Cayman
Showing 22201–22350 of 45550 results
-
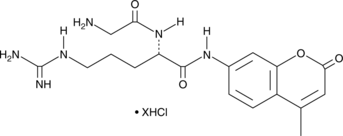
Gly-Arg-AMC is a fluorogenic substrate for cathepsin C.{52029} Upon enzymatic cleavage by cathepsin C, 7-amino-4-methylcoumarin (AMC) is released and its fluorescence can be used to quantify cathepsin C activity. AMC displays excitation/emission maxima of 340-360/440-460 nm, respectively.
Brand:CaymanSKU:27580 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Gly-Arg-AMC is a fluorogenic substrate for cathepsin C.{52029} Upon enzymatic cleavage by cathepsin C, 7-amino-4-methylcoumarin (AMC) is released and its fluorescence can be used to quantify cathepsin C activity. AMC displays excitation/emission maxima of 340-360/440-460 nm, respectively.
Brand:CaymanSKU:27580 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Gly-Arg-AMC is a fluorogenic substrate for cathepsin C.{52029} Upon enzymatic cleavage by cathepsin C, 7-amino-4-methylcoumarin (AMC) is released and its fluorescence can be used to quantify cathepsin C activity. AMC displays excitation/emission maxima of 340-360/440-460 nm, respectively.
Brand:CaymanSKU:27580 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
Gly-Arg-AMC is a fluorogenic substrate for cathepsin C.{52029} Upon enzymatic cleavage by cathepsin C, 7-amino-4-methylcoumarin (AMC) is released and its fluorescence can be used to quantify cathepsin C activity. AMC displays excitation/emission maxima of 340-360/440-460 nm, respectively.
Brand:CaymanSKU:27580 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
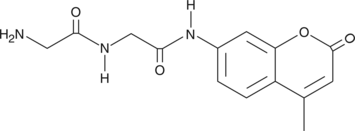
Gly-Gly-AMC is a fluorogenic peptide substrate. It has been used to assess the activity of bacterial proteases from P. aeruginosa and S. aureus.{38188} Activity can be quantified by fluorescent detection of free AMC (also known as 7-amino-4-methylcoumarin), which is excited at 340-360 nm and emits at 440-460 nm.
Brand:CaymanSKU:85140 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Gly-Gly-AMC is a fluorogenic peptide substrate. It has been used to assess the activity of bacterial proteases from P. aeruginosa and S. aureus.{38188} Activity can be quantified by fluorescent detection of free AMC (also known as 7-amino-4-methylcoumarin), which is excited at 340-360 nm and emits at 440-460 nm.
Brand:CaymanSKU:85140 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Gly-Gly-AMC is a fluorogenic peptide substrate. It has been used to assess the activity of bacterial proteases from P. aeruginosa and S. aureus.{38188} Activity can be quantified by fluorescent detection of free AMC (also known as 7-amino-4-methylcoumarin), which is excited at 340-360 nm and emits at 440-460 nm.
Brand:CaymanSKU:85140 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
Gly-Gly-AMC is a fluorogenic peptide substrate. It has been used to assess the activity of bacterial proteases from P. aeruginosa and S. aureus.{38188} Activity can be quantified by fluorescent detection of free AMC (also known as 7-amino-4-methylcoumarin), which is excited at 340-360 nm and emits at 440-460 nm.
Brand:CaymanSKU:85140 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
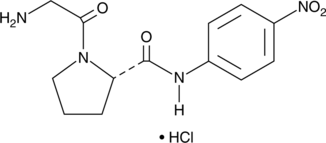
Gly-Pro-pNA is a chromogenic substrate that can be cleaved by the circulating enzyme, dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP IV).{33566} Enzyme activity can be quantified by colorimetric detection of free p-nitroanilide at 405 nm. DPP IV inactivates the two peptides responsible for a majority of nutrient-stimulated insulin secretion: glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) and glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1). This substrate can be used to screen for DPP IV inhibitors, which have emerged as a new class of experimental antidiabetic agents.{29892}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21244 -Out of stock
Gly-Pro-pNA is a chromogenic substrate that can be cleaved by the circulating enzyme, dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP IV).{33566} Enzyme activity can be quantified by colorimetric detection of free p-nitroanilide at 405 nm. DPP IV inactivates the two peptides responsible for a majority of nutrient-stimulated insulin secretion: glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) and glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1). This substrate can be used to screen for DPP IV inhibitors, which have emerged as a new class of experimental antidiabetic agents.{29892}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21244 -Out of stock
Gly-Pro-pNA is a chromogenic substrate that can be cleaved by the circulating enzyme, dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP IV).{33566} Enzyme activity can be quantified by colorimetric detection of free p-nitroanilide at 405 nm. DPP IV inactivates the two peptides responsible for a majority of nutrient-stimulated insulin secretion: glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) and glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1). This substrate can be used to screen for DPP IV inhibitors, which have emerged as a new class of experimental antidiabetic agents.{29892}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21244 -Out of stock
Gly-Pro-pNA is a chromogenic substrate that can be cleaved by the circulating enzyme, dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP IV).{33566} Enzyme activity can be quantified by colorimetric detection of free p-nitroanilide at 405 nm. DPP IV inactivates the two peptides responsible for a majority of nutrient-stimulated insulin secretion: glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) and glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1). This substrate can be used to screen for DPP IV inhibitors, which have emerged as a new class of experimental antidiabetic agents.{29892}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21244 -Out of stock
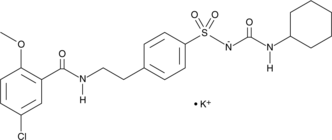
Glyburide is a sulfonylurea and an inhibitor of sulfonylurea receptor 1 (SUR1) linked to ATP-sensitive potassium channel Kir6.2 (IC50 = 4.3 nM).{22674} It binds to microsomes derived from RINm5F pancreatic β-cells (Kd = 0.3 nM) and inhibits 86Rb+ efflux from intact RINm5 cells with a half-maximal inhibition (K0.5) value of 0.06 nM.{22672} Glyburide (5 mg/kg) reduces blood glucose levels and increases the activity of hepatic glutathione-S-transferase (GST) and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PDH) in a rat model of diabetes induced by streptozotocin (STZ; Item No. 13104).{43282} It inhibits ATP-induced increases in caspase-1 activation and IL-1β and IL-18 secretion in a concentration-dependent manner in LPS-primed bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs).{22671} Glyburide (80 mg/ml) also reduces lesion growth in mice infected with L. mexicana.{22673} Formulations containing glyburide have been used in the treatment of type 2 diabetes.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Glyburide is a sulfonylurea and an inhibitor of sulfonylurea receptor 1 (SUR1) linked to ATP-sensitive potassium channel Kir6.2 (IC50 = 4.3 nM).{22674} It binds to microsomes derived from RINm5F pancreatic β-cells (Kd = 0.3 nM) and inhibits 86Rb+ efflux from intact RINm5 cells with a half-maximal inhibition (K0.5) value of 0.06 nM.{22672} Glyburide (5 mg/kg) reduces blood glucose levels and increases the activity of hepatic glutathione-S-transferase (GST) and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PDH) in a rat model of diabetes induced by streptozotocin (STZ; Item No. 13104).{43282} It inhibits ATP-induced increases in caspase-1 activation and IL-1β and IL-18 secretion in a concentration-dependent manner in LPS-primed bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs).{22671} Glyburide (80 mg/ml) also reduces lesion growth in mice infected with L. mexicana.{22673} Formulations containing glyburide have been used in the treatment of type 2 diabetes.
