Description
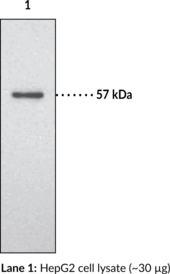
ApoA1 is a major protein component in high-density lipoproteins (HDLs). It acts as an acceptor for sequential transfers of phospholipids and free cholesterol from peripheral tissues as well as transporting cholesterol to the liver and other tissues for excretion and steroidogenesis.{14038} Serum ApoA1 levels are inversely related to the risk of developing atherosclerosis.{14039} Loss-of-function mutations in ApoA1 are causes of diseases such as HDL deficiency type 1 (or Tangier disease) and type 2 (familial hypoalphalipoproteinemia), and systemic non-neuropathic amyloidosis.{14037,14040} Liver and small intestine are two main sources of the protein. Cayman’s ApoA1 Polyclonal Antibody detects the protein by WB analysis at 25 kDa in tissue/cell samples such as liver, intestine, and HepG2 cells.
Synonyms: Apolipoprotein A1
Immunogen: Synthetic peptide from an internal region of human ApoA1
Formulation: 500 μl of peptide affinity-purified antibody
Isotype:
Applications: IF, IHC, and WB
Origin: Animal/Rabbit
Stability: 365 days
Application|Immunofluorescence||Application|Immunohistochemistry||Application|Western Blot||Product Type|Antibodies|Polyclonal Antibodies||Research Area|Cardiovascular System|Cardiovascular Diseases|Atherosclerosis||Research Area|Cardiovascular System|Lipids & Lipoproteins|Lipoproteins||Research Area|Endocrinology & Metabolism|Inborn Errors of Metabolism||Research Area|Endocrinology & Metabolism|Metabolic Diseases|Dyslipidemias