Description
A potent, cell-permeable, and selective inhibitor of γ-secretase, blocking the cleavage of both APP and Notch CTFs with IC50 values of ~0.3 nM; induces neuronal differentiation, impairs ovarian folliculogenesis, and suppresses thymocyte development by preventing Notch activation by γ-secretase
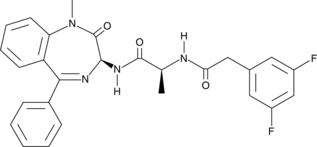
Formal name: N-[(1S)-2-[[(3S)-2,3-dihydro-1-methyl-2-oxo-5-phenyl-1H-1,4-benzodiazepin-3-yl]amino]-1-methyl-2-oxoethyl]-3,5-difluoro-benzeneacetamide
Synonyms: γ-Secretase Inhibitor XXI
Molecular weight: 490.5
CAS: 209986-17-4
Purity: ≥98%
Formulation: A crystalline solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Small Molecule Inhibitors|Peptidases & Proteases||Research Area|Cell Biology|Cell Signaling|Notch Signaling||Research Area|Cell Biology|Proteolysis|Cytosolic & Secreted Proteases||Research Area|Cell Biology|Proteolysis|Lysosomal Proteases||Research Area|Endocrinology & Metabolism|Reproductive Biology||Research Area|Neuroscience|Neurodegenerative Disorders|Alzheimer’s Disease