Description
An activator of STING; induces expression of IFN-β and the pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-6, and Mcp-1 in murine BMMs isolated from wild-type, but not STING-/-, mice; induces IFN-β expression in PBMCs isolated from donors carrying STINGWT/WT, STINGWT/REF, and STINGWT/HAQ alleles; initiates tumor regression and prevents tumor growth upon tumor cell reimplantation in 4T1 breast and CT26 colon cancer mouse xenograft models,
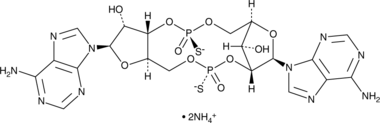
Formal name: [P(R)]-5′-O-[(R)-hydroxymercaptophosphinyl]-P-thioadenylyl-(2’→5′)-adenosine, cyclic nucleotide, diammonium salt
Synonyms: STING Inducer-1
Molecular weight: 724.6
CAS: 1638750-96-5
Purity: ≥98%
Formulation: A solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Small Molecule Activators||Research Area|Cancer||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Autoimmunity||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Innate Immunity|Pattern Recognition||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Innate Immunity|STING||Research Area|Infectious Disease