Description
A cell-permeable inhibitor of the dimerization of c-Myc and Max at 64 µM, preventing c-Myc-dependent gene expression and cell proliferation; induces cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, and myeloid differentiation at 100 µM in human acute myeloid leukemia cells; inhibits the nuclear Myc protein, N-Myc, at 50 µM
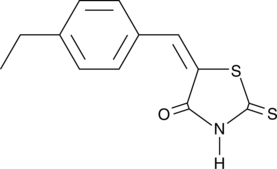
Formal name: 5-[(4-ethylphenyl)methylene]-2-thioxo-4-thiazolidinone
Synonyms:
Molecular weight: 249.4
CAS: 403811-55-2
Purity: ≥95%
Formulation: A crystalline solid
Product Type|Biochemicals||Research Area|Cancer|Cell Cycle||Research Area|Cancer|Cell Death|Apoptosis||Research Area|Cancer|Transcription Factors