Description
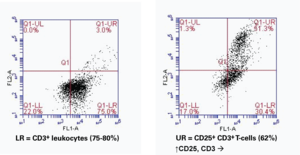
Interleukin-2 (IL-2) elicits its effects by binding to a multi-subunit cell-surface receptor that is inducible by various mitogens.{18182,18183,18184} The highest affinity for IL-2 is achieved when all 3 subunits (IL-2Rα or CD25, IL-2Rβ or CD122, and IL-2Rγ or CD132) are expressed together forming a heterotrimeric complex{6128}. CD25 is inducible in T-cells by antigen, mitogen or antibodies bound to the T-cell receptor CD3.{18183,18185} Binding of IL-2 to IL-2R on NK cells results in their conversion to LAK cells, which release several other cytokines (TNF, INF-γ, and GM-CSF).{6128,6349} Activated T-cells will respond to IL-2 by proliferating and secreting cytokines and cytolytic molecules. Activated B cells will proliferate and secrete antibodies.{11282}
Synonyms: IL-2Rα|Interleukin-2 receptor α subunit|p55|Tac
Immunogen:
Formulation: 100 µg of affinity purified, PE labeled monoclonal antibody
Isotype:
Applications: (+) FC, ICC, and IHC (frozen sections); (−) WB
Origin:
Stability: 365 days
Application|Flow Cytometry||Application|Immunocytochemistry||Application|Immunohistochemistry||Product Type|Antibodies|Monoclonal Antibodies||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Adaptive Immunity