Description
A biotinylated reagent used for the detection and quantification of apurinic/apyrimidinic (AP) sites in damaged DNA; reacts with aldehyde groups formed when reactive oxygen species depurinate DNA, thereby covalently linking biotin to these AP sites.
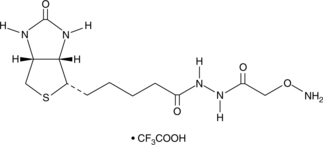
Formal name: (6aR)-hexahydro-2-oxo-2-[(aminooxy)acetyl]hydrazide,1H-thieno[3aS,4S-d]imidazole-4-pentanoic acid, trifluoroacetate salt
Synonyms: ARP|O-(Biotinylcarbazoylmethyl) Hydroxylamine
Molecular weight: 445.4
CAS: 627090-10-2
Purity: ≥95%
Formulation: A crystalline solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Labeling & Detection|Reactive Probes||Research Area|Oxidative Stress & Reactive Species|DNA/RNA Oxidative Damage