Description
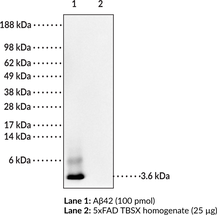
Amyloid plaques composed primarily of the 42 amino acid form of amyloid-β peptide (Aβ42) are a hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). However, the roles of the various amyloid β peptide(s), especially Aβ42, related to the neurotoxicity characteristic of AD remains unclear. A major hindrance to evaluating the role of Aβ in AD pathology has been the availability of anti-Aβ antibodies to selectively detect Aβ versus amyloid precursor protein (APP), Aβ40 versus Aβ42, and specific conformations of the peptide, particularly oligomeric forms. MOAB-2 (mouse IgG2b) is a pan-specific antibody specific to Aβ (residues 1-4) that differentiates intracellular Aβ from APP. MOAB-2 does not detect APP in cell culture media/lysates or in brain homogenates from transgenic mice expressing 5 familial AD mutation (5xFAD mice). Intraneuronal Aβ was confirmed by co-localization of MOAB-2 immunoreactivity with C-terminal antibodies specific for Aβ40 and Aβ42, and with cathepsin-D, a lysosomal marker. Additionally, MOAB-2 demonstrates strong intraneuronal and extra-cellular immunoreactivity in 5xFAD and 3xTg mouse brain tissues.{20683}
Synonyms: Aβ
Immunogen: Oligomeric form of amyloid-β peptide (Aβ42)
Formulation: 200 µg of protein G-purified antibody
Isotype: IgG2b
Applications: ELISA, ICC, IP, and WB
Origin:
Stability: 365 days
Application|Immunohistochemistry||Application|Immunoprecipitation||Application|Western Blot||Product Type|Antibodies|Monoclonal Antibodies||Research Area|Neuroscience|Neurodegenerative Disorders|Alzheimer’s Disease