Description
An inhibitor of UCH-L1 activity (IC50 = 0.88 Ki = 0.4 μM) that demonstrates selectivity for UCH-L1 compared to UCH-L3 (IC50 = 25 μM); leads to cell death through the apoptosis pathway due to an impaired ubiquitin-proteasome pathway
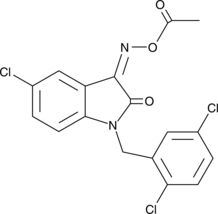
Formal name: 5-chloro-1-[(2,5-dichlorophenyl)methyl]-1H-indole-2,3-dione 3-(O-acetyloxime)
Synonyms: Ubiquitin C-terminal Hydrolase L1 Inhibitor|UCH-L1 Inhibitor
Molecular weight: 397.6
CAS: 668467-91-2
Purity: ≥95%
Formulation: A crystalline solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Small Molecule Inhibitors|MMPs||Product Type|Biochemicals|Small Molecule Inhibitors|Ubiquitin Ligase System||Research Area|Cell Biology|Cell Death|Apoptosis||Research Area|Cell Biology|Proteolysis|Ubiquitin/Proteasome System||Research Area|Neuroscience