Description
A phenol with diverse biological activities; active against the bacteria B. subtilis, S. aureus, and M. smegmatis (MIC = 2.5 µg/ml for all) and the fungus T. mentagrophytes (MIC = 1.25 µg/ml); inhibits LPS-induced activation of NF-kB and production of NO in RAW 264.7 macrophages at 10 and 30 µM; reduces carrageenan-induced paw edema in mice at 20 and 200 mg/kg; reduces neuronal apoptosis and escape latency in the Morris water maze in a mouse model of Aβ42-induced Alzheimer’s disease at 1 mg/kg; reduces plasma cholesterol and triglyceride levels, ameliorates hepatic steatosis, and improves insulin resistance in a mouse model of high-fat diet-induced obesity
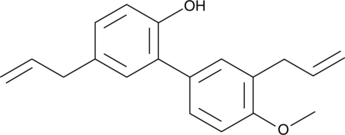
Formal name: 4′-methoxy-3′,5-di-2-propen-1-yl-[1,1′-biphenyl]-2-ol
Synonyms: 4-Methoxyhonokiol|NSC 293101
Molecular weight: 280.4
CAS: 68592-15-4
Purity: ≥98%
Formulation: A solution in Ethanol
Product Type|Biochemicals|Antibiotics||Product Type|Biochemicals|Antifungals||Product Type|Biochemicals|Natural Products|Polyphenols||Research Area|Cardiovascular System|Lipids & Lipoproteins|Lipoproteins||Research Area|Cell Biology|Cell Signaling|NF-κB Signaling||Research Area|Cell Biology|Cell Signaling|Nitric Oxide Signaling||Research Area|Endocrinology & Metabolism|Metabolic Diseases|Diabetes||Research Area|Endocrinology & Metabolism|Metabolic Diseases|Dyslipidemias||Research Area|Endocrinology & Metabolism|Metabolic Diseases|Obesity||Research Area|Epigenetics, Transcription, & Translation|Transcription Factors||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Innate Immunity||Research Area|Infectious Disease|Bacterial Diseases||Research Area|Infectious Disease|Fungal Diseases||Research Area|Neuroscience|Behavioral Neuroscience|Learning & Memory||Research Area|Neuroscience|Neurodegenerative Disorders|Alzheimer’s Disease