administration of doses ranging from 25-200 mg/kg. It also inhibits SPT in rabbit aorta and several aminotransferases in vitro and in vivo in rat.{39382,39383} L-Cycloserine inhibits the growth of M. tuberculosis through branched chain aminotransferase inactivation, and it does so more rapidly and potently than D-cycloserine (MICs = 0.3 and 2.3 µg/ml, respectively).{39380}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
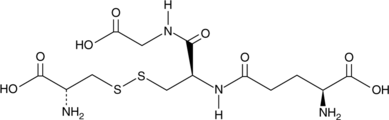
L-Cysteine-glutathione disulfide, a glutathione derivative endogenous to mammalian cells, is comprised of the oxidized form of free glutathione tripeptide linked via a disulfide bond to L-cysteine.{28543} It has been shown to protect mice against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity.{28542}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
L-Cysteine-glutathione disulfide, a glutathione derivative endogenous to mammalian cells, is comprised of the oxidized form of free glutathione tripeptide linked via a disulfide bond to L-cysteine.{28543} It has been shown to protect mice against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity.{28542}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
L-Cysteine-glutathione disulfide, a glutathione derivative endogenous to mammalian cells, is comprised of the oxidized form of free glutathione tripeptide linked via a disulfide bond to L-cysteine.{28543} It has been shown to protect mice against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity.{28542}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
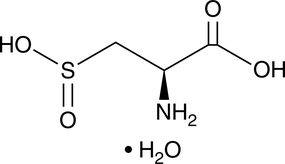
L-Cysteinesulfinic acid is an excitatory amino acid and agonist of metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs).{49465,49466} It increases intracellular inositol phosphate levels in CHO cells expressing mGluR1, mGluR5, or mGluR8 (EC50s = 120, 30, and 110 μM, respectively) and inhibits forskolin-induced cAMP production in CHO cells expressing mGluR2 or mGluR6 and hamster kidney cells expressing mGluR4 (EC50s = 100, 100, and 2,000 μM, respectively).{49466} It selectively binds to mGluR1α (Ki = 3,510 nM) over adrenergic, dopamine, histamine, muscarinic, nicotinic, or serotonin receptors (Kis = >10,000 nM for all). L-Cysteinesulfinic acid (1 mM) decreases mean arterial blood pressure and heart rate in rats when microinjected into the nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS).{49465} L-Cysteinesulfinic acid can be formed via oxidation of L-cysteine by reactive oxygen species (ROS), and conversion of cysteine to L-cysteinesulfinic acid in cysteine-containing peptide probes has been used to measure oxidative stress.{49467}
Brand:CaymanSKU:29597 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
L-Cysteinesulfinic acid is an excitatory amino acid and agonist of metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs).{49465,49466} It increases intracellular inositol phosphate levels in CHO cells expressing mGluR1, mGluR5, or mGluR8 (EC50s = 120, 30, and 110 μM, respectively) and inhibits forskolin-induced cAMP production in CHO cells expressing mGluR2 or mGluR6 and hamster kidney cells expressing mGluR4 (EC50s = 100, 100, and 2,000 μM, respectively).{49466} It selectively binds to mGluR1α (Ki = 3,510 nM) over adrenergic, dopamine, histamine, muscarinic, nicotinic, or serotonin receptors (Kis = >10,000 nM for all). L-Cysteinesulfinic acid (1 mM) decreases mean arterial blood pressure and heart rate in rats when microinjected into the nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS).{49465} L-Cysteinesulfinic acid can be formed via oxidation of L-cysteine by reactive oxygen species (ROS), and conversion of cysteine to L-cysteinesulfinic acid in cysteine-containing peptide probes has been used to measure oxidative stress.{49467}
Brand:CaymanSKU:29597 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
L-Cysteinesulfinic acid is an excitatory amino acid and agonist of metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs).{49465,49466} It increases intracellular inositol phosphate levels in CHO cells expressing mGluR1, mGluR5, or mGluR8 (EC50s = 120, 30, and 110 μM, respectively) and inhibits forskolin-induced cAMP production in CHO cells expressing mGluR2 or mGluR6 and hamster kidney cells expressing mGluR4 (EC50s = 100, 100, and 2,000 μM, respectively).{49466} It selectively binds to mGluR1α (Ki = 3,510 nM) over adrenergic, dopamine, histamine, muscarinic, nicotinic, or serotonin receptors (Kis = >10,000 nM for all). L-Cysteinesulfinic acid (1 mM) decreases mean arterial blood pressure and heart rate in rats when microinjected into the nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS).{49465} L-Cysteinesulfinic acid can be formed via oxidation of L-cysteine by reactive oxygen species (ROS), and conversion of cysteine to L-cysteinesulfinic acid in cysteine-containing peptide probes has been used to measure oxidative stress.{49467}
Brand:CaymanSKU:29597 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
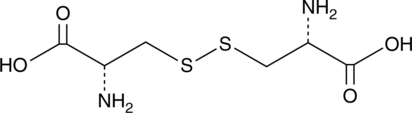
L-Cystine is a dimeric form of cysteine that is formed by the covalent oxidative linkage of two cysteine residues.{61138} It accumulates in the lysosomes of patients with cystinosis, an autosomal recessive lysosomal storage disorder, and is associated with renal Fanconi syndrome and loss of glomerular function.{61139}
Brand:CaymanSKU:31727 - 100 gAvailable on backorder
L-Cystine is a dimeric form of cysteine that is formed by the covalent oxidative linkage of two cysteine residues.{61138} It accumulates in the lysosomes of patients with cystinosis, an autosomal recessive lysosomal storage disorder, and is associated with renal Fanconi syndrome and loss of glomerular function.{61139}
Brand:CaymanSKU:31727 - 250 gAvailable on backorder