Description
An activator of SIRT1 that decreases TNF-α levels from 325 pg/ml (control) to 104 and 53 pg/ml at 20 and 60 µM, respectively; exhibits a significant dose-dependent effect on fat mobilization in differentiated adipocytes
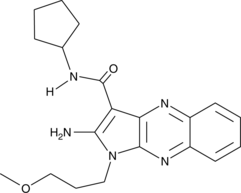
Formal name: 2-amino-N-cyclopentyl-1-(3-methoxypropyl)-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]quinoxaline-3-carboxamide
Synonyms: SIRT1 Activator 3|Sirtuin 1 Activator 3
Molecular weight: 367.5
CAS: 839699-72-8
Purity: ≥98%
Formulation: A crystalline solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Small Molecule Activators|Deacetylases||Product Type|Biochemicals|Small Molecule Inhibitors|TNF-α/NF-κB Signaling||Research Area|Endocrinology & Metabolism|Metabolic Diseases|Diabetes||Research Area|Endocrinology & Metabolism|Metabolic Diseases|Obesity||Research Area|Epigenetics, Transcription, & Translation|Erasers|Histone Deacetylation||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Innate Immunity