Description
An inhibitor of fungal protein synthesis; binds to EF-2 in the presence of ribosomes; inhibits the uncoupled GTPase activity of equimolar mixtures of EF-2 and ribosomes from C. albicans (IC50 = 0.1 μM); inhibits protein synthesis in cell-free lysates of C. albicans, C. glabrata, and C. neoformans (IC50s = 0.01, 0.2, and 0.06 μg/ml, respectively) but not in rabbit reticulocytes (IC50 = >100 μg/ml); inhibits the growth of C. albicans (MIC = 8 μg/ml) but not C. glabrata or C. neoformans (MICs = >125 μg/ml)
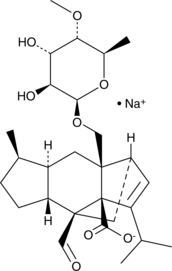
Formal name: (1R,3aR,4S,4aR,7R,7aR,8aS)-8a-[[(6-deoxy-4-O-methyl-β-D-altropyranosyl)oxy]methyl]-4-formyl-4,4a,5,6,7,7a,8,8a-octahydro-7-methyl-3-(1-methylethyl)-1,4-methano-s-indacene-3a(1H)-carboxylic acid, monosodium salt
Synonyms:
Molecular weight: 514.6
CAS: 463356-00-5
Purity: ≥98%
Formulation: A solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Antifungals||Product Type|Biochemicals|Natural Products|Microbial Metabolites||Product Type|Biochemicals|Small Molecule Inhibitors|GTPases||Product Type|Biochemicals|Small Molecule Inhibitors|Nucleic Acid Turnover/Signaling||Research Area|Cell Biology|Cell Signaling|GTPases||Research Area|Epigenetics, Transcription, & Translation|RNA, DNA, & Protein Synthesis||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation||Research Area|Infectious Disease|Fungal Diseases|Candidiasis