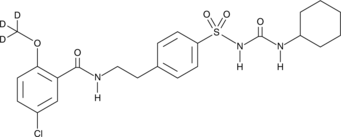
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Glyburide-d3 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of glyburide (Item No. 15009) by GC- or LC-MS. Glyburide is a sulfonylurea and an inhibitor of sulfonylurea receptor 1 (SUR1) linked to ATP-sensitive potassium channel Kir6.2 (IC50 = 4.3 nM).{22674} It binds to microsomes derived from RINm5F pancreatic β-cells (Kd = 0.3 nM) and inhibits 86Rb+ efflux from intact RINm5 cells with a half-maximal inhibition (K0.5) value of 0.06 nM.{22672} Glyburide (5 mg/kg) reduces blood glucose levels and increases the activity of hepatic glutathione-S-transferase (GST) and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PDH) in a rat model of diabetes induced by streptozotocin (STZ; Item No. 13104).{43282} It inhibits ATP-induced increases in caspase-1 activation and IL-1β and IL-18 secretion in a concentration-dependent manner in LPS-primed bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs).{22671} Glyburide (80 mg/ml) also reduces lesion growth in mice infected with L. mexicana.{22673} Formulations containing glyburide have been used in the treatment of type 2 diabetes.
Brand:CaymanSKU:25740 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Glyburide-d3 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of glyburide (Item No. 15009) by GC- or LC-MS. Glyburide is a sulfonylurea and an inhibitor of sulfonylurea receptor 1 (SUR1) linked to ATP-sensitive potassium channel Kir6.2 (IC50 = 4.3 nM).{22674} It binds to microsomes derived from RINm5F pancreatic β-cells (Kd = 0.3 nM) and inhibits 86Rb+ efflux from intact RINm5 cells with a half-maximal inhibition (K0.5) value of 0.06 nM.{22672} Glyburide (5 mg/kg) reduces blood glucose levels and increases the activity of hepatic glutathione-S-transferase (GST) and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PDH) in a rat model of diabetes induced by streptozotocin (STZ; Item No. 13104).{43282} It inhibits ATP-induced increases in caspase-1 activation and IL-1β and IL-18 secretion in a concentration-dependent manner in LPS-primed bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs).{22671} Glyburide (80 mg/ml) also reduces lesion growth in mice infected with L. mexicana.{22673} Formulations containing glyburide have been used in the treatment of type 2 diabetes.
Brand:CaymanSKU:25740 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Glyburide-d3 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of glyburide (Item No. 15009) by GC- or LC-MS. Glyburide is a sulfonylurea and an inhibitor of sulfonylurea receptor 1 (SUR1) linked to ATP-sensitive potassium channel Kir6.2 (IC50 = 4.3 nM).{22674} It binds to microsomes derived from RINm5F pancreatic β-cells (Kd = 0.3 nM) and inhibits 86Rb+ efflux from intact RINm5 cells with a half-maximal inhibition (K0.5) value of 0.06 nM.{22672} Glyburide (5 mg/kg) reduces blood glucose levels and increases the activity of hepatic glutathione-S-transferase (GST) and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PDH) in a rat model of diabetes induced by streptozotocin (STZ; Item No. 13104).{43282} It inhibits ATP-induced increases in caspase-1 activation and IL-1β and IL-18 secretion in a concentration-dependent manner in LPS-primed bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs).{22671} Glyburide (80 mg/ml) also reduces lesion growth in mice infected with L. mexicana.{22673} Formulations containing glyburide have been used in the treatment of type 2 diabetes.
Brand:CaymanSKU:25740 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
In mammals, triglycerides are constantly synthesized from fatty acids and segregated into cytosolic lipid droplets, mainly in adipocytes, as the major energy storage depot. During fasting, triglycerides stored in adipose tissue and liver are hydrolyzed by hormone-sensitive lipase and adipose triglyceride lipase to produce free fatty acids and glycerol. Cayman’s Cell-Based Assay Kit provides a convenient tool for studying triglycerides/fatty acid cycling and its regulation in adipocytes or hepatocytes. This kit will allow investigators to screen compounds involved in lipid storage and metabolism. Chloroquine is included in the kit as a positive control for screening pharmaceuticals that induce lipid droplet accumulation and free glycerol release from hepatocytes.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10011725 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
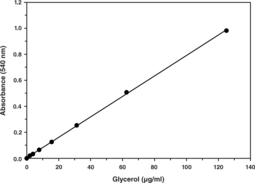
Glycerol is the backbone of triglycerides and an important intermediate in energy metabolism being involved in both oxidative and synthetic processes. The measurement of circulating levels of glycerol and free fatty acids are considered to reflect lipolysis and are therefore useful parameters to evaluate in various conditions. The measurements of glycerol is also useful for correction of glycerol interference when measuring triglycerides in reference materials and in serum from patients with elevated glycerol concentrations. Cayman’s Glycerol Assay provides a simple, reproducible, and sensitive tool for measurement of glycerol in plasma and serum. The assay employs a coupled enzymatic reaction system that yields a brilliant purple product with an absorbance maximum at 540 nm.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10010755 - 96 wellsAvailable on backorder
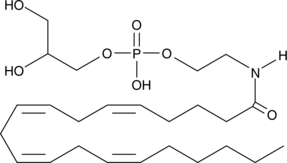
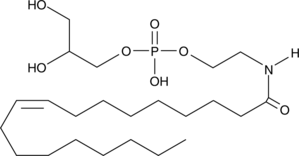
N-Acylated ethanolamines (NAE) are naturally-occurring lipids that have diverse bioactivities. The different types of NAE can be derived from glycerophospho-linked precursors by the activity of glycerophosphodiesterase 1 (GDE1).{15460} Glycerophospho-N-arachidonoyl ethanolamine is the precursor of arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA), also known as anandamide. AEA is an endogenous cannabinoid neurotransmitter that binds to both central cannabinoid (CB1) and peripheral cannabinoid (CB2) receptors.{2713} It inhibits the specific binding of [3H]-HU-243 to synaptosomal membranes with a Ki value of 52 nM, compared to 46 nM for Δ9-THC.{1134}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10011347 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
N-Acylated ethanolamines (NAE) are naturally-occurring lipids that have diverse bioactivities. The different types of NAE can be derived from glycerophospho-linked precursors by the activity of glycerophosphodiesterase 1 (GDE1).{15460} Glycerophospho-N-arachidonoyl ethanolamine is the precursor of arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA), also known as anandamide. AEA is an endogenous cannabinoid neurotransmitter that binds to both central cannabinoid (CB1) and peripheral cannabinoid (CB2) receptors.{2713} It inhibits the specific binding of [3H]-HU-243 to synaptosomal membranes with a Ki value of 52 nM, compared to 46 nM for Δ9-THC.{1134}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10011347 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
N-Acylated ethanolamines (NAE) are naturally-occurring lipids that have diverse bioactivities. The different types of NAE can be derived from glycerophospho-linked precursors by the activity of glycerophosphodiesterase 1 (GDE1).{15460} Glycerophospho-N-arachidonoyl ethanolamine is the precursor of arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA), also known as anandamide. AEA is an endogenous cannabinoid neurotransmitter that binds to both central cannabinoid (CB1) and peripheral cannabinoid (CB2) receptors.{2713} It inhibits the specific binding of [3H]-HU-243 to synaptosomal membranes with a Ki value of 52 nM, compared to 46 nM for Δ9-THC.{1134}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10011347 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
N-Acylated ethanolamines (NAE) are naturally-occurring lipids that have diverse bioactivities. For example, arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA) is an endogenous cannabinoid neurotransmitter that evokes cellular responses by activating the cannabinoid receptors, central cannabinoid (CB1) and peripheral cannabinoid (CB2). The different types of NAE are derived from glycerophospho-linked precursors by the activity of glycerophosphodiesterase 1 (GDE1).{15460} Glycerophospho-N-oleoyl ethanolamine is the precursor of oleoyl ethanolamide (OEA). OEA is an endogenous, potent agonist for PPARα, exhibiting an EC50 value of 120 nM in a transactivation assay.{11423} Systemic administration of OEA suppresses food intake and reduces weight gain in rats (10 mg/kg intraperitoneally) and PPARα wild-type mice, but not in PPARα knockout mice.{11423, 9302} Like AEA, OEA is metabolized by fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH).
