Description
Butaprost is a structural analog of PGE2 with good selectivity for the EP2 receptor subtype. Butaprost has frequently been used to pharmacologically define the EP receptor expression profile of various human and animal tissues and cells.{3317,1752} Serious confusion as to the structure of Butaprost was generated by Gardiner in 1986,{3326} when he reported that the epimer of butaprost showing this selective activity was the C-16 (R)-epimer (See reference {3326} and Note). Butaprost binds with about 1/10 the affinity of PGE2 to the recombinant murine EP2 receptor, and does not bind appreciably to any of the other murine EP receptors or DP, FP, IP, or TP receptors.{6640} The pharmacology of (R)-butaprost has not been carefully studied, but it is generally considered to be the less active epimer.{3178} (NOTE: In the Gardiner paper in the 1986 British Journal of Pharmacology, butaprost appears on page 46 where it is given the name TR 4979. The structure as drawn is incorrect, in that the author was using and referring to the more active C-16 epimer, which is actually 16(S). The structure on page 46 shows the structure as 16(R). It was not until the late 1990’s that careful studies both in the US and Japan correctly identified the actual configuration of C-16 in the compound called butaprost is 16(S).){3326}
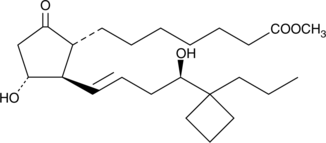
Formal name: 9-oxo-11α,16R-dihydroxy-17-cyclobutyl-prost-13E-en-1-oic acid, methyl ester
Synonyms: (±)-15-deoxy-16R-hydroxy-17-cyclobutyl PGE1 methyl ester|15-deoxy-16R-hydroxy-17-cyclobutyl PGE1 methyl ester|TR 4978
Molecular weight: 408.6
CAS: 69648-38-0
Purity: ≥98%
Formulation: A solution in methyl acetate
Product Type|Biochemicals|Lipids|Prostaglandins||Product Type|Biochemicals|Receptor Pharmacology|Agonists||Research Area|Lipid Biochemistry|Cyclooxygenase Pathway