Description
A vasopressin V1A and V2 receptor antagonist (Kis = 0.48 and 3.04 nM for rat liver V1A and kidney V2, respectively); competitively inhibits oxytocin binding to rat uterine oxytocin receptors (Ki = 44 nM) but has no effect on AVP binding to anterior pituitary V1B receptors at concentrations up to 100 μM in a radioligand binding assay; suppresses AVP-induced increases in intracellular calcium in VSMCs and the pressor response in pithed rats; increases urine output and decreases urine osmolality in dehydrated conscious rats in a dose-dependent manner; reduces brain edema and blood-brain barrier disruption in a mouse experimental stroke model,
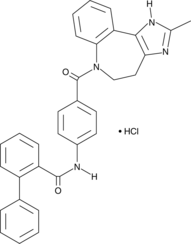
Formal name: N-[4-[(4,5-dihydro-2-methylimidazo[4,5-d][1]benzazepin-6(1H)-yl)carbonyl]phenyl]-[1,1′-biphenyl]-2-carboxamide, monohydrochloride
Synonyms: YM-087
Molecular weight: 535
CAS: 168626-94-6
Purity: ≥95%
Formulation: A solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Receptor Pharmacology|Antagonists||Research Area|Cardiovascular System|Cardiovascular Diseases|Hypertension||Research Area|Cardiovascular System|Cardiovascular Diseases|Stroke||Research Area|Cardiovascular System|Kidney & Renal Disease||Research Area|Cardiovascular System|Vasculature|Smooth Muscle Cells||Research Area|Neuroscience|Neuroprotection|Ischemia