Brand:CaymanSKU:10011357 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
N-Acylated ethanolamines (NAE) are naturally-occurring lipids that have diverse bioactivities. For example, arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA) is an endogenous cannabinoid neurotransmitter that evokes cellular responses by activating the cannabinoid receptors, central cannabinoid (CB1) and peripheral cannabinoid (CB2). The different types of NAE are derived from glycerophospho-linked precursors by the activity of glycerophosphodiesterase 1 (GDE1).{15460} Glycerophospho-N-oleoyl ethanolamine is the precursor of oleoyl ethanolamide (OEA). OEA is an endogenous, potent agonist for PPARα, exhibiting an EC50 value of 120 nM in a transactivation assay.{11423} Systemic administration of OEA suppresses food intake and reduces weight gain in rats (10 mg/kg intraperitoneally) and PPARα wild-type mice, but not in PPARα knockout mice.{11423, 9302} Like AEA, OEA is metabolized by fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH).
Brand:CaymanSKU:10011357 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
N-Acylated ethanolamines (NAE) are naturally-occurring lipids that have diverse bioactivities. For example, arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA) is an endogenous cannabinoid neurotransmitter that evokes cellular responses by activating the cannabinoid receptors, central cannabinoid (CB1) and peripheral cannabinoid (CB2). The different types of NAE are derived from glycerophospho-linked precursors by the activity of glycerophosphodiesterase 1 (GDE1).{15460} Glycerophospho-N-oleoyl ethanolamine is the precursor of oleoyl ethanolamide (OEA). OEA is an endogenous, potent agonist for PPARα, exhibiting an EC50 value of 120 nM in a transactivation assay.{11423} Systemic administration of OEA suppresses food intake and reduces weight gain in rats (10 mg/kg intraperitoneally) and PPARα wild-type mice, but not in PPARα knockout mice.{11423, 9302} Like AEA, OEA is metabolized by fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH).
Brand:CaymanSKU:10011357 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
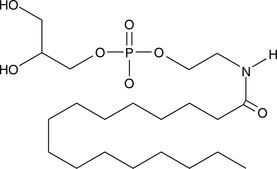
N-Acylated ethanolamines (NAE) are naturally-occurring lipids that have diverse bioactivities. For example, arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA) is an endogenous neurotransmitter that evokes cellular responses by activating the cannabinoid receptors, central cannabinoid (CB1) and peripheral cannabinoid (CB2). The different types of NAE are derived from glycerophospho-linked precursors by the activity of glycerophosphodiesterase 1 (GDE1).{15460} Glycerophospho-N-palmitoyl ethanolamine (GP-NPEA) is the metabolic precursor of palmitoyl ethanolamide (PEA). PEA is an endogenous cannabinoid found in brain, liver, and other mammalian tissues,{2415} that has potent anti-inflammatory activity in vivo.{16742} PEA has low affinity for peripheral cannabinoid (CB2) and no appreciable affinity for central cannabinoid (CB1),{1134} suggesting that its efficacy is through a different receptor.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10011356 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
N-Acylated ethanolamines (NAE) are naturally-occurring lipids that have diverse bioactivities. For example, arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA) is an endogenous neurotransmitter that evokes cellular responses by activating the cannabinoid receptors, central cannabinoid (CB1) and peripheral cannabinoid (CB2). The different types of NAE are derived from glycerophospho-linked precursors by the activity of glycerophosphodiesterase 1 (GDE1).{15460} Glycerophospho-N-palmitoyl ethanolamine (GP-NPEA) is the metabolic precursor of palmitoyl ethanolamide (PEA). PEA is an endogenous cannabinoid found in brain, liver, and other mammalian tissues,{2415} that has potent anti-inflammatory activity in vivo.{16742} PEA has low affinity for peripheral cannabinoid (CB2) and no appreciable affinity for central cannabinoid (CB1),{1134} suggesting that its efficacy is through a different receptor.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10011356 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
N-Acylated ethanolamines (NAE) are naturally-occurring lipids that have diverse bioactivities. For example, arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA) is an endogenous neurotransmitter that evokes cellular responses by activating the cannabinoid receptors, central cannabinoid (CB1) and peripheral cannabinoid (CB2). The different types of NAE are derived from glycerophospho-linked precursors by the activity of glycerophosphodiesterase 1 (GDE1).{15460} Glycerophospho-N-palmitoyl ethanolamine (GP-NPEA) is the metabolic precursor of palmitoyl ethanolamide (PEA). PEA is an endogenous cannabinoid found in brain, liver, and other mammalian tissues,{2415} that has potent anti-inflammatory activity in vivo.{16742} PEA has low affinity for peripheral cannabinoid (CB2) and no appreciable affinity for central cannabinoid (CB1),{1134} suggesting that its efficacy is through a different receptor.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10011356 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Glycine is an important inhibitory transmitter in the brain stem and spinal cord. Glycine receptors are members of the ligand-gated ion channel family (LGICs) that mediate rapid chemical neurotransmission.{14450} The binding of glycine to its receptor produces a large increase in chloride conductance, which causes membrane hyperpolarization. Glycine receptors are anchored at inhibitory chemical synapses by a cytoplasmic protein, gephyrin.{14448} The glycine receptor has been used to great advantage in the identification of the binding sites for alcohol on the LGIC family of proteins.{14445,14449} These receptors have also been extremely useful in studies of synaptic clustering of receptors.{14447} The glycine receptor may also act in concert with an NMDAR subunit to form an excitatory receptor.{14446}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10009399 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Antigen: peptide from N-terminal region of the α1-subunit of the rat glycine receptor • Host: rabbit • Cross Reactivity: (+) human, mouse, and rat glycine receptor • Application(s): IHC (frozen sections) and WB • Glycine is an important inhibitory neurotransmitter whose binding to its receptor produces a large increase in chloride conductance, which causes membrane hyperpolarization. Glycine receptors are anchored at inhibitory chemical synapses. They have been used to great advantage in the identification of the binding sites for alcohol and have also been extremely useful in studies of synaptic clustering of receptors.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10009399- 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Antigen: peptide from N-terminal region of the α1-subunit of the rat glycine receptor • Host: rabbit • Cross Reactivity: (+) human, mouse, and rat glycine receptor • Application(s): IHC (frozen sections) and WB • Glycine is an important inhibitory neurotransmitter whose binding to its receptor produces a large increase in chloride conductance, which causes membrane hyperpolarization. Glycine receptors are anchored at inhibitory chemical synapses. They have been used to great advantage in the identification of the binding sites for alcohol and have also been extremely useful in studies of synaptic clustering of receptors.
