Description
An inhibitor of XPO1/CRM1 with anticancer and antiviral activities; inhibits the growth of OCI-Ly3, OCI-Ly10, and CLBL1 DLBCL cells (IC50s = 2.1, 41.8, and 8.5 nM, respectively); inhibits XPO1/CRM1-mediated nuclear transport of RSV M protein at >1 μM; reduces RSV A2 replication (IC50 = 0.96 μM) without affecting viability of A549 cells (CC50 = >38 μM); reduces virus shedding, pulmonary TNF-α, IL-6, MCP01, and IFN-γ expression, and leukocyte infiltration into the bronchoalveolar space in a mouse model of influenza A viral infection at 20 mg/kg
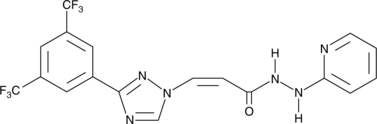
Formal name: (2Z)-3-[3-[3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl]-2-propenoic acid, 2-(2-pyridinyl)hydrazide
Synonyms: KPT-335
Molecular weight: 442.3
CAS: 1392136-43-4
Purity: ≥98%
Formulation: A crystalline solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Antivirals||Product Type|Biochemicals|Small Molecule Inhibitors||Research Area|Cancer||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Innate Immunity||Research Area|Infectious Disease|Viral Diseases|Influenza||Research Area|Infectious Disease|Viral Diseases|RSV Infections