Description
A flavonoid with diverse biological activities; inhibits PAF-, arachidonic acid-, and ADP-induced platelet aggregation (IC50s = 20, 4, and 13 μM, respectively); inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclastic differentiation of RAW 264.7 cells and BMMs; inhibits LPS-induced bone resorption in mice at 25 μg/kg; inhibits tumor growth in a Caki-2 mouse xenograft model; reduces sevoflurane-induced cognitive deficits in aged rats at 40 mg/kg; decreases infarct size and brain edema in a rat model of focal cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury
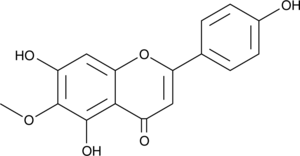
Formal name: 5,7-dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-6-methoxy-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one
Synonyms: 6-Methoxyapigenin|Dinatin|NSC 122415
Molecular weight: 300.3
CAS: 1447-88-7
Purity: ≥95%
Formulation: A solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Kinase Inhibitors|Other Lipid Kinases||Product Type|Biochemicals|Natural Products|Flavonoids||Product Type|Biochemicals|Small Molecule Inhibitors|Kinases||Product Type|Biochemicals|Small Molecule Inhibitors|Sphingolipid Turnover||Research Area|Cancer|Cell Death|Apoptosis||Research Area|Endocrinology & Metabolism|Bone Growth & Remodeling||Research Area|Neuroscience|Behavioral Neuroscience|Learning & Memory||Research Area|Neuroscience|Neuroprotection|Ischemia