Description
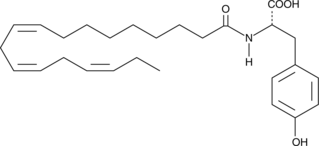
A simple α-amide conjugate between the ω-3 essential fatty acid α-linolenate and the amino acid tyrosine that was prepared as a mechanism for enhancing CNS dopamine content by facilitated transport of the tyrosine precursor across the blood-brain barrier; increased CNS dopamine levels and exhibited an activity profile consistent with an anti-Parkinson’s therapeutic agent in experimental rat models of dopamine insufficiency
Formal name: N-(L-tyrosine)-9Z,12Z,15Z-octadecatrienamide
Synonyms: NALT
Molecular weight: 441.6
CAS: 259143-19-6
Purity: ≥98%
Formulation: A solution in ethanol
Product Type|Biochemicals|Lipids|Fatty Amides||Product Type|Biochemicals|Lipids|Octadecanoids||Research Area|Lipid Biochemistry|Fatty Acids||Research Area|Neuroscience|Neurodegenerative Disorders|Parkinson’s Disease