Description
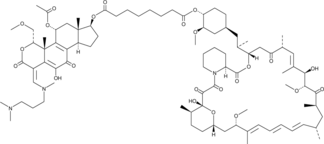
Consists of analogs of 17-hydroxy wortmannin and rapamycin conjugated via a prodrug linker, which are released upon hydrolysis of the prodrug linker in vivo; inhibits the growth of tumors in mice better than rapamycin alone
Formal name: 1-(4S,4aR,5R,6aS,7S,9aR,E)-1-(((3-(dimethylamino)propyl)(methyl)amino)methylene)-7,11-dihydroxy-4-(methoxymethyl)-4a,6a-dimethyl-2,10-dioxo-1,2,4,4a,5,6,6a,7,8,9,9a,10-dodecahydroindeno[4,5-h]isochromen-5-yl acetate 8-(7E,15E,17E,19E)-9,10,12,13,14,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,32,33,34aS-hexadecahydro-9R,27-dihydroxy-3S-[(1R)-2-[(1S,3R,4R)-4-hydroxy-3-methoxycyclohexyl]-1-methylethyl]-10R,21S-dimethoxy-6R,8,12R,14S,20,26R-hexamethyl-23S,27R-epoxy-3H-pyrido[2,1-c][1,4]oxaazacyclohentriacontine-1,5,11,28,29(4H,6H,31H)-pentone octanedioate
Synonyms:
Molecular weight: 1,598.90
CAS: 1067892-47-0
Purity: ≥98%
Formulation: A crystalline solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Kinase Inhibitors|mTOR||Product Type|Biochemicals|Kinase Inhibitors|PI3K||Product Type|Biochemicals|Small Molecule Inhibitors|Kinases||Research Area|Cancer|Cell Signaling|PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling