Description
An inhibitor of CRT (IC50 = 40.3 nM); inhibits β-catenin/Tcf4 binding (Kis = 53.51 μM); inhibits Notch, Hh, and JAK/STAT signaling (IC50s = 69.2, 194, and 70 nM, respectively); reduces proliferation and initial tumor growth rate in mouse xenografts of colon carcinoma (50 mg/kg i.p.); inhibits proliferation of leukemia cell lines; suppresses ATP-driven migration of the MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell lines
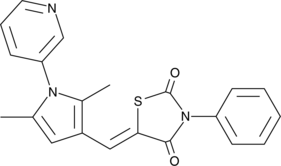
Formal name: 5-[[2,5-dimethyl-1-(3-pyridinyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl]methylene]-3-phenyl-2,4-thiazolidinedione
Synonyms:
Molecular weight: 375.4
CAS: 677331-12-3
Purity: ≥98%
Formulation: A crystalline solid
Product Type|Biochemicals||Research Area|Cancer|Cell Migration & Metastasis||Research Area|Cancer|Cell Signaling|Hedgehog Signaling||Research Area|Cancer|Cell Signaling|JAK/STAT Signaling||Research Area|Cancer|Cell Signaling|Notch Signaling||Research Area|Cancer|Cell Signaling|Wnt Signaling||Research Area|Cancer|Transcription Factors|STATs||Research Area|Cell Biology|Cell Signaling|Hedgehog Signaling||Research Area|Cell Biology|Cell Signaling|Notch Signaling||Research Area|Cell Biology|Cell Signaling|Wnt Signaling