Description
A toxic metabolite of benzene; formed via hepatic metabolism of benzene to 1,4-hydroquinone followed by myeloperoxidase processing of 1,4-hydroquinone in bone marrow; decreases levels of cytochrome P450 in a concentration-dependent manner in minipig liver microsomes; induces DNA mutations in human W138-VA13 and mouse HL18 cells; disrupts mitochondrial membrane potential at 10 and 20 μM and reduces viability, increases production of ROS, and induces apoptosis in a concentration-dependent manner in HL-60 cells
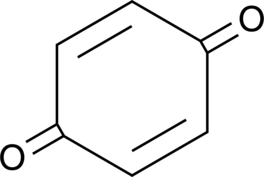
Formal name: 2,5-cyclohexadiene-1,4-dione
Synonyms: p-Benzoquinone|p-Quinone|NSC 36324
Molecular weight: 108.1
CAS: 106-51-4
Purity: ≥98%
Formulation: A crystalline solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Ox Stress Reagents|Free Radical Generators||Product Type|Biochemicals|Xenobiotic Metabolites||Research Area|Cancer|Cell Death|Apoptosis||Research Area|Cancer|DNA Damage and Repair||Research Area|Cell Biology|Mitochondrial Biology||Research Area|Toxicology|Cell Health & Viability|Mitochondrial (dys)Function||Research Area|Toxicology|Drug Metabolism|Cytochrome P450||Research Area|Toxicology|Drug Metabolism|Drug Metabolites