Description
A sodium channel blocker and local anesthetic; inhibits sodium currents in rat dorsal horn neurons in a concentration-dependent manner; increases the firing threshold in rat sympathetic ganglia at 200 nM; blocks cardiac sodium channels in a use-dependent manner at 10 µM; inhibits respiration in cardiac cell mitochondria when palmitoyl-carnitine or acetyl-carnitine are used as substrates (IC50s = 0.78 and 0.37 mM, respectively); reduces thermal hyperplasia in a rat model of sciatic ligation injury when 0.6 ml of a 0.5% solution is administered into the perinerve space
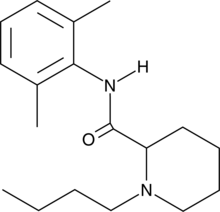
Formal name: 1-butyl-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-2-piperidinecarboxamide
Synonyms:
Molecular weight: 288.4
CAS: 38396-39-3
Purity: ≥98%
Formulation: A crystalline solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Ion Channel Modulation|Blockers||Product Type|Biochemicals|Transporter & Exchanger Modulators||Research Area|Neuroscience|Pain Research