Description
A potent, bioavailable pan-Trk inhibitor that blocks the proliferation of cells expressing TEL-TrkA, TEL-TrkB, and TEL-TrkC (IC50s = 7, 9, and 11 nM, respectively); inhibits the growth of Ba/F3 and RIE cells expressing both TrkA and NGF with IC50 values of 42 and 17 nM, respectively
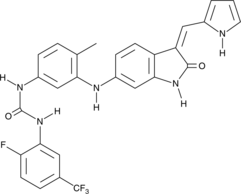
Formal name: N-[3-[[2,3-dihydro-2-oxo-3-(1H-pyrrol-2-ylmethylene)-1H-indol-6-yl]amino]-4-methylphenyl]-N’-[2-fluoro-5-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-urea
Synonyms:
Molecular weight: 535.5
CAS: 1033769-28-6
Purity: ≥95%
Formulation: A crystalline solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Kinase Inhibitors|Other Receptor Tyrosine Kinases||Product Type|Biochemicals|Small Molecule Inhibitors|Kinases||Research Area|Cancer|Cell Signaling|Growth Factor Receptor Signaling