Description
An SSRI; inhibits depletion of 5-HT induced by 4-methyl-α-ethyl-m-tyramine in rat cerebral cortex, hippocampus, hypothalamus, and striatum (EC50s = 18, 4, 8, and 12 mg/kg, respectively); inhibits NMDA-evoked currents and depolarization-induced voltage-dependent potassium currents in rat hippocampal neurons (IC50s = 1.1 and 6.9 μM, respectively); increases SIRT1 levels in N2a murine neuroblastoma cells expressing ApoE4 (IC50 = 2.3 μM) and in the hippocampus in the FXFAD-ApoE4 transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease at 20 mg/kg twice daily; decreases immobility time in the forced swim test in rats at 40 mg/kg
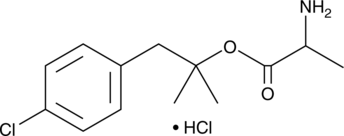
Formal name: alanine, 2-(4-chlorophenyl)-1,1-dimethylethyl ester, monohydrochloride
Synonyms: A03|GEA 654
Molecular weight: 292.2
CAS: 60719-83-7
Purity: ≥95%
Formulation: A crystalline solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Ion Channel Modulation|Blockers||Product Type|Biochemicals|Transporter & Exchanger Modulators||Research Area|Neuroscience|Behavioral Neuroscience|Depression||Research Area|Neuroscience|Neurodegenerative Disorders|Alzheimer’s Disease