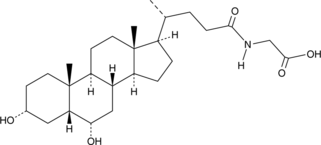
Brand:CaymanSKU:10009399- 1 eaGlycine-β-muricholic acid (GβMCA) is an intestine-selective antagonist of the farnesoid X receptor (FXR) and the glycine-conjugated form of the murine-specific primary bile acid β-muricholic acid (Item No. 20287).{36870,45190} It inhibits expression of the FXR target genes Shp and Fgf15 induced by the FXR ligands chenodeoxycholic acid (Item No. 10011286) and GW 4064 (Item No. 10006611) in Caco-2 cells when used at a concentration of 100 μM. GβMCA is resistant to hydrolysis by fecal bile salt hydrolase (BSH) isolated from gut microbiota, indicating gut stability. Dietary administration of GβMCA (10 mg/kg) decreases Shp and Fgf15 mRNA expression in ileum, but not liver, and reduces ceramide levels and expression of the ceramide synthesis-related genes Sptlc2, Sptlc3, Cers2, Cers4, Degs1, Degs2, Smpd3, and Smpd4 in ileum of mice with high-fat diet-induced obesity and db/db mice. It also prevents weight gain, reduces blood glucose levels, and increases insulin sensitivity as well as prevents development of cholestasis and necrotic lesions in liver of mice with high-fat diet-induced obesity.
Brand:CaymanSKU:9003230 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Glycine-β-muricholic acid (GβMCA) is an intestine-selective antagonist of the farnesoid X receptor (FXR) and the glycine-conjugated form of the murine-specific primary bile acid β-muricholic acid (Item No. 20287).{36870,45190} It inhibits expression of the FXR target genes Shp and Fgf15 induced by the FXR ligands chenodeoxycholic acid (Item No. 10011286) and GW 4064 (Item No. 10006611) in Caco-2 cells when used at a concentration of 100 μM. GβMCA is resistant to hydrolysis by fecal bile salt hydrolase (BSH) isolated from gut microbiota, indicating gut stability. Dietary administration of GβMCA (10 mg/kg) decreases Shp and Fgf15 mRNA expression in ileum, but not liver, and reduces ceramide levels and expression of the ceramide synthesis-related genes Sptlc2, Sptlc3, Cers2, Cers4, Degs1, Degs2, Smpd3, and Smpd4 in ileum of mice with high-fat diet-induced obesity and db/db mice. It also prevents weight gain, reduces blood glucose levels, and increases insulin sensitivity as well as prevents development of cholestasis and necrotic lesions in liver of mice with high-fat diet-induced obesity.
Brand:CaymanSKU:9003230 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Glycine-β-muricholic acid (GβMCA) is an intestine-selective antagonist of the farnesoid X receptor (FXR) and the glycine-conjugated form of the murine-specific primary bile acid β-muricholic acid (Item No. 20287).{36870,45190} It inhibits expression of the FXR target genes Shp and Fgf15 induced by the FXR ligands chenodeoxycholic acid (Item No. 10011286) and GW 4064 (Item No. 10006611) in Caco-2 cells when used at a concentration of 100 μM. GβMCA is resistant to hydrolysis by fecal bile salt hydrolase (BSH) isolated from gut microbiota, indicating gut stability. Dietary administration of GβMCA (10 mg/kg) decreases Shp and Fgf15 mRNA expression in ileum, but not liver, and reduces ceramide levels and expression of the ceramide synthesis-related genes Sptlc2, Sptlc3, Cers2, Cers4, Degs1, Degs2, Smpd3, and Smpd4 in ileum of mice with high-fat diet-induced obesity and db/db mice. It also prevents weight gain, reduces blood glucose levels, and increases insulin sensitivity as well as prevents development of cholestasis and necrotic lesions in liver of mice with high-fat diet-induced obesity.
Brand:CaymanSKU:9003230 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
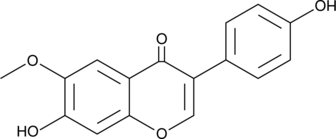
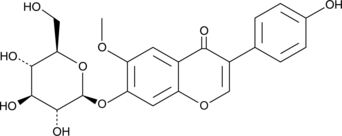
Glycitein is an O-methylated isoflavone that comprises 5-10% of the total isoflavones in soy food products. This phytoestrogen is reported to have weak estrogenic activity, displacing estradiol binding at the estrogen receptor in vitro with an IC50 value of 3.94 μM.{22750} It suppresses the proliferation of osteoblasts and promotes differentiation from its progenitor.{22747} It has also been used to attenuate proliferation (10 μM) of aortic smooth muscle cells related to atherosclerotic vascular change in stroke-prone hypertensive rats and to protect against beta amyloid (Aβ)-induced toxicity and oxidative stress (100 μg/ml) in C. elegans expressing human Aβ.{22749,22748}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Glycitein is an O-methylated isoflavone that comprises 5-10% of the total isoflavones in soy food products. This phytoestrogen is reported to have weak estrogenic activity, displacing estradiol binding at the estrogen receptor in vitro with an IC50 value of 3.94 μM.{22750} It suppresses the proliferation of osteoblasts and promotes differentiation from its progenitor.{22747} It has also been used to attenuate proliferation (10 μM) of aortic smooth muscle cells related to atherosclerotic vascular change in stroke-prone hypertensive rats and to protect against beta amyloid (Aβ)-induced toxicity and oxidative stress (100 μg/ml) in C. elegans expressing human Aβ.{22749,22748}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Glycitein is an O-methylated isoflavone that comprises 5-10% of the total isoflavones in soy food products. This phytoestrogen is reported to have weak estrogenic activity, displacing estradiol binding at the estrogen receptor in vitro with an IC50 value of 3.94 μM.{22750} It suppresses the proliferation of osteoblasts and promotes differentiation from its progenitor.{22747} It has also been used to attenuate proliferation (10 μM) of aortic smooth muscle cells related to atherosclerotic vascular change in stroke-prone hypertensive rats and to protect against beta amyloid (Aβ)-induced toxicity and oxidative stress (100 μg/ml) in C. elegans expressing human Aβ.{22749,22748}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Glycitein is an O-methylated isoflavone that comprises 5-10% of the total isoflavones in soy food products. This phytoestrogen is reported to have weak estrogenic activity, displacing estradiol binding at the estrogen receptor in vitro with an IC50 value of 3.94 μM.{22750} It suppresses the proliferation of osteoblasts and promotes differentiation from its progenitor.{22747} It has also been used to attenuate proliferation (10 μM) of aortic smooth muscle cells related to atherosclerotic vascular change in stroke-prone hypertensive rats and to protect against beta amyloid (Aβ)-induced toxicity and oxidative stress (100 μg/ml) in C. elegans expressing human Aβ.{22749,22748}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Glycitin is a natural isoflavone isolated from legumes, including soy and kudzu. Like other isoflavones, glycitin promotes the proliferation of bone marrow stromal cells and osteoblasts and suppresses bone turnover.{22650,22649}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Glycitin is a natural isoflavone isolated from legumes, including soy and kudzu. Like other isoflavones, glycitin promotes the proliferation of bone marrow stromal cells and osteoblasts and suppresses bone turnover.{22650,22649}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Glycitin is a natural isoflavone isolated from legumes, including soy and kudzu. Like other isoflavones, glycitin promotes the proliferation of bone marrow stromal cells and osteoblasts and suppresses bone turnover.{22650,22649}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Glycitin is a natural isoflavone isolated from legumes, including soy and kudzu. Like other isoflavones, glycitin promotes the proliferation of bone marrow stromal cells and osteoblasts and suppresses bone turnover.{22650,22649}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Glyco-obeticholic acid is an active metabolite of obeticholic acid, which is a farnesoid X receptor (FXR) agonist and semisynthetic derivative of chenodeoxycholic acid (Item No. 10011286).{46303} Glyco-obeticholic acid is formed from obeticholic acid by glycine conjugation in the liver but can be reconverted back to obeticholic acid by microorganism-mediated deconjugation in the ileum and colon. It has been used as a precursor in the synthesis of bile acid analogs as agonists of the farnesoid X receptor (FXR) and TGR5.{45287}
Brand:CaymanSKU:28242 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Glyco-obeticholic acid is an active metabolite of obeticholic acid, which is a farnesoid X receptor (FXR) agonist and semisynthetic derivative of chenodeoxycholic acid (Item No. 10011286).{46303} Glyco-obeticholic acid is formed from obeticholic acid by glycine conjugation in the liver but can be reconverted back to obeticholic acid by microorganism-mediated deconjugation in the ileum and colon. It has been used as a precursor in the synthesis of bile acid analogs as agonists of the farnesoid X receptor (FXR) and TGR5.{45287}
