Description
A sulfatide; interacts with LMIR5 to increase activation of NFAT; an immunodominant species that is bound by CD1d in vitro; reduces symptoms, increases survival, and decreases inflammatory lesions in a mouse model of chronic relapsing-remitting EAE (20 µg)
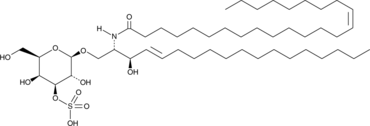
Formal name: N-[(1S)-2R-hydroxy-1-[[(3-O-sulfo-β-D-galactopyranosyl)oxy]methyl]-3E-heptadecen-1-yl]-15Z-tetracosenamide
Synonyms: (3’-sulfo)Galβ-Cer(d18:1/24:1)|cis-Tetracosenoyl Sulfatide|C24:1 Sulfatide|N-Nervonoyl Sulfatide|N-Tetracosenoyl (cis-15) Sulfatide
Molecular weight: 890.3
CAS: 151057-28-2
Purity: ≥98%
Formulation: A solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Lipids|Sphingolipids||Product Type|Biochemicals|Receptor Pharmacology||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Autoimmunity||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Innate Immunity||Research Area|Lipid Biochemistry|Sphingolipids||Research Area|Neuroscience