Description
A nonpeptide NK1 receptor antagonist (Ki = 0.25 nM in a radioligand binding assay); selective for NK1 over NK2 and NK3 receptors (Kis = >10 μM for both); inhibits excitation of guinea pig locus coeruleus cells induced by substance P in vitro (IC50 = 25 nM); inhibits increases in horizontal locomotor activity induced by [Sar9,Met(O2)11]-substance P in guinea pigs (ID50 = 0.59 mg/kg); inhibits aerosolized capsaicin-induced plasma extravasation in guinea pig lung (ID50 = 4 mg/kg); exhibits anti-emetic effects in ferret models of emesis induced by copper sulfate, loperamide, or cisplatin at 0.3 and 1 mg/kg
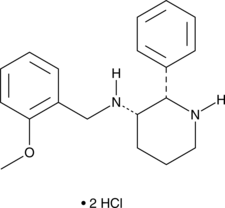
Formal name: (2S,3S)-N-[(2-methoxyphenyl)methyl]-2-phenyl-3-piperidinamine, dihydrochloride
Synonyms:
Molecular weight: 369.3
CAS: 145148-39-6
Purity: ≥98%
Formulation: A solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Receptor Pharmacology|Antagonists||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Pulmonary Diseases||Research Area|Neuroscience