Brand:CaymanSKU:28242 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Glycochenodeoxycholic acid (GCDCA) is a glycine-conjugated form of the primary bile acid chenodeoxycholic acid (Item No. 10011286).{57144} It reduces formation of cholic acid (Item No. 20250) in primary human hepatocytes when used at a concentration of 100 µM.{57145} GCDCA (50, 75, and 100 µM) reduces the number LC3 puncta, a marker of autophagy, and is cytotoxic to L-02 hepatocytes.{57144} GCDCA (50 µM) induces apoptosis in isolated rat hepatocytes, an effect that can be blocked by the protein kinase C (PKC) inhibitor chelerythrine (Item No. 11314).{57146} Fecal levels of GCDCA are decreased in a rat model of high-fat diet-induced obesity compared with rats fed a normal diet.{54007} Glycochenodeoxycholic acid MaxSpec® standard is a quantitative grade standard of glycochenodeoxycholic acid (Item No. 16942) that has been prepared specifically for mass spectrometry and related applications where quantitative reproducibility is required. The solution has been prepared gravimetrically and is supplied in a deactivated glass ampule sealed under argon. The concentration was verified by comparison to an independently prepared calibration standard. This Glycochenodeoxycholic acid MaxSpec® standard is guaranteed to meet identity, purity, stability, and concentration specifications and is provided with a batch-specific certificate of analysis. Ongoing stability testing is performed to ensure the concentration remains accurate throughout the shelf life of the product. Note: The amount of solution added to the vial is in excess of the listed amount. Therefore, it is necessary to accurately measure volumes for preparation of calibration standards. Follow recommended storage and handling conditions to maintain product quality.
Brand:CaymanSKU:31363 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
An internal standard for the quantification of glycochenodeoxycholic acid (GCDCA; Item No. 16942) by GC- or LC-MS. GCDCA is a glycine-conjugated form of the primary bile acid chenodeoxycholic acid (Item No. 10011286).{57144} It reduces formation of cholic acid (Item No. 20250) in primary human hepatocytes when used at a concentration of 100 µM.{57145} GCDCA (50, 75, and 100 µM) reduces the number LC3 puncta, a marker of autophagy, and is cytotoxic to L-02 hepatocytes.{57144} GCDCA (50 µM) induces apoptosis in isolated rat hepatocytes, an effect that can be blocked by the protein kinase C (PKC) inhibitor chelerythrine (Item No. 11314).{57146} Fecal levels of GCDCA are decreased in a rat model of high-fat diet-induced obesity compared with rats fed a normal diet.{54007}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21890 -Out of stock
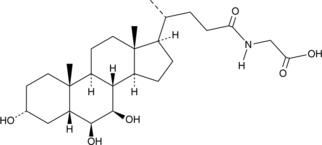
Glycocholic acid is a glycine-conjugated form of the primary bile acid cholic acid (Item No. 20250) and has roles in the emulsification of fats.{48223,54310} It reduces expression of the gene encoding the farnesoid X receptor (FXR) and increases expression of the genes encoding the bile acid receptors TGR5 and S1PR2 in SNU-245 cells when used at a concentration of 1.6 μmol/ml.{54311} Glycocholic acid (250 μM) increases the intracellular accumulation and cytotoxicity of epirubicin (Item No. 12091) in Caco-2 cells, as well as decreases expression of the genes encoding multidrug resistance protein 1 (MDR1), MDR-associated protein 1 (MRP1), and MRP2 when used alone or in combination with epirubicin.{54312} It increases absorption of epirubicin into everted sacs of rat ileum and jejunum when used at a concentration of 250 μM. The bile acid composition ratio of glycocholic acid is elevated in bile of patients with cholangiocarcinoma compared with patients with pancreatic cancer or benign biliary diseases.{54311} Serum levels of glycocholic acid are elevated in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma compared with healthy individuals.{54310}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20276 -Available on backorder
Glycocholic acid is a glycine-conjugated form of the primary bile acid cholic acid (Item No. 20250) and has roles in the emulsification of fats.{48223,54310} It reduces expression of the gene encoding the farnesoid X receptor (FXR) and increases expression of the genes encoding the bile acid receptors TGR5 and S1PR2 in SNU-245 cells when used at a concentration of 1.6 μmol/ml.{54311} Glycocholic acid (250 μM) increases the intracellular accumulation and cytotoxicity of epirubicin (Item No. 12091) in Caco-2 cells, as well as decreases expression of the genes encoding multidrug resistance protein 1 (MDR1), MDR-associated protein 1 (MRP1), and MRP2 when used alone or in combination with epirubicin.{54312} It increases absorption of epirubicin into everted sacs of rat ileum and jejunum when used at a concentration of 250 μM. The bile acid composition ratio of glycocholic acid is elevated in bile of patients with cholangiocarcinoma compared with patients with pancreatic cancer or benign biliary diseases.{54311} Serum levels of glycocholic acid are elevated in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma compared with healthy individuals.{54310}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20276 -Available on backorder
Glycocholic acid is a glycine-conjugated form of the primary bile acid cholic acid (Item No. 20250) and has roles in the emulsification of fats.{48223,54310} It reduces expression of the gene encoding the farnesoid X receptor (FXR) and increases expression of the genes encoding the bile acid receptors TGR5 and S1PR2 in SNU-245 cells when used at a concentration of 1.6 μmol/ml.{54311} Glycocholic acid (250 μM) increases the intracellular accumulation and cytotoxicity of epirubicin (Item No. 12091) in Caco-2 cells, as well as decreases expression of the genes encoding multidrug resistance protein 1 (MDR1), MDR-associated protein 1 (MRP1), and MRP2 when used alone or in combination with epirubicin.{54312} It increases absorption of epirubicin into everted sacs of rat ileum and jejunum when used at a concentration of 250 μM. The bile acid composition ratio of glycocholic acid is elevated in bile of patients with cholangiocarcinoma compared with patients with pancreatic cancer or benign biliary diseases.{54311} Serum levels of glycocholic acid are elevated in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma compared with healthy individuals.{54310}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20276 -Available on backorder
Glycocholic acid is a glycine-conjugated form of the primary bile acid cholic acid (Item No. 20250) and has roles in the emulsification of fats.{48223,54310} It reduces expression of the gene encoding the farnesoid X receptor (FXR) and increases expression of the genes encoding the bile acid receptors TGR5 and S1PR2 in SNU-245 cells when used at a concentration of 1.6 μmol/ml.{54311} Glycocholic acid (250 μM) increases the intracellular accumulation and cytotoxicity of epirubicin (Item No. 12091) in Caco-2 cells, as well as decreases expression of the genes encoding multidrug resistance protein 1 (MDR1), MDR-associated protein 1 (MRP1), and MRP2 when used alone or in combination with epirubicin.{54312} It increases absorption of epirubicin into everted sacs of rat ileum and jejunum when used at a concentration of 250 μM. The bile acid composition ratio of glycocholic acid is elevated in the bile of patients with cholangiocarcinoma compared with patients with pancreatic cancer or benign biliary diseases.{54311} Serum levels of glycocholic acid are elevated in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma compared with healthy individuals.{54310} Glycocholic acid MaxSpec® standard is a quantitative grade standard of glycocholic acid (Item No. 20276) that has been prepared specifically for mass spectrometry and related applications where quantitative reproducibility is required. The solution has been prepared gravimetrically and is supplied in a deactivated glass ampule sealed under argon. The concentration was verified by comparison to an independently prepared calibration standard. This glycocholic acid MaxSpec® standard is guaranteed to meet identity, purity, stability, and concentration specifications and is provided with a batch-specific certificate of analysis. Ongoing stability testing is performed to ensure the concentration remains accurate throughout the shelf life of the product. Note: The amount of solution added to the vial is in excess of the listed amount. Therefore, it is necessary to accurately measure volumes for preparation of calibration standards. Follow recommended storage and handling conditions to maintain product quality.
