Description
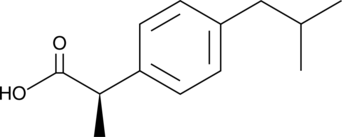
An enantiomer of ibuprofen that does not inhibit COX; inhibits NF-κB activation (IC50 = 121.8 µM) in response to T-cell stimulation; blocks superoxide formation, β-glucuronidase release, and LTB4 generation by stimulated neutrophils (IC50s = 40-100 µM); can be inverted to (S)-ibuprofen in humans after oral administration
Formal name: α-methyl-4-(2-methylpropyl)-(αR)-benzeneacetic acid
Synonyms: (-)-Ibuprofen
Molecular weight: 206.3
CAS: 51146-57-7
Purity: ≥98%
Formulation: A crystalline solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Small Molecule Inhibitors|Cyclooxygenases||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Adaptive Immunity||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Innate Immunity||Research Area|Lipid Biochemistry|Cyclooxygenase Pathway||Research Area|Lipid Biochemistry|Glycerolipids||Research Area|Lipid Biochemistry|Lipoxygenase Pathways