Description
A phenothiazine compound with anti-adrenergic (Kis = 24, 653, 163, and 391 nM for α1A, α2A, α2B, and α2C receptors, respectively) and antidopaminergic (Kd = 0.96 nM for the dopamine D2-like receptor) actions typical of antipsychotic agents; also antagonizes calmodulin and alters the calcium-binding properties of calsequestrin
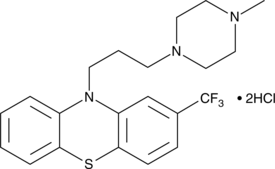
Formal name: 10-[3-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)propyl]-2-(trifluoromethyl)-10H-phenothiazine, dihydrochloride
Synonyms: SKF 5019|TFP
Molecular weight: 480.4
CAS: 440-17-5
Purity: ≥98%
Formulation: A crystalline solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Ion Channel Modulation|Activators||Product Type|Biochemicals|Receptor Pharmacology|Antagonists||Research Area|Cell Biology|Cell Signaling|Calcium Mobilization||Research Area|Neuroscience|Behavioral Neuroscience|Schizophrenia & Psychosis