Brand:CaymanSKU:31351 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Glycocholic acid-d4 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of glycocholic acid (Item No. 20276) by GC- or LC-MS. Glycocholic acid is a glycine-conjugated form of the primary bile acid cholic acid (Item No. 20250) and has roles in the emulsification of fats.{48223,54310} It reduces expression of the gene encoding the farnesoid X receptor (FXR) and increases expression of the genes encoding the bile acid receptors TGR5 and S1PR2 in SNU-245 cells when used at a concentration of 1.6 μmol/ml.{54311} Glycocholic acid (250 μM) increases the intracellular accumulation and cytotoxicity of epirubicin (Item No. 12091) in Caco-2 cells, as well as decreases expression of the genes encoding multidrug resistance protein 1 (MDR1), MDR-associated protein 1 (MRP1), and MRP2 when used alone or in combination with epirubicin.{54312} It increases absorption of epirubicin into everted sacs of rat ileum and jejunum when used at a concentration of 250 μM. The bile acid composition ratio of glycocholic acid is elevated in bile of patients with cholangiocarcinoma compared with patients with pancreatic cancer or benign biliary diseases.{54311} Serum levels of glycocholic acid are elevated in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma compared with healthy individuals.{54310}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21889 -Out of stock
Glycocholic acid-d4 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of glycocholic acid (Item No. 20276) by GC- or LC-MS. Glycocholic acid is a glycine-conjugated form of the primary bile acid cholic acid (Item No. 20250) and has roles in the emulsification of fats.{48223,54310} It reduces expression of the gene encoding the farnesoid X receptor (FXR) and increases expression of the genes encoding the bile acid receptors TGR5 and S1PR2 in SNU-245 cells when used at a concentration of 1.6 μmol/ml.{54311} Glycocholic acid (250 μM) increases the intracellular accumulation and cytotoxicity of epirubicin (Item No. 12091) in Caco-2 cells, as well as decreases expression of the genes encoding multidrug resistance protein 1 (MDR1), MDR-associated protein 1 (MRP1), and MRP2 when used alone or in combination with epirubicin.{54312} It increases absorption of epirubicin into everted sacs of rat ileum and jejunum when used at a concentration of 250 μM. The bile acid composition ratio of glycocholic acid is elevated in bile of patients with cholangiocarcinoma compared with patients with pancreatic cancer or benign biliary diseases.{54311} Serum levels of glycocholic acid are elevated in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma compared with healthy individuals.{54310}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21889 -Out of stock
Glycocholic acid-d4 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of glycocholic acid (Item No. 20276) by GC- or LC-MS. Glycocholic acid is a glycine-conjugated form of the primary bile acid cholic acid (Item No. 20250) and has roles in the emulsification of fats.{48223,54310} It reduces expression of the gene encoding the farnesoid X receptor (FXR) and increases expression of the genes encoding the bile acid receptors TGR5 and S1PR2 in SNU-245 cells when used at a concentration of 1.6 μmol/ml.{54311} Glycocholic acid (250 μM) increases the intracellular accumulation and cytotoxicity of epirubicin (Item No. 12091) in Caco-2 cells, as well as decreases expression of the genes encoding multidrug resistance protein 1 (MDR1), MDR-associated protein 1 (MRP1), and MRP2 when used alone or in combination with epirubicin.{54312} It increases absorption of epirubicin into everted sacs of rat ileum and jejunum when used at a concentration of 250 μM. The bile acid composition ratio of glycocholic acid is elevated in bile of patients with cholangiocarcinoma compared with patients with pancreatic cancer or benign biliary diseases.{54311} Serum levels of glycocholic acid are elevated in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma compared with healthy individuals.{54310} Glycocholic acid-d4 MaxSpec® standard is a quantitative grade standard of glycocholic acid-d4 (Item No. 21889) that has been prepared specifically for mass spectrometry and related applications where quantitative reproducibility is required. The solution has been prepared gravimetrically and is supplied in a deactivated glass ampule sealed under argon. The concentration was verified by comparison to an independently prepared calibration standard. This glycocholic acid-d4 MaxSpec® standard is guaranteed to meet identity, purity, stability, and concentration specifications and is provided with a batch-specific certificate of analysis. Ongoing stability testing is performed to ensure the concentration remains accurate throughout the shelf life of the product. Note: The amount of solution added to the vial is in excess of the listed amount. Therefore, it is necessary to accurately measure volumes for preparation of calibration standards. Follow recommended storage and handling conditions to maintain product quality.
