Description
A sulfonamide with anticancer activity (IC50s = 0.11 and 94 μg/ml, for HCT116 and NCI-H596 cells, respectively); increases the number of P388 murine leukemia cells in the G1 phase of the cell cycle in a dose-dependent manner; exerts time-dependent cytotoxicity against HCT116 cells; suppresses tumor growth and decreases tumor volume in murine HCT116, SW620, and HCT15 colorectal and LX-1 and PC9 lung cancer xenograft models; induces proteasomal degradation of RBM39 through association with the CUL4-DCAF15 E3 ubiquitin ligase in vitro; an inhibitor of carbonic anhydrase in H. pylori (Ki = 310-562 nM),
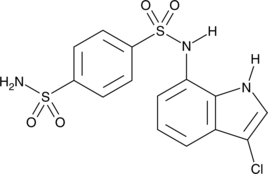
Formal name: N1-(3-chloro-1H-indol-7-yl)-1,4-benzenedisulfonamide
Synonyms: E-7070
Molecular weight: 385.8
CAS: 165668-41-7
Purity: ≥98%
Formulation: A crystalline solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Small Molecule Inhibitors|Carbonic Anhydrase||Research Area|Cancer|Cell Cycle|G1||Research Area|Cancer|Cell Death||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation||Research Area|Infectious Disease|Bacterial Diseases