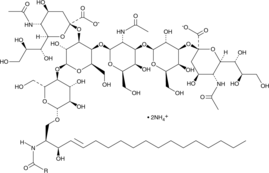
Description
A mixture of porcine ganglioside GD1a molecular species with primarily C18:0 fatty acyl chain lengths, as well as a lower amount of C20:0 fatty acyl chain lengths, among various others; found in brain, erythrocytes, bone marrow, testis, spleen, and liver; can be shed from the surface of tumor cells into the microenvironment where it influences tumor-host cell interactions to promote tumor cell proliferation, invasion, and metastasis; increases endothelial cell proliferation; acts as a functional coreceptor for TLR2
Formal name:
Synonyms: Ganglioside B1|Ganglioside G3
Molecular weight: 1,872.20
CAS: 12707-58-3
Purity: ≥98%
Formulation: A solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Lipids|Sphingolipids||Product Type|Biochemicals|Receptor Pharmacology||Research Area|Cancer|Cell Migration & Metastasis||Research Area|Cancer|Tumor Microenvironment||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Innate Immunity|Pattern Recognition||Research Area|Infectious Disease|Bacterial Diseases||Research Area|Lipid Biochemistry|Sphingolipids