Brand:CaymanSKU:31352 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
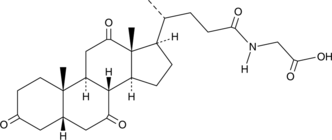
Glycodehydrocholic acid is a glycine-conjugated form of the synthetic bile acid dehydrocholic acid (Item No. 29176).{49590}
Brand:CaymanSKU:29892 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Glycodehydrocholic acid is a glycine-conjugated form of the synthetic bile acid dehydrocholic acid (Item No. 29176).{49590}
Brand:CaymanSKU:29892 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
Glycodehydrocholic acid is a glycine-conjugated form of the synthetic bile acid dehydrocholic acid (Item No. 29176).{49590}
Brand:CaymanSKU:29892 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Glycodehydrocholic acid is a glycine-conjugated form of the synthetic bile acid dehydrocholic acid (Item No. 29176).{49590}
Brand:CaymanSKU:29892 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
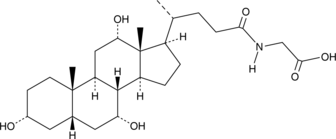
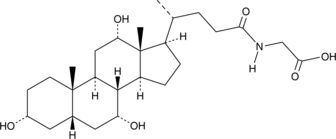
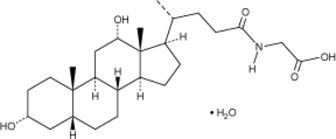
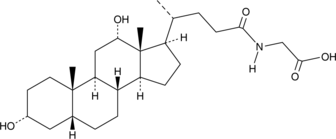
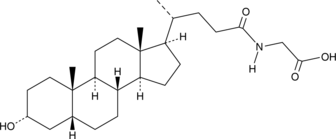
Glycodeoxycholic acid (GDCA) is a glycine-conjugated form of the secondary bile acid deoxycholic acid (Item Nos. 18231 | 20756).{48223} It induces a reversible, concentration-dependent reduction in myogenic tone in rats and decreases expression of the gene encoding the cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoform 7A1 (CYP7A1) in rabbits.{33912,33913} Serum levels of GDCA are elevated in non-surviving patients with acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure (AALF) compared with survivors.{33914} GDCA levels are also increased in the plasma of patients with asthma.{33911}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20274 -Available on backorder
Glycodeoxycholic acid (GDCA) is a glycine-conjugated form of the secondary bile acid deoxycholic acid (Item Nos. 18231 | 20756).{48223} It induces a reversible, concentration-dependent reduction in myogenic tone in rats and decreases expression of the gene encoding the cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoform 7A1 (CYP7A1) in rabbits.{33912,33913} Serum levels of GDCA are elevated in non-surviving patients with acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure (AALF) compared with survivors.{33914} GDCA levels are also increased in the plasma of patients with asthma.{33911}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20274 -Available on backorder
Glycodeoxycholic acid (GDCA) is a glycine-conjugated form of the secondary bile acid deoxycholic acid (Item Nos. 18231 | 20756).{48223} It induces a reversible, concentration-dependent reduction in myogenic tone in rats and decreases expression of the gene encoding the cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoform 7A1 (CYP7A1) in rabbits.{33912,33913} Serum levels of GDCA are elevated in non-surviving patients with acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure (AALF) compared with survivors.{33914} GDCA levels are also increased in the plasma of patients with asthma.{33911}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20274 -Available on backorder
Glycodeoxycholic acid (GDCA) is a glycine-conjugated form of the secondary bile acid deoxycholic acid (Item Nos. 18231 | 20756).{48223} It induces a reversible, concentration-dependent reduction in myogenic tone in rats and decreases expression of the gene encoding the cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoform 7A1 (CYP7A1) in rabbits.{33912,33913} Serum levels of GDCA are elevated in non-surviving patients with acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure (AALF) compared with survivors.{33914} GDCA levels are also increased in the plasma of patients with asthma.{33911}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20274 -Available on backorder
Glycodeoxycholic acid (GDCA) is a glycine-conjugated form of the secondary bile acid deoxycholic acid (Item Nos. 18231 | 20756).{48223} It induces a reversible, concentration-dependent reduction in myogenic tone in rats and decreases expression of the gene encoding the cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoform 7A1 (CYP7A1) in rabbits.{33912,33913} Serum levels of GDCA are elevated in non-surviving patients with acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure (AALF) compared with survivors.{33914} GDCA levels are also increased in the plasma of patients with asthma.{33911} GDCA MaxSpec® standard is a quantitative grade standard of glycodeoxycholic acid (Item No. 20274) that has been prepared specifically for mass spectrometry and related applications where quantitative reproducibility is required. The solution has been prepared gravimetrically and is supplied in a deactivated glass ampule sealed under argon. The concentration was verified by comparison to an independently prepared calibration standard. This GDCA MaxSpec® standard is guaranteed to meet identity, purity, stability, and concentration specifications and is provided with a batch-specific certificate of analysis. Ongoing stability testing is performed to ensure the concentration remains accurate throughout the shelf life of the product. Note: The amount of solution added to the vial is in excess of the listed amount. Therefore, it is necessary to accurately measure volumes for preparation of calibration standards. Follow recommended storage and handling conditions to maintain product quality.
Brand:CaymanSKU:31599 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
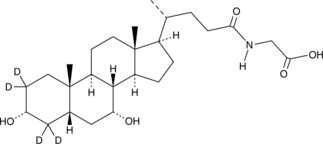
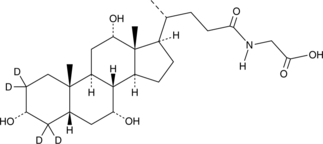
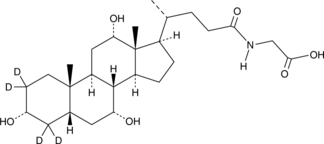
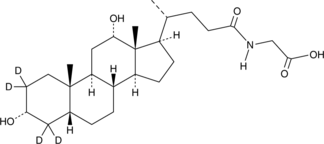
Glycodeoxycholic acid-d4 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of glycodeoxycholic acid (Item No. 20274) by GC- or LC-MS. Glycodeoxycholic acid (GDCA) is a glycine-conjugated form of the secondary bile acid deoxycholic acid (Item Nos. 18231 | 20756).{48223} It induces a reversible, concentration-dependent reduction in myogenic tone in rats and decreases expression of the gene encoding the cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoform 7A1 (CYP7A1) in rabbits.{33912,33913} Serum levels of GDCA are elevated in non-surviving patients with acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure (AALF) compared with survivors.{33914} GDCA levels are also increased in the plasma of patients with asthma.{33911}
Brand:CaymanSKU:31310 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Glycodeoxycholic acid-d4 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of glycodeoxycholic acid (Item No. 20274) by GC- or LC-MS. Glycodeoxycholic acid (GDCA) is a glycine-conjugated form of the secondary bile acid deoxycholic acid (Item Nos. 18231 | 20756).{48223} It induces a reversible, concentration-dependent reduction in myogenic tone in rats and decreases expression of the gene encoding the cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoform 7A1 (CYP7A1) in rabbits.{33912,33913} Serum levels of GDCA are elevated in non-surviving patients with acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure (AALF) compared with survivors.{33914} GDCA levels are also increased in the plasma of patients with asthma.{33911}
Brand:CaymanSKU:31310 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Glycodeoxycholic acid-d4 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of glycodeoxycholic acid (Item No. 20274) by GC- or LC-MS. Glycodeoxycholic acid (GDCA) is a glycine-conjugated form of the secondary bile acid deoxycholic acid (Item Nos. 18231 | 20756).{48223} It induces a reversible, concentration-dependent reduction in myogenic tone in rats and decreases expression of the gene encoding the cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoform 7A1 (CYP7A1) in rabbits.{33912,33913} Serum levels of GDCA are elevated in non-surviving patients with acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure (AALF) compared with survivors.{33914} GDCA levels are also increased in the plasma of patients with asthma.{33911}
Brand:CaymanSKU:31310 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:700482 - 14 mlAvailable on backorder
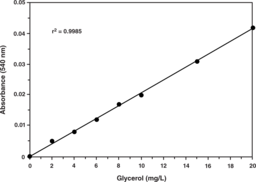
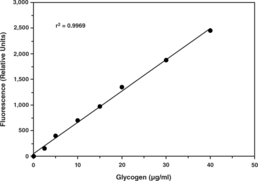
Glycogen is a polysaccharide that is the principal storage form of glucose in animal and human cells. Glycogen is made primarily by the liver and muscles, but it can also be made by glycogenesis within the brain and stomach. Cayman’s Glycogen Assay provides a simple, reproducible, and sensitive tool for assaying glycogen from tissue. In this assay, glycogen is hydrolyzed by amyloglucosidase to form β-D-glucose, which is then specifically oxidized to D-glucono-δ-lactone by glucose oxidase forming hydrogen peroxide in the process. Hydrogen peroxide, in the presence of horseradish peroxidase, reacts with 10-acetyl-3,7-dihydroxyphenoxazine (ADHP) in a 1:1 stoichiometry to generate the highly fluorescent product resorufin which is measure at an excitation wavelength of 530-540 nm and an emission wavelength of 585-595 nm.
