Description
A sulfonamide antibiotic; inhibits growth of E. coli (MIC = 10 μg/ml) and clinical MRSA isolates (MICs = 25-50 μg/ml); inhibits growth of MRSA in vivo in mice when administered in combination with trimethoprim (MIC = 0.8 μg/ml, ED50s = 6.4 and 9.6 mg/kg for two MRSA strains); acts by inhibiting DHPS; inhibits recombinant P. carinii DHPS (IC50 = 23 nM; Ki = 7.5 nM) and folate biosynthesis in situ by 48.6%; decreases recurrent infection in a mouse model of urinary tract infection with E. coli when administered in combination with trimethoprim
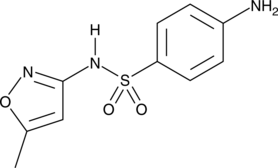
Formal name: 4-amino-N-(5-methyl-3-isoxazolyl)-benzenesulfonamide
Synonyms: NSC 147832|Ro 4-2130
Molecular weight: 253.3
CAS: 723-46-6
Purity: ≥98%
Formulation: A crystalline solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Antibiotics|Sulfonamides||Product Type|Biochemicals|Small Molecule Inhibitors|Nucleic Acid Turnover/Signaling||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation||Research Area|Infectious Disease|Bacterial Diseases|MRSA