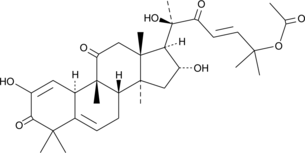
Description
A natural triterpene; reduces MPP+-induced death of neuronal PC12 cells through inhibition of autophagy in vitro; inhibits growth of T24 bladder, MDA-MB-468 and MCF-7 breast, PC3 prostate, and colorectal cancer cell lines (IC50s = 50-1,000 nM) through induction of G2/M arrest and apoptosis; increases bilirubin binding to HSA in human plasma in a dose-dependent manner; inhibits depolymerization of actin filaments isolated from rabbit skeletal muscle actin and in HeLa cells,
Formal name: (9β,10α,16α,23E)-25-(acetyloxy)-2,16,20-trihydroxy-9-methyl-19-norlanosta-1,5,23-triene-3,11,22-trione
Synonyms: NSC 106399|NSC 521775
Molecular weight: 556.7
CAS: 18444-66-1
Purity: ≥98%
Formulation: A crystalline solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Natural Products|Terpenes||Research Area|Cancer|Cell Cycle|G2/M||Research Area|Cancer|Cell Death|Apoptosis||Research Area|Cell Biology|Cytoskeleton & Motor Proteins||Research Area|Cell Biology|Endomembrane System & Vesicular Trafficking|Autophagy||Research Area|Neuroscience