Brand:CaymanSKU:700480 - 96 wellsAvailable on backorder
Glycogen phosphorylase in the liver, muscle, and brain initiate glycogenolysis by releasing glucose-1-phosphate from glycogen. Glycogen phosphorylase inhibitor is a cell-permeable acyl urea first identified as an inhibitor of human liver glycogen phosphorylase (IC50 = 53 nM).{28561} It blocks glucagon-induced hepatic glycogenolysis in vivo.{28561} Glycogen phosphorylase inhibitor has been used to study glycogen utilization in human liver HepG2 cells, retinal explants, and human T lymphocyte Kit 225 cells.{28560,28558,28559}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
Glycogen phosphorylase in the liver, muscle, and brain initiate glycogenolysis by releasing glucose-1-phosphate from glycogen. Glycogen phosphorylase inhibitor is a cell-permeable acyl urea first identified as an inhibitor of human liver glycogen phosphorylase (IC50 = 53 nM).{28561} It blocks glucagon-induced hepatic glycogenolysis in vivo.{28561} Glycogen phosphorylase inhibitor has been used to study glycogen utilization in human liver HepG2 cells, retinal explants, and human T lymphocyte Kit 225 cells.{28560,28558,28559}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
Glycohyocholic acid (GHCA) is a glycine-conjugated form of the primary bile acid hyocholic acid (Item No. 20293).{40620} GHCA is upregulated 6.6-fold in the serum of patients with cirrhosis induced by hepatitis C virus (HCV) compared to healthy controls.{40624} Plasma levels of GHCA increase in patients who are no longer diabetic following gastric bypass surgery.{40625}
Brand:CaymanSKU:22670 -Out of stock
Glycohyocholic acid (GHCA) is a glycine-conjugated form of the primary bile acid hyocholic acid (Item No. 20293).{40620} GHCA is upregulated 6.6-fold in the serum of patients with cirrhosis induced by hepatitis C virus (HCV) compared to healthy controls.{40624} Plasma levels of GHCA increase in patients who are no longer diabetic following gastric bypass surgery.{40625}
Brand:CaymanSKU:22670 -Out of stock
Glycohyocholic acid (GHCA) is a glycine-conjugated form of the primary bile acid hyocholic acid (Item No. 20293).{40620} GHCA is upregulated 6.6-fold in the serum of patients with cirrhosis induced by hepatitis C virus (HCV) compared to healthy controls.{40624} Plasma levels of GHCA increase in patients who are no longer diabetic following gastric bypass surgery.{40625}
Brand:CaymanSKU:22670 -Out of stock
Glycohyocholic acid (GHCA) is a glycine-conjugated form of the primary bile acid hyocholic acid (Item No. 20293).{40620} GHCA is upregulated 6.6-fold in the serum of patients with cirrhosis induced by hepatitis C virus (HCV) compared to healthy controls.{40624} Plasma levels of GHCA increase in patients who are no longer diabetic following gastric bypass surgery.{40625}
Brand:CaymanSKU:22670 -Out of stock
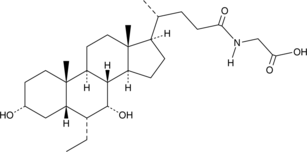
Glycohyodeoxycholic acid is a major metabolite of the secondary bile acid hyodeoxycholic acid (Item No. 20294) in humans.{37127} Glycohyodeoxycholic acid supplementation in prairie dogs fed a lithogenic diet decreases the frequency of cholesterol crystals in the gallbladder and inhibits the activity of cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase.{37126}
Brand:CaymanSKU:22643 -Out of stock
Glycohyodeoxycholic acid is a major metabolite of the secondary bile acid hyodeoxycholic acid (Item No. 20294) in humans.{37127} Glycohyodeoxycholic acid supplementation in prairie dogs fed a lithogenic diet decreases the frequency of cholesterol crystals in the gallbladder and inhibits the activity of cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase.{37126}
Brand:CaymanSKU:22643 -Out of stock
Glycohyodeoxycholic acid is a major metabolite of the secondary bile acid hyodeoxycholic acid (Item No. 20294) in humans.{37127} Glycohyodeoxycholic acid supplementation in prairie dogs fed a lithogenic diet decreases the frequency of cholesterol crystals in the gallbladder and inhibits the activity of cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase.{37126}
Brand:CaymanSKU:22643 -Out of stock
Glycohyodeoxycholic acid is a major metabolite of the secondary bile acid hyodeoxycholic acid (Item No. 20294) in humans.{37127} Glycohyodeoxycholic acid supplementation in prairie dogs fed a lithogenic diet decreases the frequency of cholesterol crystals in the gallbladder and inhibits the activity of cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase.{37126}
Brand:CaymanSKU:22643 -Out of stock
Glycohyodeoxycholic acid is a major metabolite of the secondary bile acid hyodeoxycholic acid (Item No. 20294) in humans.{37127} Glycohyodeoxycholic acid supplementation in prairie dogs fed a lithogenic diet decreases the frequency of cholesterol crystals in the gallbladder and inhibits the activity of cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase.{37126} Glycohyodeoxycholic acid MaxSpec® standard is a quantitative grade standard of glycohyodeoxycholic acid (Item No. 22643) that has been prepared specifically for mass spectrometry and related applications where quantitative reproducibility is required. The solution has been prepared gravimetrically and is supplied in a deactivated glass ampule sealed under argon. The concentration was verified by comparison to an independently prepared calibration standard. This glycohyodeoxycholic acid MaxSpec® standard is guaranteed to meet identity, purity, stability, and concentration specifications and is provided with a batch-specific certificate of analysis. Ongoing stability testing is performed to ensure the concentration remains accurate throughout the shelf life of the product. Note: The amount of solution added to the vial is in excess of the listed amount. Therefore, it is necessary to accurately measure volumes for preparation of calibration standards. Follow recommended storage and handling conditions to maintain product quality.
Brand:CaymanSKU:31600 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
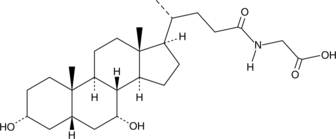
Glycolithocholic acid is a glycine-conjugated form of the secondary bile acid lithocholic acid (Item No. 20253).{48223} It is increased in the liver of mice fed a diet supplemented with ursodeoxycholic acid (Item No. 15121).{30823} Glycolithocholic acid levels are decreased in the plasma following subcutaneous administration of PEG-obestatin(Cys10, Cys13), a modified peptide hormone, in lean or diet-induced obese mice.{32037} Serum glycolithocholic acid levels increase with age in children.{32038}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21723 -Out of stock
Glycolithocholic acid is a glycine-conjugated form of the secondary bile acid lithocholic acid (Item No. 20253).{48223} It is increased in the liver of mice fed a diet supplemented with ursodeoxycholic acid (Item No. 15121).{30823} Glycolithocholic acid levels are decreased in the plasma following subcutaneous administration of PEG-obestatin(Cys10, Cys13), a modified peptide hormone, in lean or diet-induced obese mice.{32037} Serum glycolithocholic acid levels increase with age in children.{32038}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21723 -Out of stock
Glycolithocholic acid is a glycine-conjugated form of the secondary bile acid lithocholic acid (Item No. 20253).{48223} It is increased in the liver of mice fed a diet supplemented with ursodeoxycholic acid (Item No. 15121).{30823} Glycolithocholic acid levels are decreased in the plasma following subcutaneous administration of PEG-obestatin(Cys10, Cys13), a modified peptide hormone, in lean or diet-induced obese mice.{32037} Serum glycolithocholic acid levels increase with age in children.{32038}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21723 -Out of stock