Description
A nucleoside analog and prodrug form of ara-CTP; triphosphorylated to ara-CTP by the successive actions of deoxycytidine kinase, deoxycytidylate kinase, and nucleoside diphosphate kinase; inhibits proliferation of HL-60, ML-1, Raji, and Jurkat human leukemia cell lines (IC50s = 37, 17, 16, and 72 nM, respectively); induces cell cycle arrest at the G0/G1 phase in HL-60 cells at 2.5 and 15 µM; reduces tumor growth and increases tumor caspase-3 activity in an MOLM-13 mouse xenograft model at 75 mg/kg per day intraperitoneally; increases survival and reduces brain herpesvirus titers in infected rats at 80 and 320 mg/kg subcutaneously
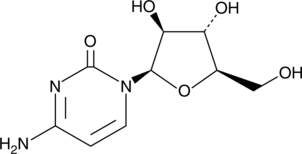
Formal name: 4-amino-1-β-D-arabinofuranosyl-2(1H)-pyrimidinone
Synonyms: 1-β-D-Arabinofuranosylcytosine|NSC 287459|NSC 63878|U-19920A
Molecular weight: 243.2
CAS: 147-94-4
Purity: ≥95%
Formulation: A crystalline solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Antivirals||Product Type|Biochemicals|Nucleotides/Nucleosides||Product Type|Biochemicals|Small Molecule Inhibitors|Nucleic Acid Turnover/Signaling||Research Area|Cancer|Cell Cycle||Research Area|Cancer|Cell Death|Apoptosis||Research Area|Cancer|DNA Damage and Repair||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation||Research Area|Infectious Disease|Viral Diseases|HSV