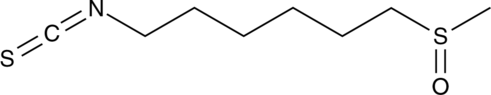
Description
An isothiocyanate with diverse biological activities; inhibits NO production in mouse peritoneal exudate macrophages at 5 µM; inhibits arachidonic acid-induced aggregation of isolated human platelets (IC50 = 21.9 µM); reduces cell survival in a panel of breast, brain, colon, lung, ovarian, renal, and prostate cancer cell lines (mean IC50 = 43.7 µM); reduces apoptosis of substantia nigral dopaminergic neurons and motor dysfunction in a mouse model of 6-OHDA-induced Parkinson’s disease at 5 mg/kg twice weekly; reduces the number of lung metastases in a B16/F10 murine melanoma model
Formal name: 1-isothiocyanato-6-(methylsulfinyl)-hexane
Synonyms: 6-MSITC
Molecular weight: 205.3
CAS: 4430-35-7
Purity: ≥98%
Formulation: A solution in ethanol
Product Type|Biochemicals|Natural Products|Isothiocyanates||Research Area|Cancer|Cell Death||Research Area|Cancer|Cell Migration & Metastasis||Research Area|Cardiovascular System|Blood|Coagulation & Hemostasis||Research Area|Cell Biology|Cell Signaling|Nitric Oxide Signaling||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Innate Immunity||Research Area|Neuroscience|Neurodegenerative Disorders|Parkinson’s Disease