Description
An inhibitor of L-glutamate transport (Ki = 4.6 μM in rat brain synaptosomes); inhibits radioligand binding to NMDA receptors by 13% but has no effect on AMPA or kainate receptors (100 μM); neurotoxic to astrocyte-rich and astrocyte-poor rat cortical cultures (EC50s = 320 and 50 μM, respectively); prevents amphetamine-induced hyperlocomotion in a dose-dependent manner in rats (0.05-0.2 μg/side in nucleus accumbens); increases bladder ICI in rats
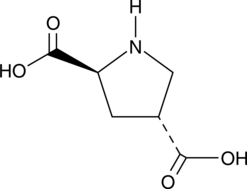
Formal name: 2S,4R-pyrrolidinedicarboxylic acid
Synonyms: L-trans-2,4-PDC
Molecular weight: 159.1
CAS: 64769-66-0
Purity: ≥98%
Formulation: A crystalline solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Receptor Pharmacology||Research Area|Neuroscience